Title
题目
Pancreatic Cancer Detection on CT Scans with Deep
Learning: A Nationwide Population-based Study
胰腺癌在CT扫描中通过深度学习检测:一项全国性的基于人群的研究
01
文献速递介绍
胰腺癌(PC)的五年生存率是所有癌症中最低的,预计到2030年将成为美国癌症死亡的第二大原因。由于一旦肿瘤体积超过2厘米,预后会急剧恶化,因此早期检测是改善PC的悲观预后最有效的策略。CT是用于帮助检测PC的主要成像方式,但其对小肿瘤的敏感性适中,大约40%的小于2厘米的肿瘤会被漏检。此外,CT的诊断性能依赖于解释者,并且可能受到放射科医师可用性和专业知识差异的影响。因此,需要一个有效的工具来辅助放射科医师提高PC检测的敏感性,这是一个主要的未满足的医疗需求。
近期在深度学习(DL)方面的进步在医学图像分析中显示出巨大的潜力。在我们之前的单中心概念验证研究中,我们展示了一个卷积神经网络(CNN)能够准确地区分PC和非癌性胰腺。然而,在那项研究中,胰腺的分割(即,识别胰腺)是由放射科医师手工执行的。胰腺的分割是最具挑战性的,因为胰腺与多个器官和结构相邻,并且在形状和大小上有着广泛的变化,特别是在PC患者中。然而,一个临床可应用的计算机辅助检测(CAD)工具应该能够在最小的人工注释或劳动下实现分割和分类(即,预测PC的存在或缺失)。
Background
背景
Approximately 40% of pancreatic tumors smaller than 2 cm are missed at abdominal CT.
大约40%的小于2厘米的胰腺肿瘤在腹部CT扫描中被遗漏。
Conclusions
结论
The deep learning–based tool enabled accurate detection of pancreatic cancer on CT scans, with reasonable sensitivity for tumors smaller than 2 cm.
基于深度学习的工具能够在CT扫描上准确检测胰腺癌,对于小于2厘米的肿瘤具有合理的敏感性。
Results
结果
A total of 546 patients with pancreatic cancer (mean age, 65 years ± 12 [SD], 297 men) and 733 control subjects were ran domly divided into training, validation, and test sets. In the internal test set, the DL tool achieved 89.9% (98 of 109; 95% CI: 82.7, 94.9) sensitivity and 95.9% (141 of 147; 95% CI: 91.3, 98.5) specificity (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve [AUC], 0.96; 95% CI: 0.94, 0.99), without a significant difference (P = .11) in sensitivity compared with the original radiologist report (96.1% [98 of 102]; 95% CI: 90.3, 98.9). In a test set of 1473 real-world CT studies (669 malignant, 804 control) from institutions throughout Taiwan, the DL tool distinguished between CT malignant and control studies with 89.7% (600 of 669; 95% CI: 87.1, 91.9) sensitivity and 92.8% specificity (746 of 804; 95% CI: 90.8, 94.5) (AUC, 0.95; 95% CI: 0.94, 0.96), with 74.7% (68 of 91; 95% CI: 64.5, 83.3) sensitivity for malignancies smaller than 2 cm.
共有546名胰腺癌患者(平均年龄65岁±12[标准差],297名男性)和733名对照对象被随机分配到训练、验证和测试集。在内部测试集中,深度学习工具达到了89.9%(109中的98个;95%置信区间:82.7,94.9)的敏感性和95.9%(147中的141个;95%置信区间:91.3,98.5)的特异性(接收器操作特性曲线下面积[AUC],0.96;95%置信区间:0.94,0.99),与原始放射科医生报告的敏感性相比没有显著差异(P = .11)(96.1%[102中的98个];95%置信区间:90.3,98.9)。在一个包含1473个真实世界CT研究的测试集中(669个恶性,804个对照),来自台湾各机构的深度学习工具以89.7%的敏感性(669中的600个;95%置信区间:87.1,91.9)和92.8%的特异性(804中的746个;95%置信区间:90.8,94.5)(AUC,0.95;95%置信区间:0.94,0.96)区分了CT恶性和对照研究,对于小于2厘米的恶性肿瘤,敏感性为74.7%(91中的68个;95%置信区间:64.5,83.3)。
Method
方法
Retrospectively collected contrast-enhanced CT studies in patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer between January 2006 and July 2018 were compared with CT studies of individuals with a normal pancreas (control group) obtained between January 2004 and December 2019. An end-to-end tool comprising a segmentation convolutional neural network (CNN) and a classifier ensembling five CNNs was developed and validated in the internal test set and a nationwide real-world validation set. The sensitivities of the computer-aided detection (CAD) tool and radiologist interpretation were compared using the McNemar test.
回顾性地收集了2006年1月至2018年7月间被诊断为胰腺癌患者的增强对比CT研究,并与2004年1月至2019年12月间获得的正常胰腺个体(对照组)的CT研究进行了比较。开发并验证了一个端到端的工具,包括一个分割卷积神经网络(CNN)和一个分类器,该分类器集成了五个CNN,在内部测试集和一个全国范围的现实世界验证集中进行了验证。使用McNemar测试比较了计算机辅助检测(CAD)工具和放射科医生解读的敏感性。
Figure
图
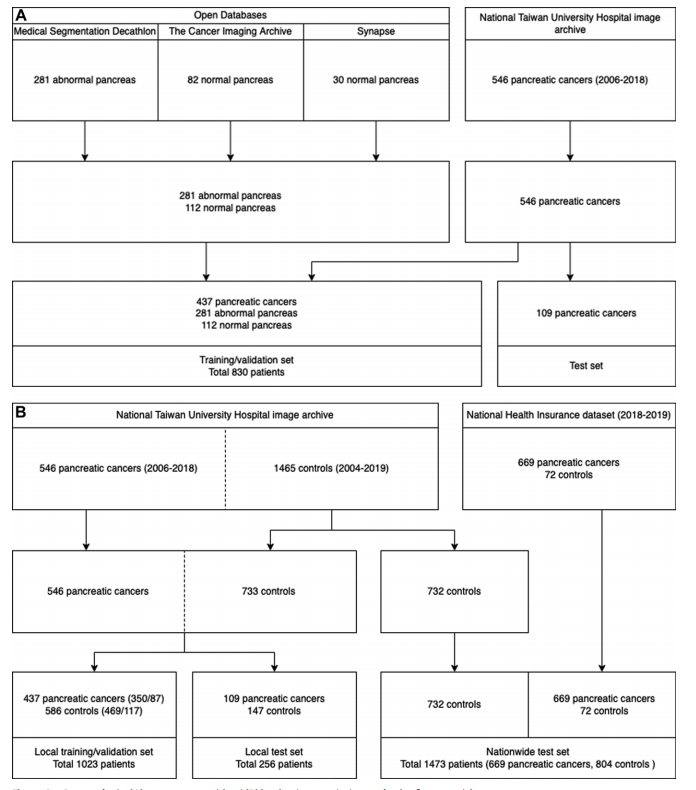
Figure 1: Data sets for the (A) segmentation model and (B) local and nationwide data sets for classification models.
图1:(A) 分割模型的数据集以及 (B) 分类模型的本地和全国范围数据集。
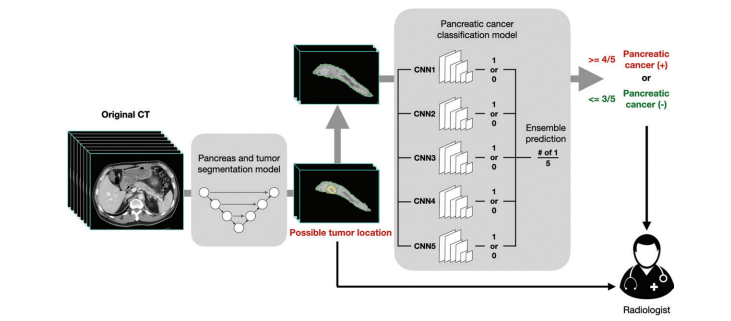
Figure 2: Workflow of the deep learning–based computer-aided detection tool. The segmentation masks passed from the segmentation convolutional neural network (CNN) to the classification CNNs included the pancreas and tumor (if present) combined, without separate delineation or identification between the pancreas and tumor. Solid arrows indicate output of the computer-aided detection tool.
图2:基于深度学习的计算机辅助检测工具的工作流程。从分割卷积神经网络(CNN)传递给分类CNN的分割掩模包括了胰腺和肿瘤(如果存在)的结合体,没有分别勾画或识别胰腺和肿瘤之间的区别。实线箭头表示计算机辅助检测工具的输出。
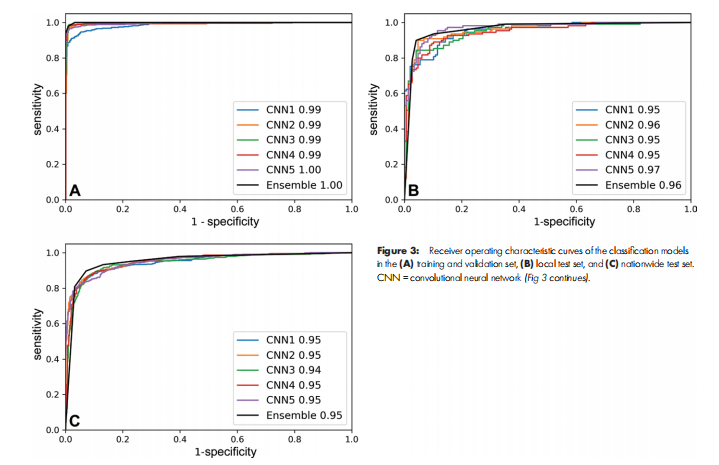
Figure 3: Receiver operating characteristic curves of the classification models in the (A) training and validation set, (B) local test set, and (C) nationwide test set. CNN = convolutional neural network (Fig 3 continues).
图3:分类模型的接收器操作特征曲线 在 (A) 训练和验证集,(B) 本地测试集,以及 (C) 全国范围测试集中。CNN = 卷积神经网络 (图3继续)。
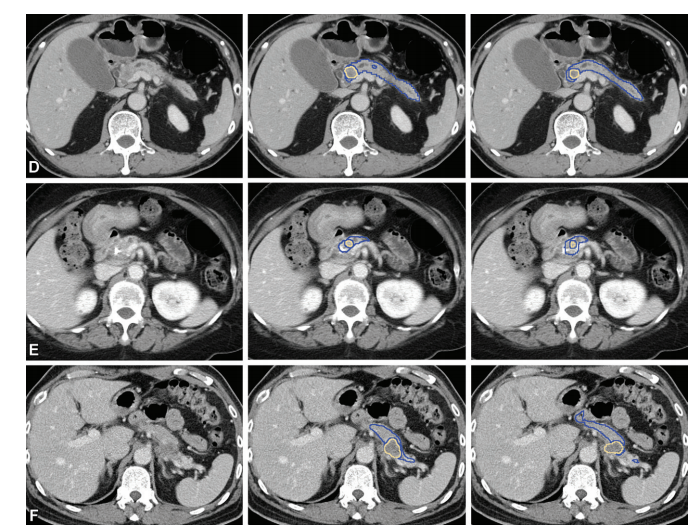
Figure 3 (continued): Representative CT scans (left column) with tumor at the pancreas (D) head, (E) body, and (F) tail show correspondence in tumor location between manual segmentation by radiologists (middle column) and predictions by the segmentation model (right column). Blue outline indicates the pancreas; yellowoutline indicates tumor.
图3 (续):代表性CT扫描(左列)显示胰腺(D)头部、(E)体部和(F)尾部的肿瘤,放射科医生的手工分割(中列)与分割模型的预测(右列)在肿瘤位置上的对应。蓝色轮廓表示胰腺;黄色轮廓表示肿瘤。
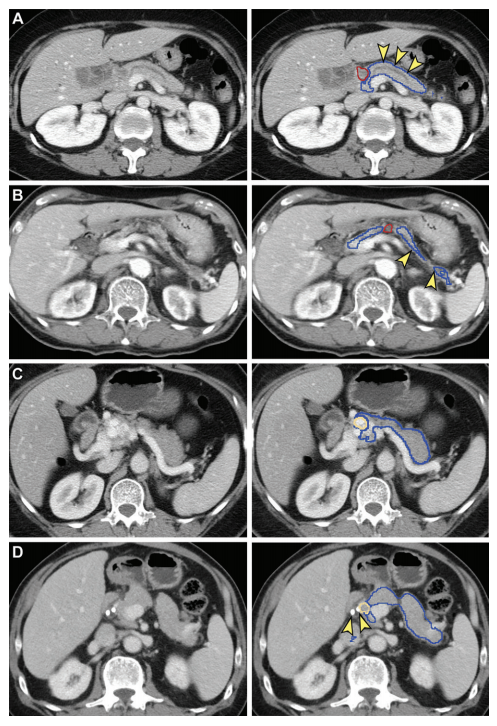
Figure 4: False-negative (A, B) and false-positive (C, D) tumor segmentation by the segmentation model. Blue and yellow outlines indicate normal pancreas and tumor segmented with the segmentation model, respectively. Images in the left column are original unannotated CT scans. (A, B) Tumors (red outline) were not segmented by the segmentation convolutional neural network. The upstream pancreas shows secondary signs of pancreatic cancer, including dilation of the pancreatic duct with abrupt cutoff (arrowhead in A) and parenchymal atrophy with dilation of the pancreatic duct(arrowhead in B). (C) Collateral veins secondary to idiopathic portal vein thrombosis were incorrectly segmented as tumor by the segmentation model. (D) Pancreatic parenchyma adjacent to biliary stents (arrowhead) placed for relieving obstructive jaundice from hepatocellular carcinoma was incorrectly segmented as tumor by the segmentation model.
图4:分割模型的假阴性(A, B)和假阳性(C, D)肿瘤分割。蓝色和黄色轮廓分别表示用分割模型分割的正常胰腺和肿瘤。左列图像是原始未标注的CT扫描。(A, B) 肿瘤(红色轮廓)未被分割卷积神经网络分割。上游胰腺显示胰腺癌的次要征兆,包括胰管扩张和突然截止(A中的箭头)以及胰腺实质萎缩和胰管扩张(B中的箭头)。(C) 由特发性门静脉血栓形成的侧支静脉被分割模型错误地分割为肿瘤。(D) 为缓解肝细胞癌引起的梗阻性黄疸而放置的胆道支架(箭头)旁的胰腺实质被分割模型错误地分割为肿瘤。
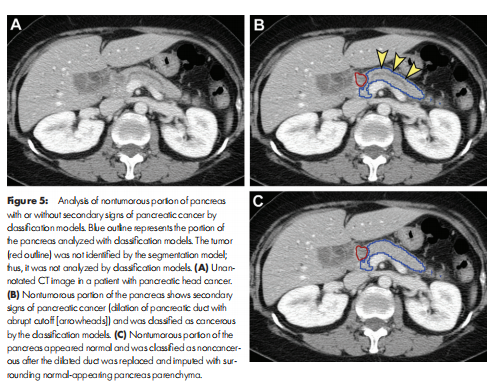
Figure 5: Analysis of nontumorous portion of pancreas with or without secondary signs of pancreatic cancer by classification models. Blue outline represents the portion of the pancreas analyzed with classification models. The tumor (red outline) was not identified by the segmentation model; thus, it was not analyzed by classification models. (A) Unan notated CT image in a patient with pancreatic head cancer. (B) Nontumorous portion of the pancreas shows secondary signs of pancreatic cancer (dilation of pancreatic duct with abrupt cutoff [arrowheads]) and was classified as cancerous by the classification models. (C) Nontumorous portion of the pancreas appeared normal and was classified as noncancer ous after the dilated duct was replaced and imputed with sur rounding normal-appearing pancreas parenchyma.
图5: 通过分类模型分析无肿瘤部分的胰腺是否有胰腺癌的次要征兆。蓝色轮廓代表了用分类模型分析的胰腺部分。肿瘤(红色轮廓)未被分割模型识别;因此,它没有被分类模型分析。(A) 一位胰腺头部癌症患者的未标注CT图像。(B) 无肿瘤部分的胰腺显示胰腺癌的次要征兆(胰管扩张和突然截止[箭头]),并被分类模型识别为癌症。(C) 无肿瘤部分的胰腺看起来正常,并在扩张的管道被替换和用周围看似正常的胰腺实质填充后,被分类为非癌症。
Table
表
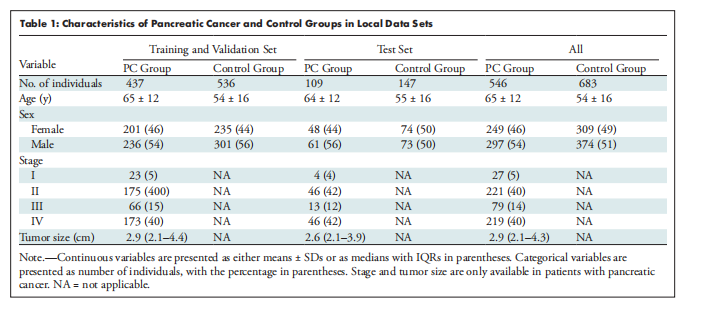
Table 1: Characteristics of Pancreatic Cancer and Control Groups in Local Data Sets
表1:本地数据集中胰腺癌和对照组的特征
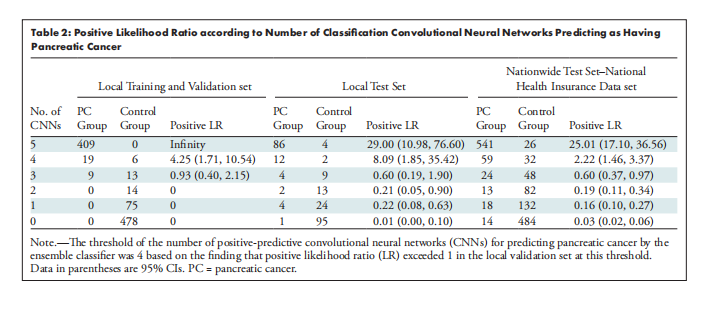
Table 2: Positive Likelihood Ratio according to Number of Classification Convolutional Neural Networks Predicting as Having Pancreatic Cancer
表2:根据预测为胰腺癌的分类卷积神经网络的数量的阳性似然比
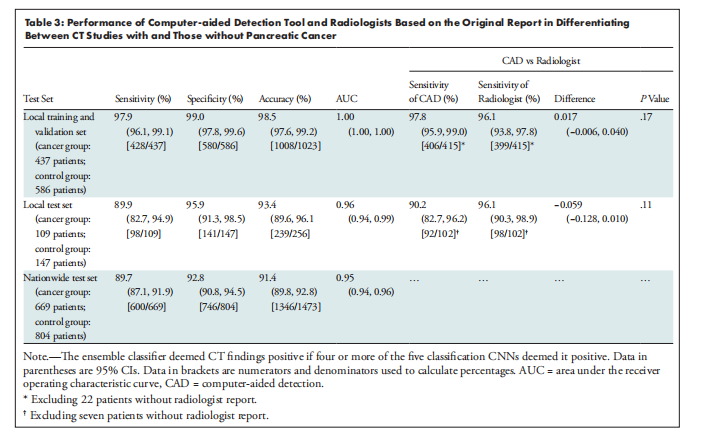
Table 3: Performance of Computer-aided Detection Tool and Radiologists Based on the Original Report in Differentiating Between CT Studies with and Those without Pancreatic Cancer
表3:基于原始报告,在区分有和没有胰腺癌的CT研究中,计算机辅助检测工具和放射科医生的表现
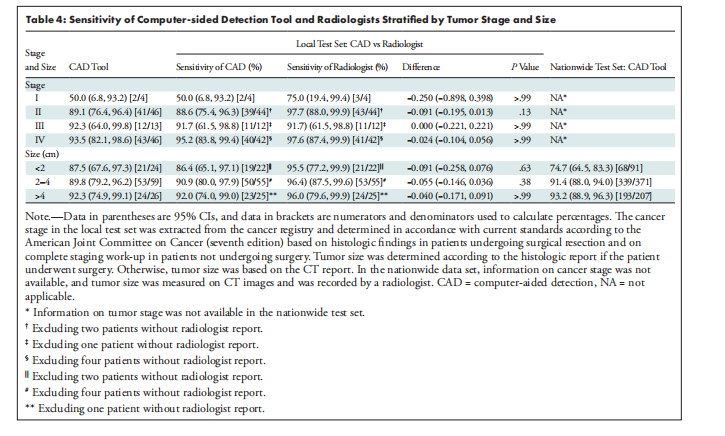
Table 4: Sensitivity of Computer-sided Detection Tool and Radiologists Stratified by Tumor Stage and Size
表4:按肿瘤分期和大小分层的计算机辅助检测工具和放射科医生的敏感性


—— 序列标注任务)







一文就够了)
)
)




)

