TreadLocal
ThreadLocal解决的是线程内部变量的问题,并不是为了解决并发与共享变量的问题。
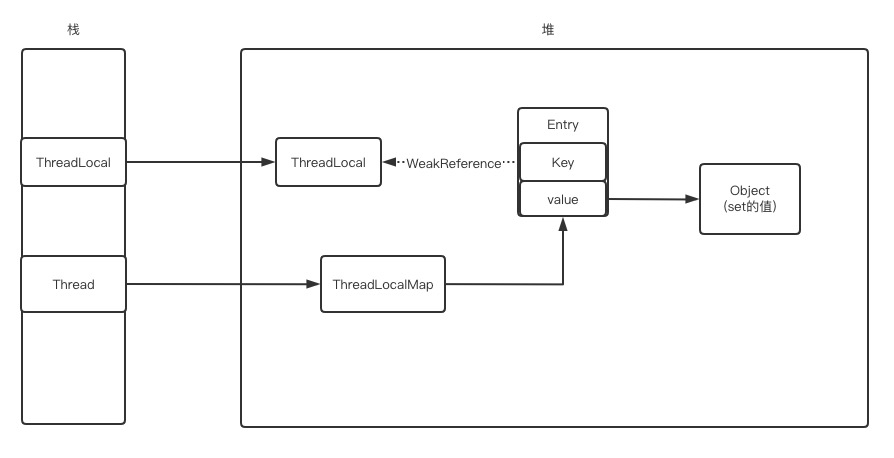
堆中有两个引用指向ThreadLocal,一个是ThreadLocal本身(强引用),一个ThreadLocalMap中Entry的key(弱引用)。
ThreadLocal的缺点?
ThreadLocal内部使用的线性探测法解决hash冲突,低效。可以使用Netty的FastLocalMap
内部变量为什么不在Thread开一个map?
现在的源码,我们无法直接访问Thread中ThreadLocaMap。如果放开的话。猜测:怕使用者用不好,更容易出现问题。
Thread 源码
Thread内部有threadLocals与inheritableThreadLocals两个变量,访问权限为包访问权限。都属于ThreadLocal的内部类,是一个map,线程的私有变量就是存储在这个结构中。内部类当做独立的类来看就行,因为编译后是两个单独的class。这样定义的原因是为了说明ThreadLocal与ThreadLocalMap相关的
public class Thread implements Runnable {/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained* by the ThreadLocal class. */ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;/** InheritableThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is* maintained by the InheritableThreadLocal class.*/ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;}
ThreadLocalMap的定义
static class ThreadLocalMap {/*** The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using* its main ref field as the key (which is always a* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.*/// key是弱引用;看super(k);key是一个ThreadLocalstatic class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */Object value;Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {super(k);value = v;}}/*** The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.*/private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;/*** The table, resized as necessary.* table.length MUST always be a power of two.*/// 是一个数组private Entry[] table;
ThreadLocal.get()逻辑
public T get() {Thread t = Thread.currentThread();ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);if (map != null) {// this就是当前threadLocal对象;找到对应的EntryThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);if (e != null) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")T result = (T)e.value;return result;}}// 找不到就返回初始化的值,一般是NUll,如果使用ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> Thread.currentThread().getName())初始化ThreadLocal;则会返回supplier的值return setInitialValue();}
getMap(t)逻辑
直接返回Thread的threadLocals变量
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {return t.threadLocals;}map.getEntry(this)逻辑
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);// 根据ThreadLocal对象的hash值计算应该取数组中的位置// 正常来说一般都使用一个threadLocal;项目中的threadlocal一般都是static final的Entry e = table[i];// e != null但是 e.get() != key 说明hash冲突了,在ThreadLocal中没有链表解决冲突,继续往后找。if (e != null && e.get() == key)return e;else// 如果找不到,就执行此方法继续找return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
getEntryAfterMiss()
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;// 继续往后找,只要往后找到一个位置是null,则说明没有这个entrywhile (e != null) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == key)return e;if (k == null) // 如果后面Entry的key是null,则清除这个Entry// 堆中的ThreadLocal对象是被两个引用指向的,一个栈上的强引用,一个key的弱引用// 一定是栈上的强引用先删除,在gc时才会触发弱引用删除// 此时key为null,意味着栈上对threadLocal的引用没有了,此时由于key是弱引用,那么只要发生gc,ThreadLocal对象就会被回收,key指向的就null,此时需要清除这个没用的EntryexpungeStaleEntry(i);elsei = nextIndex(i, len);//往下找,下标+1e = tab[i];}return null;// 找不到就返回null}
expungeStaleEntry()清除逻辑
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;// 如果entry不为null,但是key是key是null。直接删除entry。// expunge entry at staleSlottab[staleSlot].value = null;tab[staleSlot] = null;size--;// Rehash until we encounter nullEntry e;int i;for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = nextIndex(i, len)) {// 知道entry是null才ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == null) {// 如果entry不为null,但是key是key是null。直接删除entry。e.value = null;tab[i] = null;size--;} else {int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);if (h != i) {tab[i] = null;// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until// null because multiple entries could have been stale.while (tab[h] != null)h = nextIndex(h, len);tab[h] = e;}}}return i;
}
set()逻辑
public void set(T value) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread();ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);if (map != null)map.set(this, value);elsecreateMap(t, value);
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at// least as common to use set() to create new entries as// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast// path would fail more often than not.Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;// 同hash找到位置int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;// 如果不为null,说明key可能存在,看下是不是一样,一样的话就更新value。否则继续往后找e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == key) {e.value = value;return;}if (k == null) {// 如果key==null 则替换replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);return;}}tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);// 当前位置是null 则直接添加int sz = ++size;if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)// cleanSomeSlots也是删除key== null的Entryrehash();// 扩容 2倍,使用hash&新的长度。
}
关于内存泄漏
很多人都说ThreadLocal有内存泄漏的风险。从分析源码可以看下,如果栈上的强引用删除,执行完一次GC之后,此时Entry中的key是null。也就说明这个Entry此时是没有用的了。当没有触发删除entry的逻辑,entry就会一直存在内存中。
但是,ThreadLocal在设计的时候,已经想到了这些问题,所以在操作ThreadLocal的时候都会对key为null的Entry进行删除,防止内存泄漏。除此之外,ThreadLocal还提供了remove方法,手动删除此key对应的Entry。源码如下:
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {if (e.get() == key) {e.clear();expungeStaleEntry(i);return;}}
}
如果不使用线程池,那么不需要关系ThreadLoca的内存泄漏问题,因为线程执行完,整个线程都被回收了。但是我们一般使用的都是线程池,Tomcat在处理每个请求时都会从线程池中拿一个线程,但是使用完之后并不会回收,而是放回线程池。所以线程的独享变量threadLocalMap就需要手动清除,不然也可能发生数据错乱问题。
最佳实践
public void threadLocalToDo() {threadlocal.set(xxx);try {// do sth} finally {threadlocal.remove();}
}
只要在finally中手动remove(),那么肯定不会发生任何问题。
InheritableThreadLocal
这玩意可以理解为就是可以把父线程的 threadlocal 传递给子线程,所以如果要这样传递就用 InheritableThreadLocal ,不要用 threadlocal。
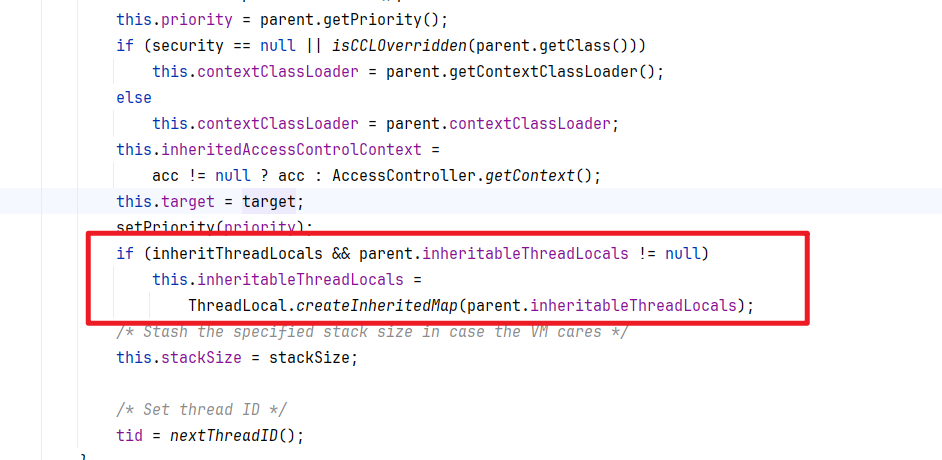
父线程在创建子线程是会判断InheritableThreadLocal 是不是null,不是就会把InheritableThreadLocal复制一份给子线程。














)
Unofficial Mirror【游记】【题解】)



