【0】README
0.1)本文描述总结于 数据结构与算法分析, 但源代码为原创;
0.2)为什么写这篇博文? 再散列的代码实现 包括了 解决冲突的方法实现;很有代表性;(本源代码采用的解决冲突方法是 平方探测法)
【1】问题+解决方法
1.0)开放定址法定义:它是一种不用链接解决冲突的方法:如果有冲突发生, 那么就要尝试选择另外的单元,知道找出空的单元为止;

1.1)出现的问题:对于使用平方探测的开放定址散列法,如果表的元素填的太满, 那么操作的运行时间将开始消耗过长,且 insert 操作可能失败, 这可能发生在有 太多的移动和插入混合的场合;
1.2)解决方法:建立另外一个大约两倍大的表(使用一个相关的新散列函数),扫描整个原始散列表,计算每个元素的新散列值并将其插入到新表中;
1.3)看个荔枝:
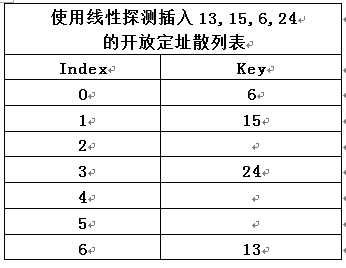
- 1)将元素13, 15, 24 和 6 插入到大小为 7 的开放定址散列表中:散列函数是 h(X) = X mod 7;设使用线性探测方法解决冲突问题, 插入结果得到的散列表表示在下图中:
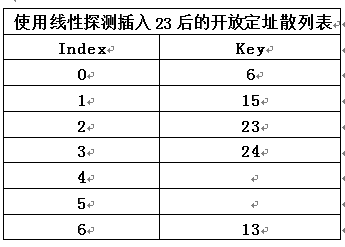
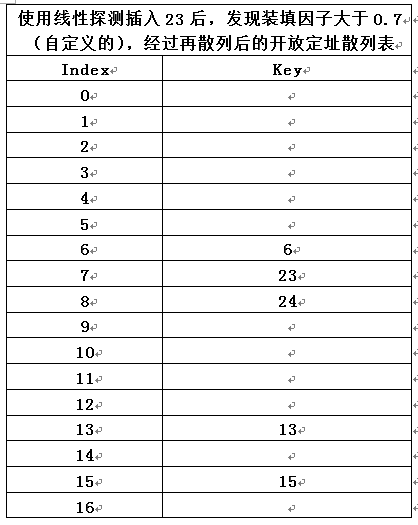
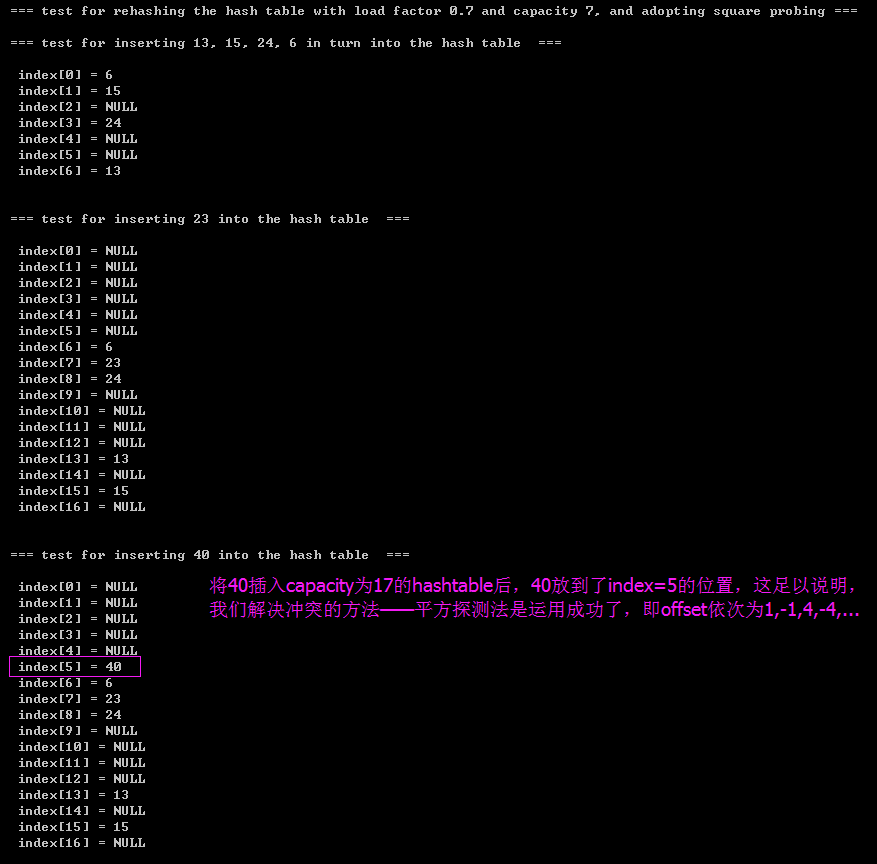
- 2)如果将 23 插入表中, 那么从下图可以看到, 插入后的表将有超过70% 的单元是满的,因为表填得过满, 所以我们建立一个新表;该表的大小为 17, 因为17是原表大小两倍后的第一个素数;新的散列函数为 h(X) = X mod 17;扫描原来的表, 并将元素 6, 15, 23 , 24 以及13 插入到新表中, 如下下图所示:
【2】再散列
2.1)定义:以上整个操作就叫做再散列;显然这是一种非常昂贵的操作, 其运行时间为 O(N),因为有N 个元素要再散列而表的大小约为2N, 不过由于不是经常发生,所以实际效果根本不是那么差;
2.2)再散列的实现:
再散列可以用平方探测以多种方法实现:
- 1)一种做法是:只要表满到一半就再散列;
- 2)另一个极端方法是:只有当插入失败时才再散列;
- 3)第3种方法即途中策略:当表到达某一个装填因子时进行再散列。由于随着装填因子的增加,表的性能有所下降, 因此,以好的截止手段实现的第三种策略, 可能是最好的策略;
2.3)再散列的作用:
再散列就是把 程序员从表大小的担心中解放出来, 这一点很重要, 因为在复杂的程序中散列表不能够做得任意地大;
【3】源代码+打印结果
3.1)解决冲突的方法:我们采用的是平方探测,1,-1,4,-4,……
3.2)Attention)在 “再散列”的代码中,我们为 HashTable 添加另一个 capacity 成员,用于和 size 相除构成 装填因子,以便于判断该装填因子是否超出某个值;
3.3)downlaod source code : https://github.com/pacosonTang/dataStructure-algorithmAnalysis/blob/master/chapter5/p123_rehash.c
3.4)source code at a glance :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <math.h>#define ElementType int
#define Error(str) printf("\n error: %s \n",str) struct HashTable;
typedef struct HashTable *HashTable;
struct HashEntry;
typedef struct HashEntry *HashEntry;
typedef HashEntry EntryArray;HashTable initHashTable(int size);
int find(ElementType key, HashTable ht);
HashTable insert(ElementType key, HashTable ht);enum EntryType {Legitimate, Empty, Deleted};struct HashEntry
{ElementType key;enum EntryType status;
};struct HashTable
{EntryArray entryArray;int capacity;int size;
};//judge whether the value is prime or not, also 1 or 0
int isPrime(int value)
{int temp;int flag;flag = 1;temp = 2;while(temp < sqrt(value)){if(value % temp == 0)flag = 0;temp++;}return flag;
}// compute the minial prime greater than the value
int nextPrime(int value)
{ value++;while(1){if(isPrime(value))break;value++;}return value;
} // hash function
int hashFunc(int key, int capacity)
{return key % capacity;
}// the rehash function to expand hash table capacity upto twice capcity
HashTable rehashFunc(HashTable ht)
{int capacity;int oldCapacity;int i;EntryArray temp;temp = ht->entryArray;oldCapacity = ht->capacity;capacity = nextPrime(ht->capacity * 2);ht = initHashTable(capacity);for(i = 0; i < oldCapacity; i++)if(temp[i].status == Legitimate)insert(temp[i].key, ht);free(temp);return ht;
}// initializing HashTable with given size and the table size should be a prime number
HashTable initHashTable(int capacity)
{HashTable ht; int i;ht = (HashTable)malloc(sizeof(struct HashTable)); // allocate memory for HashTableif(!ht) {Error("out of space, from func initHashTable");return NULL;}ht->capacity = capacity; // the table capacity should be a prime numberht->size = 0; // the number the hash table stores elementht->entryArray = (HashEntry)malloc(capacity * sizeof(struct HashEntry)); // allocate memory for entry arrayfor(i = 0; i < capacity; i++) ht->entryArray[i].status = Empty;return ht;
}// insert the entry with value key into the Hash Table
HashTable insert(ElementType key, HashTable ht)
{int index;double loadFactor = 0.7; // let the load facotr equals to 0.7, of cource load factor depends on your minddouble temp;index = find(key, ht);if(ht->entryArray[index].status != Legitimate){ht->entryArray[index].status = Legitimate;ht->entryArray[index].key = key;ht->size++;// judge whether the load facotr is greater than the certain valuetemp = (double) ht->size / ht->capacity; if(temp >= loadFactor)ht = rehashFunc(ht);}return ht;
}// find the index the entry with key should be placed into
int find(ElementType key, HashTable ht) // find the hash entry with value key
{int index; int collisionIndex; int minus = -1;int temp;collisionIndex = 0;index = hashFunc(key, ht->capacity); // call the first hash function for allocating empty position for storing the key temp = index;while(ht->entryArray[temp].status != Empty && ht->entryArray[temp].key != key ) // adopting square probing{if(minus == -1)collisionIndex++;minus *= -1;temp = collisionIndex * collisionIndex * minus; temp = (index + temp) % ht->capacity;} return temp;
}void printHashTable(HashTable ht)
{ElementType key;int i; if(!ht)Error("printing execution failure, for hashtable is null, from func printHashTable"); i = 0;while(i < ht->capacity) {printf("\n\t index[%d] = ", i);key = ht->entryArray[i].key; if(ht->entryArray[i].status == Legitimate)printf("%d", key); elseprintf("NULL");printf(" "); i++;}printf("\n\n");
}int main()
{HashTable ht = NULL;int dataSize = 4;int i;ElementType key[] = {13, 15, 24, 6};printf("\n\t=== test for rehashing the hash table with load factor 0.7 and capacity 7, and adopting square probing ===\n");ht = initHashTable(7);// the size of HashTable must be prime number;printf("\n\t=== test for inserting 13, 15, 24, 6 in turn into the hash table ===\n");for(i = 0; i< dataSize; i++) ht = insert(key[i], ht); printHashTable(ht); printf("\n\t=== test for inserting 23 into the hash table ===\n");ht = insert(23, ht); printHashTable(ht); printf("\n\t=== test for inserting 40 into the hash table ===\n");ht = insert(40, ht); printHashTable(ht); return 0;
}3.5)printing result


)

的快捷键/终端快捷键)







)


说明)

序列化和验证)

