【0】README
0.1)本文的重点在于介绍 二叉查找树的概念,以及写出 二叉查找树的操作例程的源代码, 其中当属delete 操作的源代码最不容易实现;
0.2)本文源代码均为原创, 当然 代码中的idea 是借鉴人家的;
【1】二叉查找树相关概念
1.1)定义:该树中的每个节点 X, 它的左子树中所有关键字值 小于 X 的关键字值, 而它的右子树中所有关键字值大于 X 的关键字值;
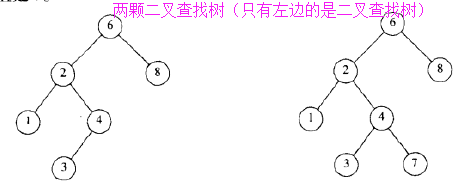
1.2)性质: 二叉查找树的平均深度是 O(log N);
1.3)编写对二叉树的操作:由于树的递归定义,通常是递归地编写这些操作的例程;
【2】 二叉查找树的操作例程(我们只选取了 find 和 delete 进行 解析)
2.1)Find
- Attention) 要知道, 不管是 find 二叉树还是 find 二叉查找树, 它的第一条执行语句一定是判断根节点 是否 为 NULL;(也即是P75 提到的, 对空树的测试放在最前面)
- Find函数的关键问题是: 首先要对是否为空树进行测试, 否则就可能在 NULL 指针上面兜圈子;
2.2) Delete
一旦发现要被删除的节点, 要考虑以下几种情况:
- case1)如果节点是一片树叶,那么它可以被立即删除;
- case2)如果节点有一个儿子, 则该节点可以在其父节点调整指针绕过该节点后被删除;
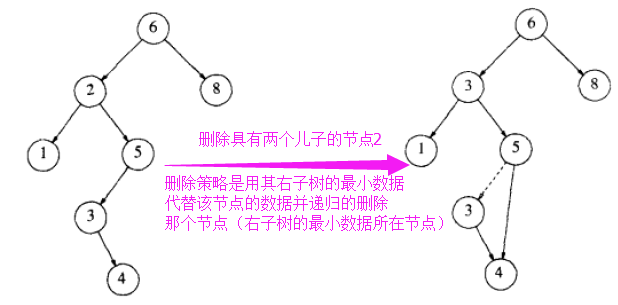
- case3)复杂的情况是处理具有两个儿子的节点。一般的删除策略是用其右子树的最小的数据代替该节点的数据并递归地删除那个节点(现在它是空的)。因为右子树中的最小节点不可能有 左儿子, 所以第二次 Delete(删除) 要容易;
- 引入懒惰删除(我的源代码中没有采用懒惰删除,这里旨在了解懒惰删除的概念):当一个元素要被删除时, 它仍留在树中, 而是只做了一个被删除的标记而已;
- 懒惰删除优点: 1.如果被删除的关键字是重新插入的, 那么分配一个新单元的开销就避免了;
2.3)关于二叉查找树的所有操作实例的源代码 + 测试结果:
1 ) download source code : https://github.com/pacosonTang/dataStructure-algorithmAnalysis/blob/master/chapter4/p74_binary_search_tree.c
2 ) source code at a glance :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>#define ElementType int
#define Error(str) printf("\n error: %s \n",str) struct BinarySearchTree;
typedef struct BinarySearchTree *BinarySearchTree;BinarySearchTree createBinarySearchTree(ElementType);
BinarySearchTree makeEmpty(BinarySearchTree);
BinarySearchTree insert(ElementType, BinarySearchTree) ;
BinarySearchTree deleteBinarySearchTree(ElementType, BinarySearchTree);// we adopt child-sibling notation
struct BinarySearchTree
{ElementType value;BinarySearchTree left;BinarySearchTree right;
};// create a BinarySearchTree with root node
BinarySearchTree createBinarySearchTree(ElementType value)
{ BinarySearchTree t;t = (BinarySearchTree)malloc(sizeof(struct BinarySearchTree));if(!t) {Error("out of space, from func createBinarySearchTree"); return NULL;} t->left = NULL;t->right = NULL; t->value = value;return t;
}// make the BinarySearchTree empty
BinarySearchTree makeEmpty(BinarySearchTree t)
{if(t){makeEmpty(t->left);makeEmpty(t->right); free(t);} return NULL;
}BinarySearchTree insert(ElementType e, BinarySearchTree root)
{ if(!root) {// find the node with its left or right being NULLroot = createBinarySearchTree(e);if(root)return root;else return NULL;}if(e > root->value) // the tree node with value e inserting into right child of the parent root->right = insert(e, root->right); else if(e < root->value) // the tree node withe value e inserting into left child of the parent root->left = insert(e, root->left); elseError(" you cannot insert the node into the tree for its value equals to one in the tree");return root; // dont't forget this line !
}// find the BinarySearchTree root node with value equaling to e
//Attention: the first statement must judge whether root is NULL or not
BinarySearchTree find(ElementType e, BinarySearchTree root)
{ if(!root) // judge whether root is NULL or notreturn NULL;if(e > root->value)return find(e, root->left); else if(e < root->value)return find(e, root->left);else return root;
} // find the minimum, (Attention for its non-recursion implementation )
BinarySearchTree findMin(BinarySearchTree root)
{if(root) {if(root->left)return findMin(root->left);elsereturn root;} return NULL;
}// find the Maximum, (Attention for its non-recursion implementation )
BinarySearchTree findMax(BinarySearchTree root)
{if(root) {if(root->right)return findMax(root->right);elsereturn root;} return NULL;
}// delete the node with given value e from the binary search tree
BinarySearchTree deleteBinarySearchTree(ElementType e, BinarySearchTree root)
{BinarySearchTree temp;if(!root)Error(" elements not found, from func deleteBinarySearchTree ");if(e > root->value) root->right = deleteBinarySearchTree(e, root->right);else if(e < root->value) root->left = deleteBinarySearchTree(e, root->left);else {// the value of root equals given eif(root->left && root->right) { // if the deleting node has both left and rightroot->value = findMin(root->right)->value; // set root's value the minimum of right tree of rootroot->right = deleteBinarySearchTree(root->value, root->right); } else { // one or zero child is not NULL// root->left = deleteBinarySearchTree(root->value, root->left); if(root->right) { // if root->right doesn't equal to NULLtemp = root;root = root->right;free(temp); }else if(root->left){ // if root->left doesn't equal to NULLtemp = root;root = root->left;free(temp); }else { // if both root->left and root->right equal to NULLfree(root);root = NULL;}}/* you can also fabricate code like this, which is reshipped from data_structure booktemp = root;if(!root->right)root = root->left;else if(!root->left)root = root->right;free(temp);*/} return root;
}// analog print directories and files name in the BinarySearchTree, which involves postorder traversal.
void printPreorder(int depth, BinarySearchTree root)
{ int i;if(root) { for(i = 0; i < depth; i++)printf(" "); printf("%d\n", root->value);printPreorder(depth + 1, root->left); printPreorder(depth + 1, root->right); // Attention: there's difference between traversing binary tree and common tree }else {for(i = 0; i < depth; i++)printf(" "); printf("NULL\n");}
}int main()
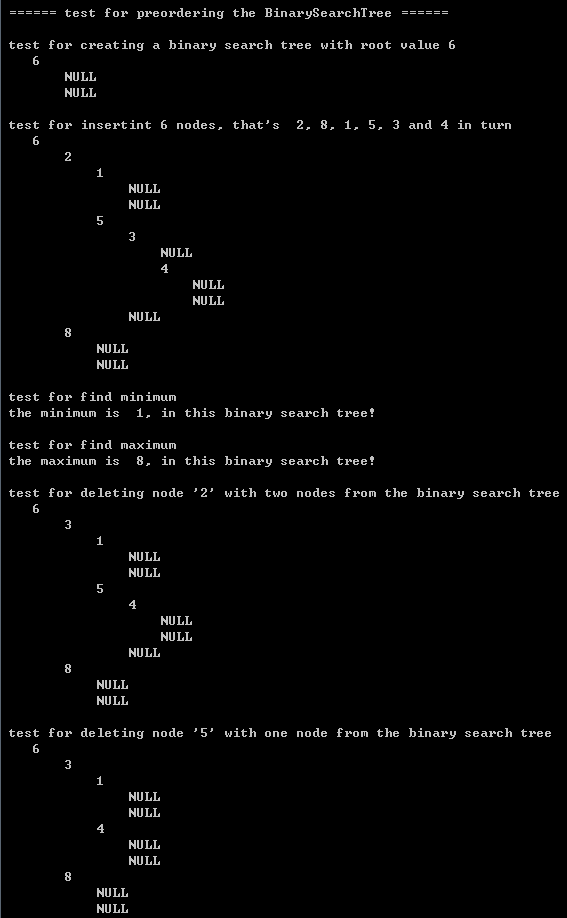
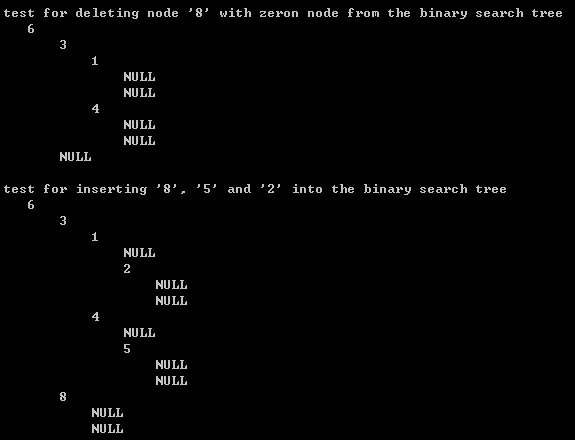
{BinarySearchTree bst; int value[] = {2, 8, 1, 5, 3, 4};int i;printf("\n ====== test for preordering the BinarySearchTree ====== \n"); printf("\n test for creating a binary search tree with root value 6 \n"); bst = createBinarySearchTree(6);printPreorder(1, bst); printf("\n test for insertint 6 nodes, that's 2, 8, 1, 5, 3 and 4 in turn \n"); for(i = 0; i < 6; i++)insert(value[i], bst); printPreorder(1, bst); printf("\n test for find minimum \n"); printf(" the minimum is %2d, in this binary search tree! \n", findMin(bst)->value);printf("\n test for find maximum \n"); printf(" the maximum is %2d, in this binary search tree! \n", findMax(bst)->value);printf("\n test for deleting node '2' with two nodes from the binary search tree \n"); deleteBinarySearchTree(2, bst);printPreorder(1, bst); printf("\n test for deleting node '5' with one node from the binary search tree \n"); deleteBinarySearchTree(5, bst);printPreorder(1, bst); printf("\n test for deleting node '8' with zeron node from the binary search tree \n"); deleteBinarySearchTree(8, bst);printPreorder(1, bst); printf("\n test for inserting '8', '5' and '2' into the binary search tree \n"); insert(8, bst);insert(5, bst);insert(2, bst);printPreorder(1, bst); return 0;
}




)










)



