首先讲下 ES的倒排序索引
创建倒排索引是对正向索引的一种特殊处理,
-
将每一个文档的数据利用算法分词,得到一个个词条
-
创建表,每行数据包括词条、词条所在文档id、位置等信息
-
因为词条唯一性,可以给词条创建索引,例如hash表结构索引

倒排索引的搜索流程
倒排索引的搜索流程如下(以搜索"华为手机"为例):
- 用户输入条件
"华为手机"进行搜索。 - 对用户输入内容分词,得到词条:
华为、手机。 - 拿着词条在倒排索引中查找,可以得到包含词条的文档id:1、2、3。
- 拿着文档id到正向索引中查找具体文档

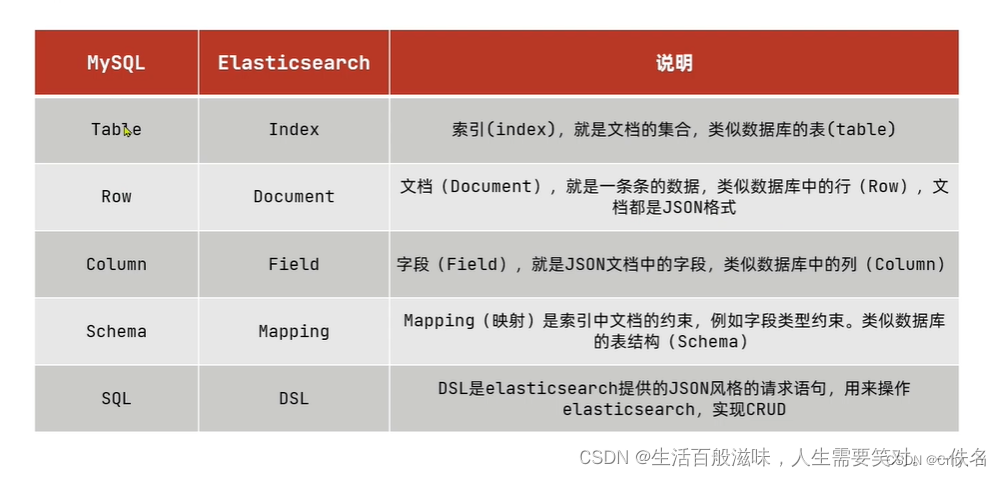
正向索引和倒排索引
正向索引:
优点:
可以给多个字段创建索引
根据索引字段搜索、排序速度非常快
缺点:
根据非索引字段,或者索引字段中的部分词条查找时,只能全表扫描
倒排索引:
优点:
根据词条搜索、模糊搜索时,速度非常快
缺点:
只能给词条创建索引,而不是字段
无法根据字段做排序

如何在ES上创建索引
首先打开kibanba
进入到控制台然后开始创建索引
之前说过es中索引对应的是mysql的数据库,所以我们应该先创建索引
创建索引语法:put shooping
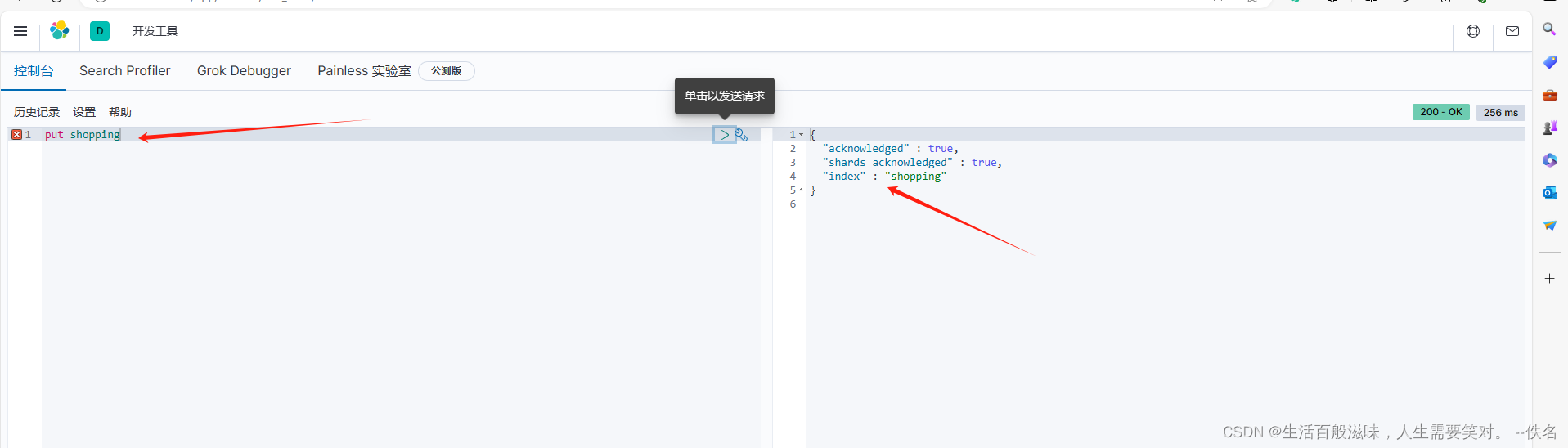
{
"acknowledged" : true,
"shards_acknowledged" : true,
"index" : "shopping"
}
会返回这几个字段,分别代表
acknowledged:代表是创建索引创建成功
shards_acjnowledged: 代表所有分片创建成功
index:代表索引的名字
然后再次put的,会出现这种情况 put是具有幂等性的

{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "resource_already_exists_exception",
"reason" : "index [shopping/32XXUAigSX-96lF9wV49Aw] already exists",
"index_uuid" : "32XXUAigSX-96lF9wV49Aw",
"index" : "shopping"
}
],
"type" : "resource_already_exists_exception",
"reason" : "index [shopping/32XXUAigSX-96lF9wV49Aw] already exists",
"index_uuid" : "32XXUAigSX-96lF9wV49Aw",
"index" : "shopping"
},
"status" : 400
}
error:表示错误
root_cause:表示错误的列表
type:表示错误类型
reason:错误的原因
index_uuid:唯一标识
index:索引名字
如果想用post请求会发送什么,post是不具有幂等性的

Incorrect HTTP method for uri [/shopping?pretty=true] and method [POST], allowed: [HEAD, PUT, GET, DELETE]",
方法不能使用post,直接报错
查询索引语法:get shopping

{
"shopping" : {
"aliases" : { },
"mappings" : { },
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"creation_date" : "1710766914710",
"number_of_shards" : "1",
"number_of_replicas" : "1",
"uuid" : "32XXUAigSX-96lF9wV49Aw",
"version" : {
"created" : "7080099"
},
"provided_name" : "shopping"
}
}
}
}
shopping:索引名字
aliases:索引别名
mappings:意识就是文档结构和字段类型
settings:设置索引的信息
index:索引级的设置
creation_date:创建时间
number_of_shards:索引分片的数量
number_of_replicas:每个分片的副本数量
uuid:uuid
version:版本号
provided_name:提供的索引名字
查询全部索引语法:get _cat/indices?v

表头 含义
health 当前服务器健康状态: green(集群完整) yellow(单点正常、集群不完整) red(单点不正常)
status 索引打开、关闭状态
index 索引名
uuid 索引统一编号
pri 主分片数量
rep 副本数量
docs.count 可用文档数量
docs.deleted 文档删除状态(逻辑删除)
store.size 主分片和副分片整体占空间大小
pri.store.size 主分片占空间大小
删除索引语法:delete shopping
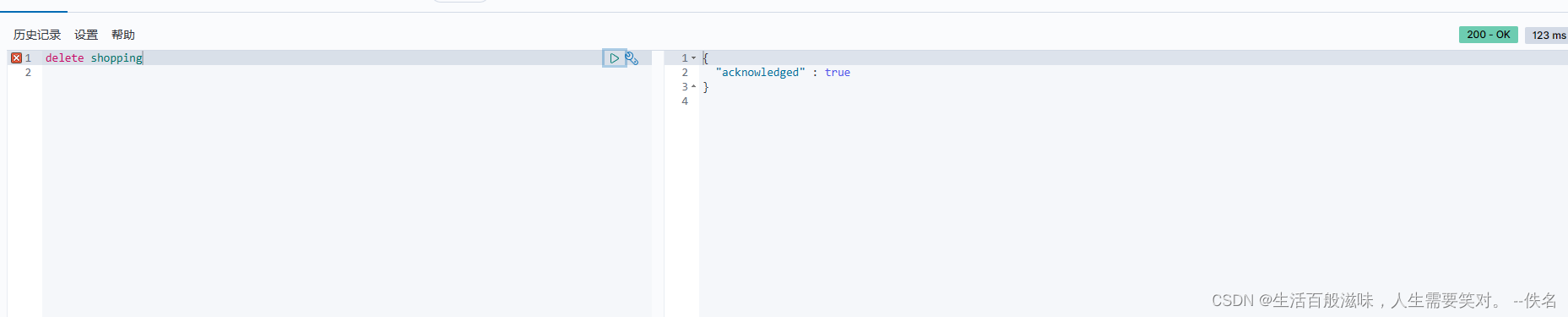
{
"acknowledged" : true
}
acknowledged:是否成功
创建es数据语法:post /shopping/_doc
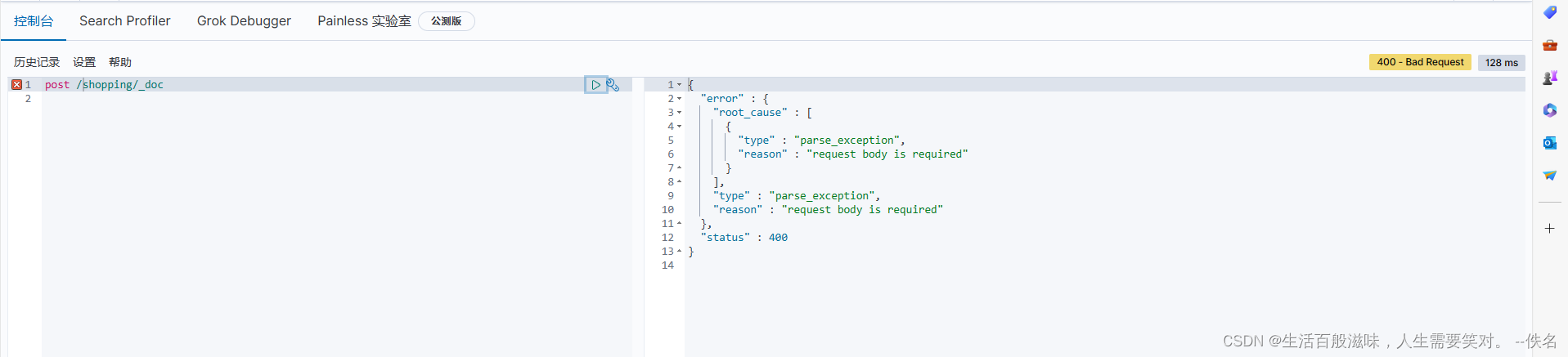
{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "parse_exception",
"reason" : "request body is required"
}
],
"type" : "parse_exception",
"reason" : "request body is required"
},
"status" : 400
}
文档对应的是数据库中数据
这个原因就是没有body数据,并且我们传递数据是json
试着这种修改一下
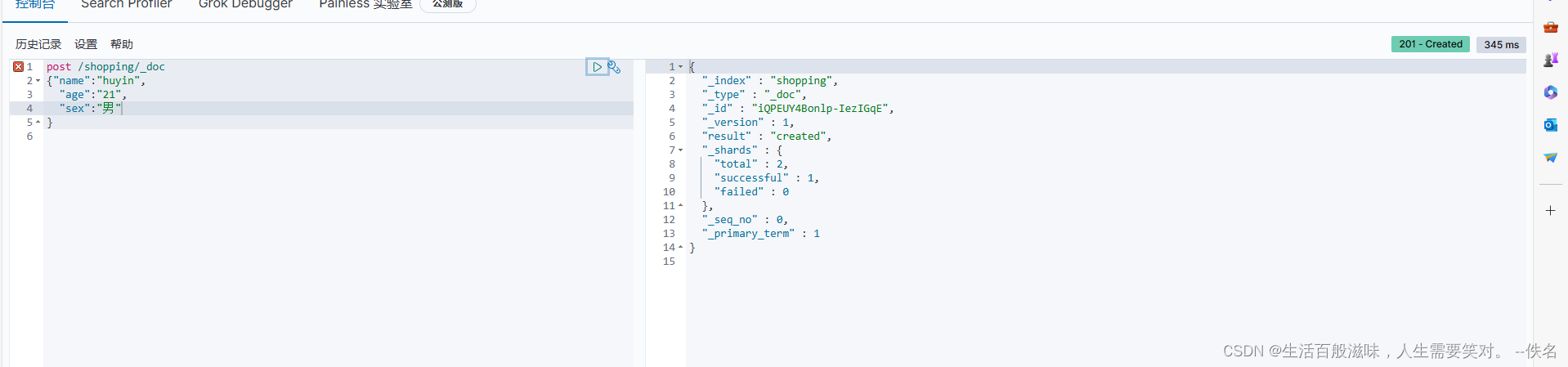
{
"_index" : "shopping",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "iQPEUY4Bonlp-IezIGqE",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1
}
index:索引
type:文档
id:唯一标识
result:结果
shards:分配
total:分片总数
successful:成功数量
failed:失败数量
seq_no:文档序列号,序列号越大标识越新
_primary_term:文档所属的主要分片的任期号
当在发送一模一样的请求
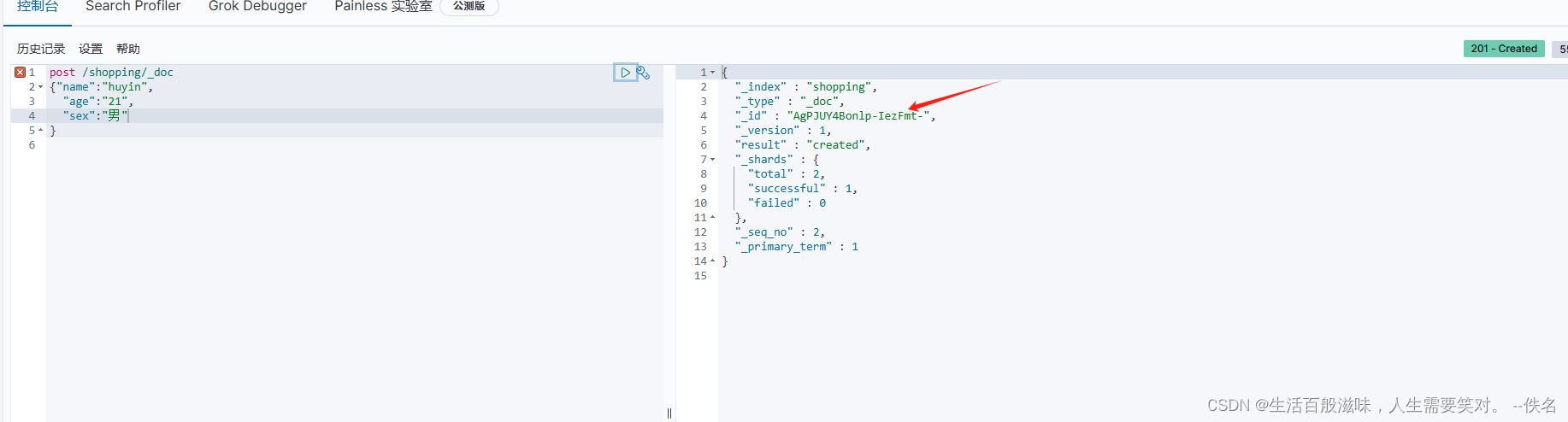
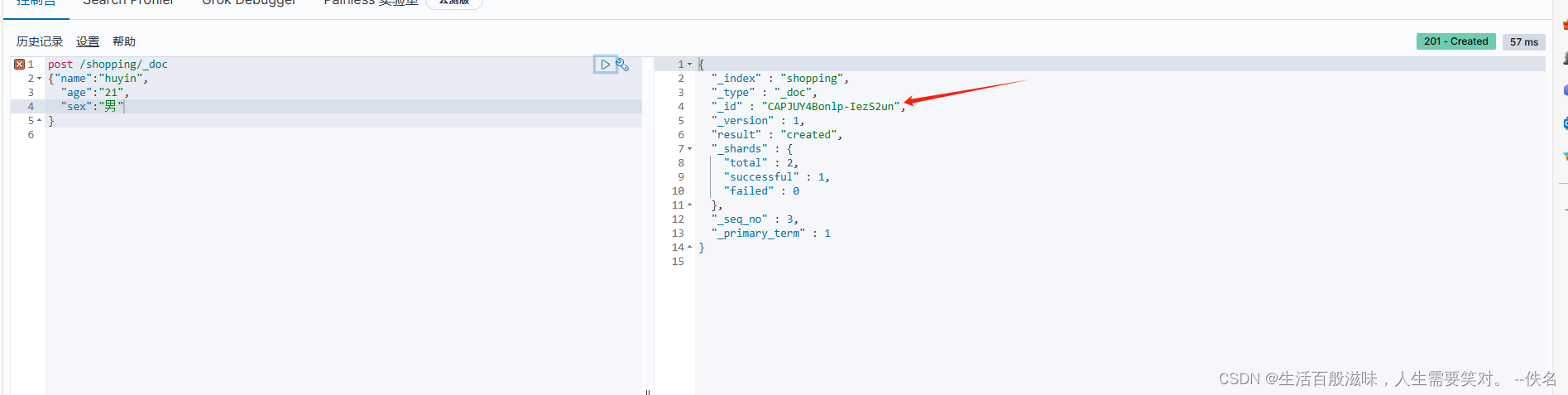
id一直在变化,如果我们想查询某个数据,id太麻烦了,如果想自定义呢
创建es数据指定id语法:post /shopping/_doc/1001

如果我们指定了id,这时候就可以用put,因为他是幂等性

主键查询和全局查询语法
主键查询:get /shopping/_doc/1001
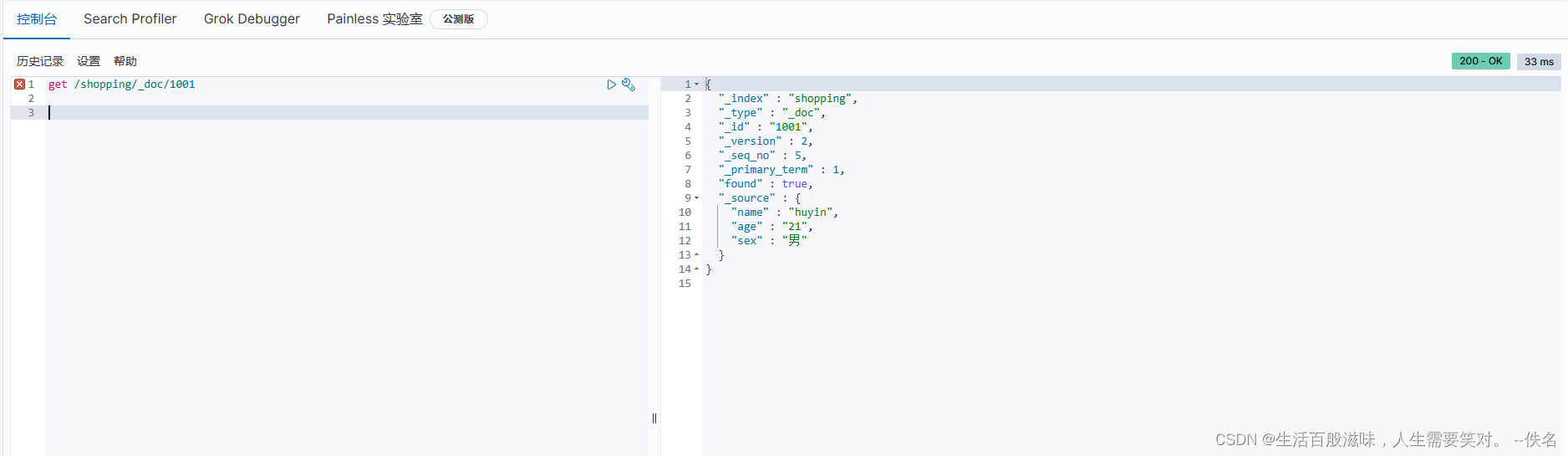
{
"_index" : "shopping", //索引
"_type" : "_doc", //类型
"_id" : "1001", //id
"_version" : 2, //版本号
"_seq_no" : 5, //序列号
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true, //成功
"_source" : { //信息
"name" : "huyin",
"age" : "21",
"sex" : "男"
}
}
查询没有的数据
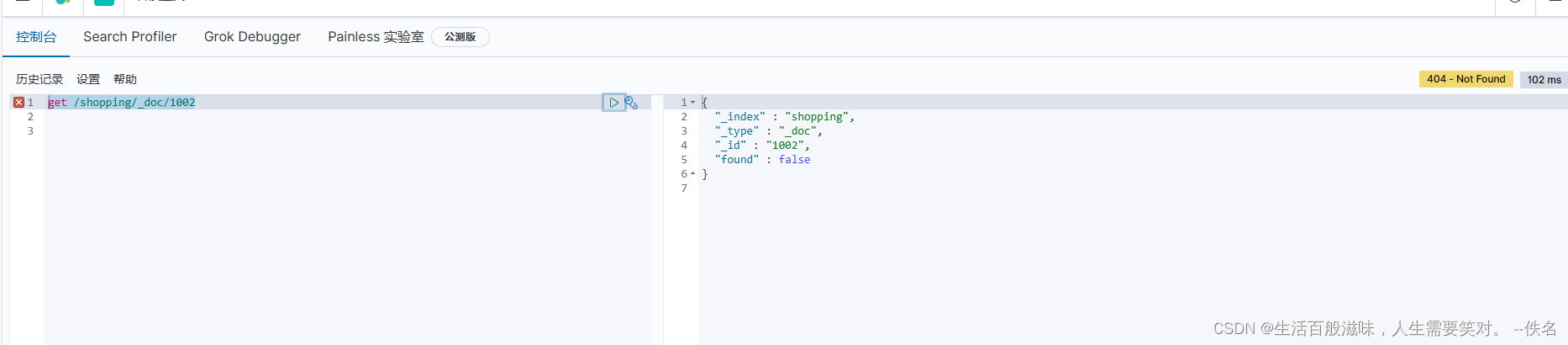
{
"_index" : "shopping",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1002",
"found" : false
}
查询全部数据语法:get /shopping/_search

{
"took" : 0, // 耗时
"timed_out" : false, // 超时
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 5,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [ //命中
{
"_index" : "shopping",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "iQPEUY4Bonlp-IezIGqE",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "huyin",
"age" : "21",
"sex" : "男"
}
},
{
"_index" : "shopping",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "AQPJUY4Bonlp-IezE2v3",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "huyin",
"age" : "21",
"sex" : "男"
},
]
}
}
全局修改和局部修改语法
全局修改:put /shopping/_doc/1001
put具有幂等性所以可以用
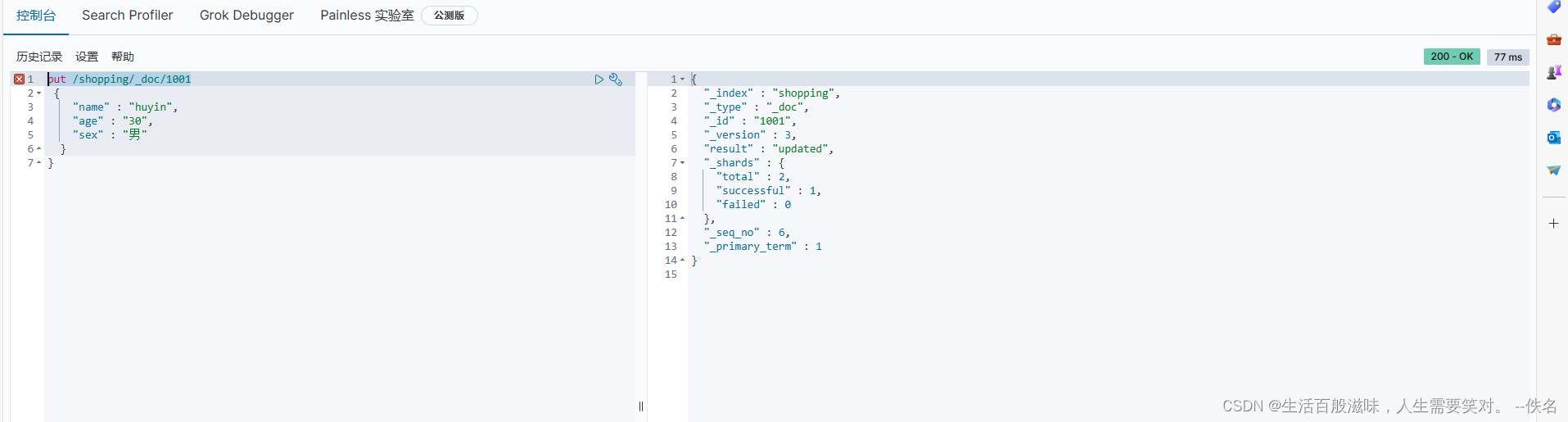
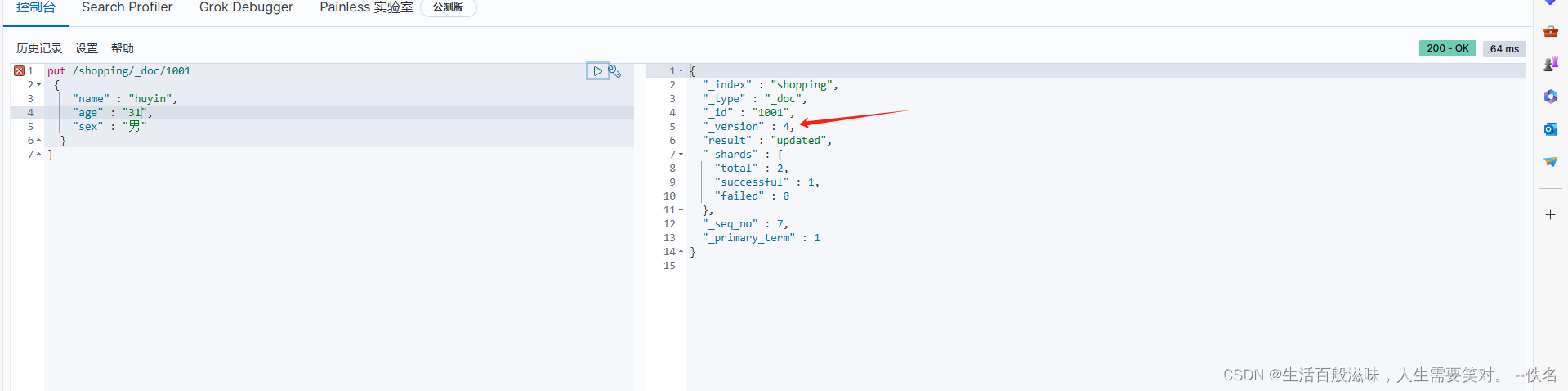 {
{
"_index" : "shopping",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1001",
"_version" : 3, // 版本号是一直变化的
"result" : "updated", 结果:updated 修改
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 6,
"_primary_term" : 1
}
局部修改:post /shopping/_update/1001
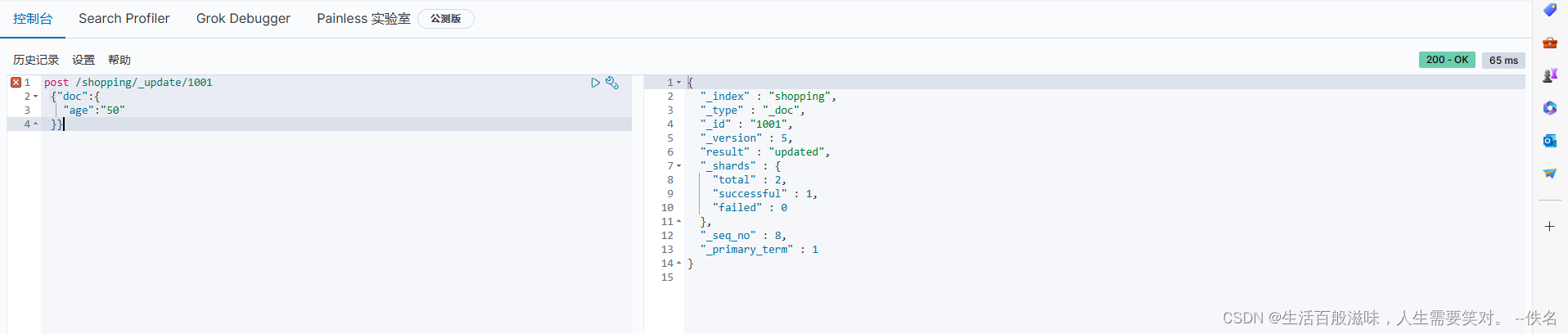
get请求一个:get /shopping/_doc/1001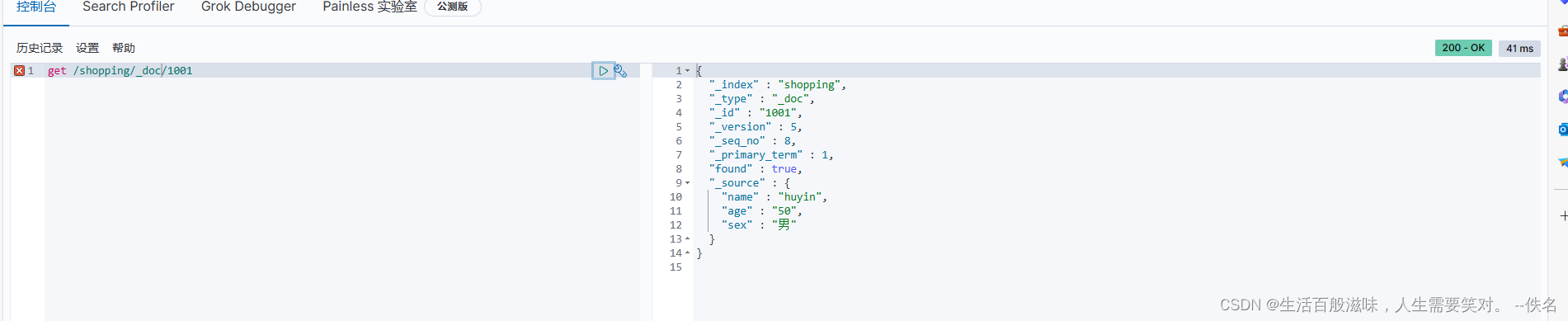
条件查询语法:get /shopping/_search 传入body
{"query":{ query 查询的意思
"match": { match 匹配的意思
"name": "huyin" name 查询那个字段 huyin 查询那个值
}
}}
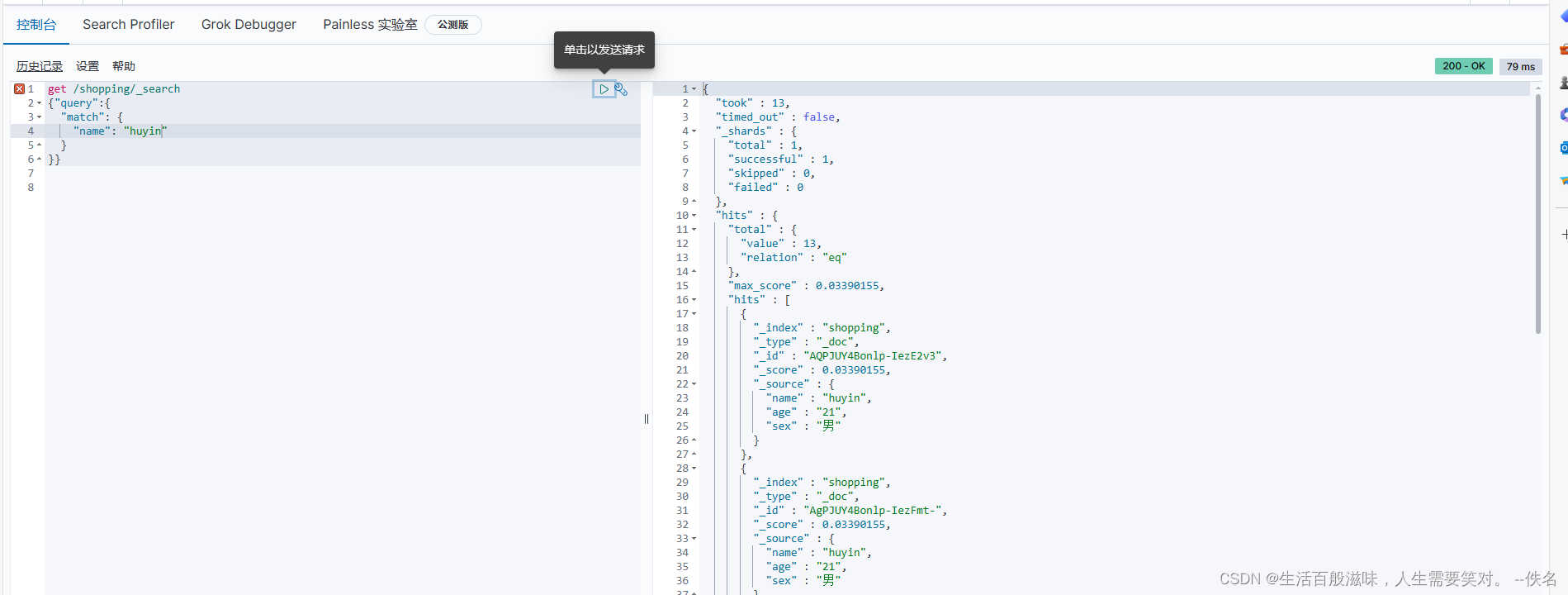
全文查询的语法:get /shopping/_search
{"query":{ query 查询的意思
"match_all": {} match_all 全部查询
}}

分页查询的语法:get /shopping/_search
{"query":{
"match_all": {}
},
"from":0, from当前页的起始位置
"size":2 每页条数
}
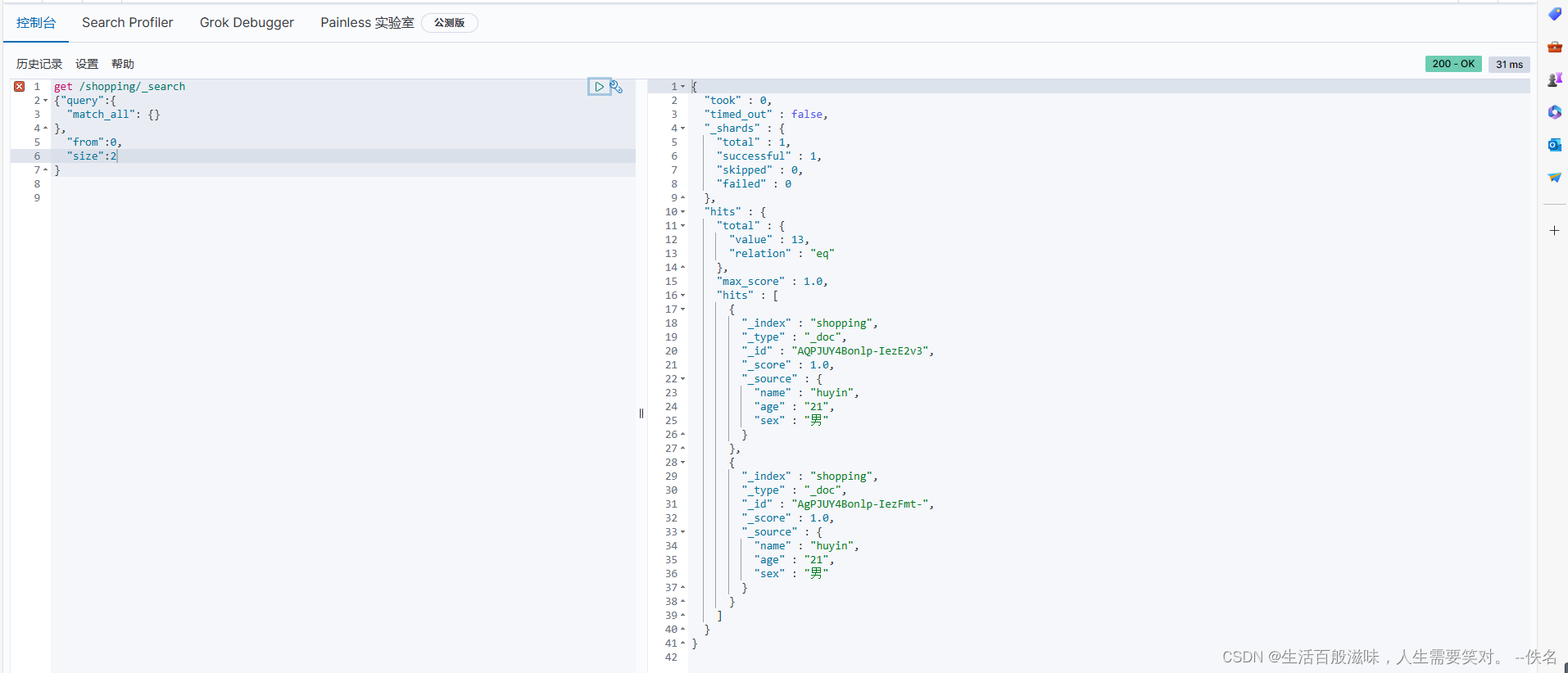
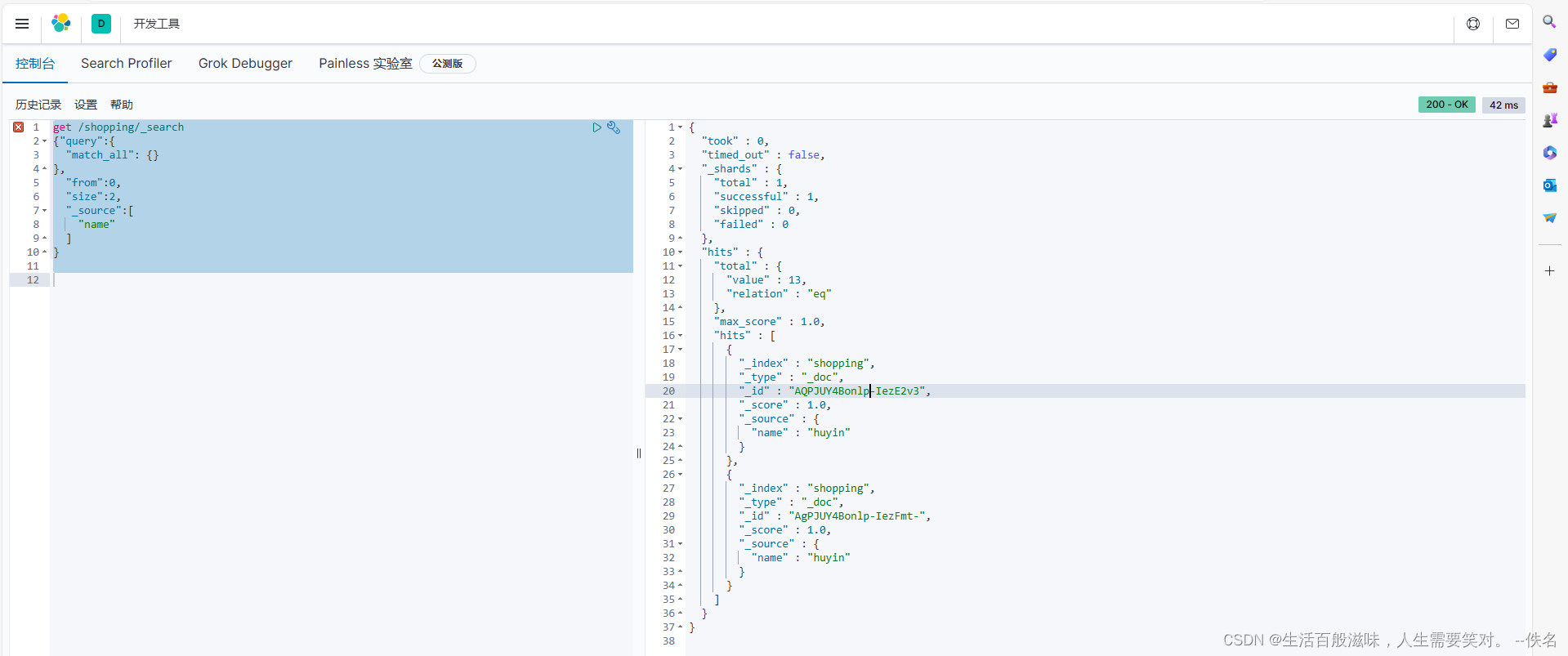
筛选出固定的字段:get /shopping/_search
{"query":{
"match_all": {}
},
"from":0,
"size":2,
"_source":[ source :数组里面是可以筛选出固定的字段
"name"
]
}
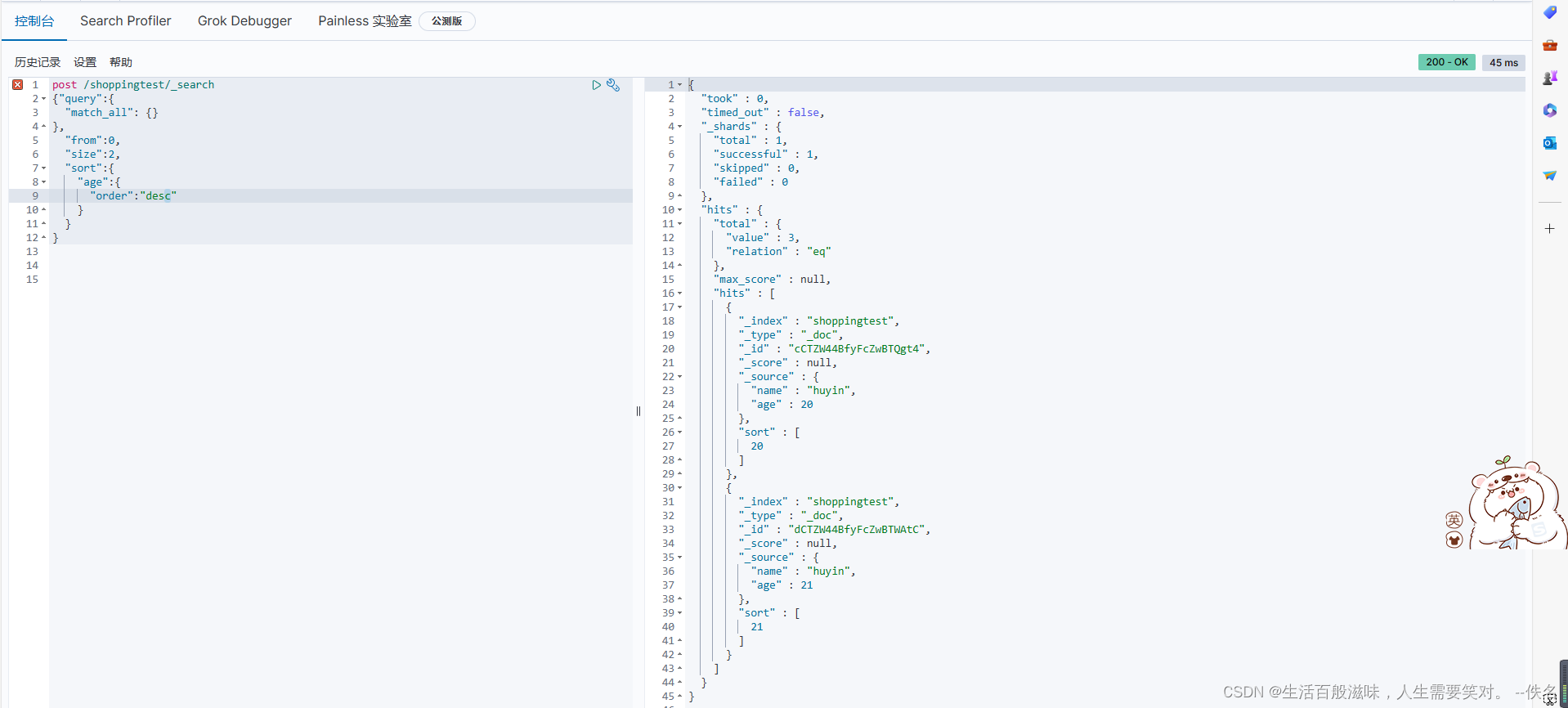
对数据进行排序:post /shoppingtest/_search
{"query":{
"match_all": {}
},
"from":0,
"size":2,
"sort":{ sort 排序 ------字段--------order(排序)-----desc(倒序)/asc(正序)
"age":{
"order":"desc"
}
}
}
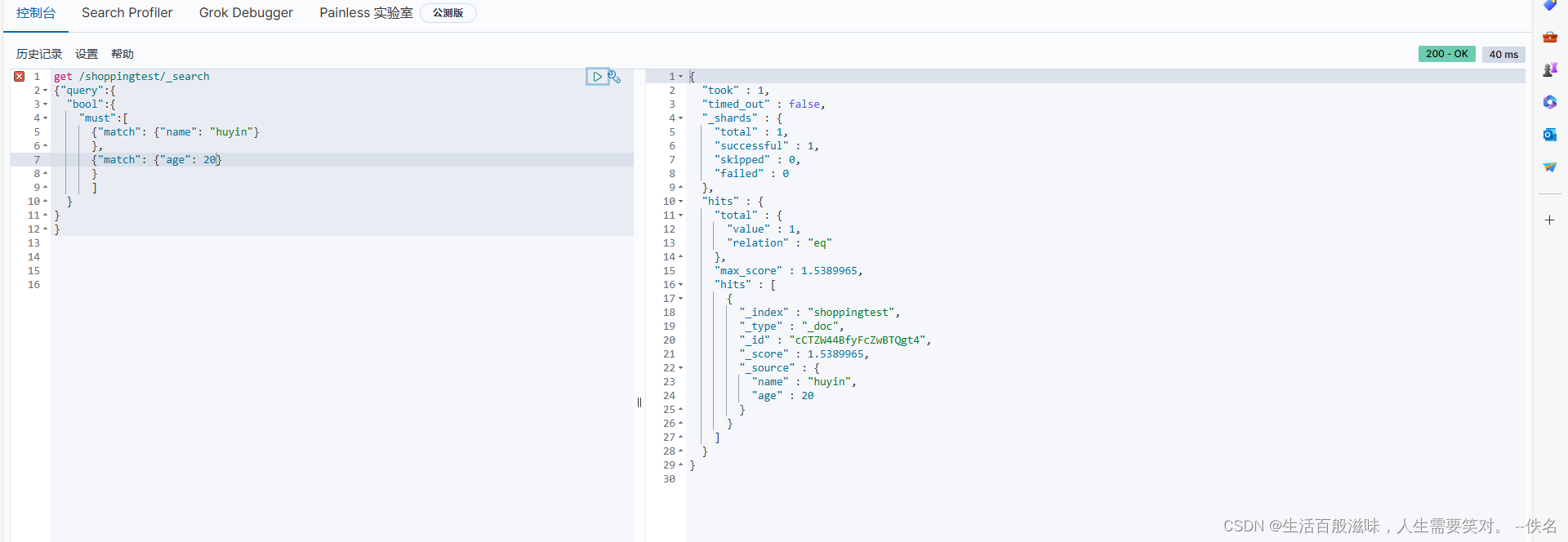
多条件查询的语法:get /shoppingtest/_search
{"query":{ query 查询
"bool":{ bool 条件
"must":[ must 必须
{"match": {"name": "huyin"}, match 匹配
{"match": {"age": 20}
}
]
}
}
}
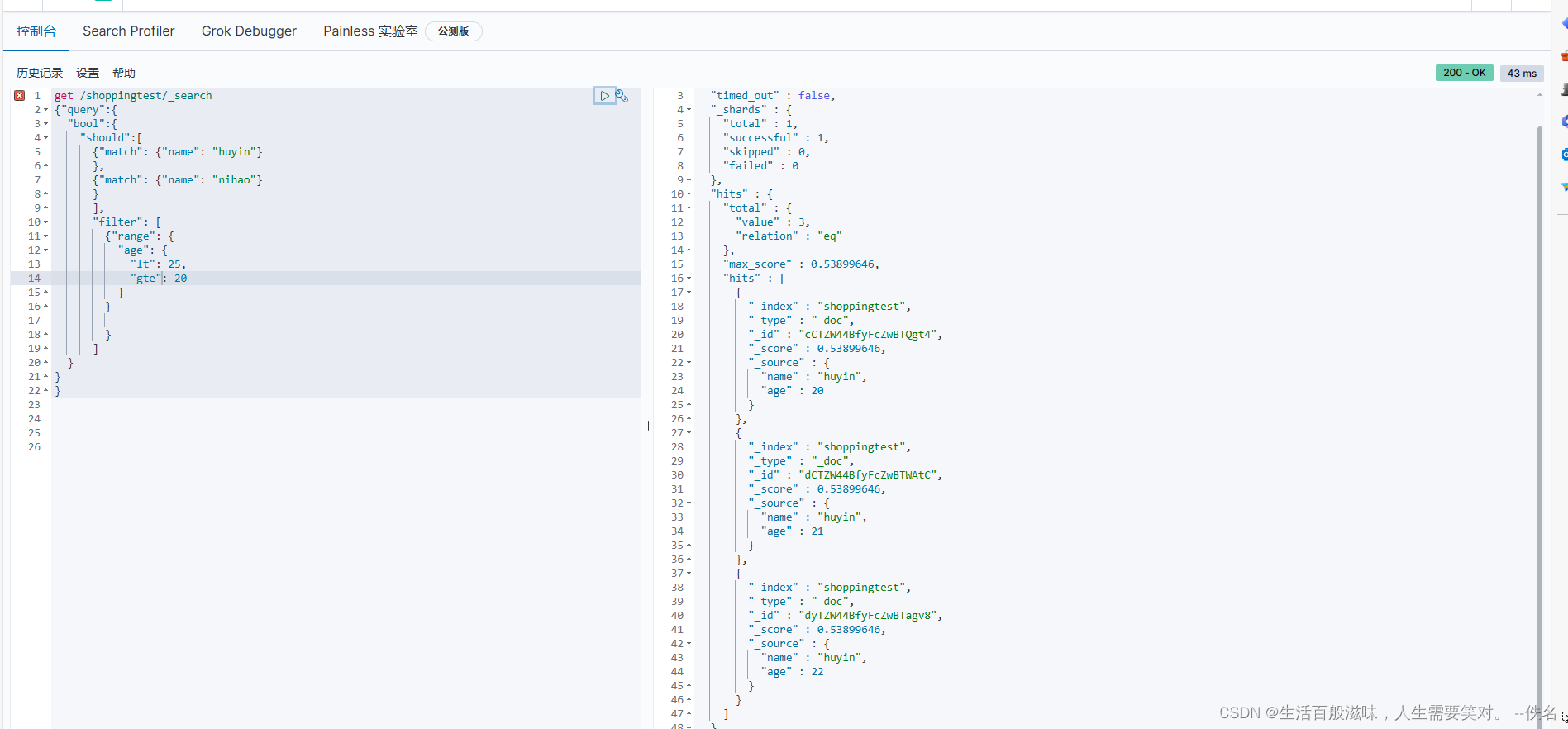
如果想要只满足一个的意思匹配数据:get /shoppingtest/_search
{"query":{
"bool":{
"should":[ should:应该的意思
{"match": {"name": "huyin"}
},
{"match": {"name": "nihao"}
}
]
}
}
}

如果想要范围匹配的语法:get /shoppingtest/_search
{"query":{
"bool":{
"should":[
{"match": {"name": "huyin"}
},
{"match": {"name": "nihao"}
}
],
"filter": [ filter 过滤
{"range": { range:范围
"age": { age:字段
"lt": 25, lt:小于
"gte": 20 gte:大于等于
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
全文检索和完全匹配和高亮查询的操作
全文检索:

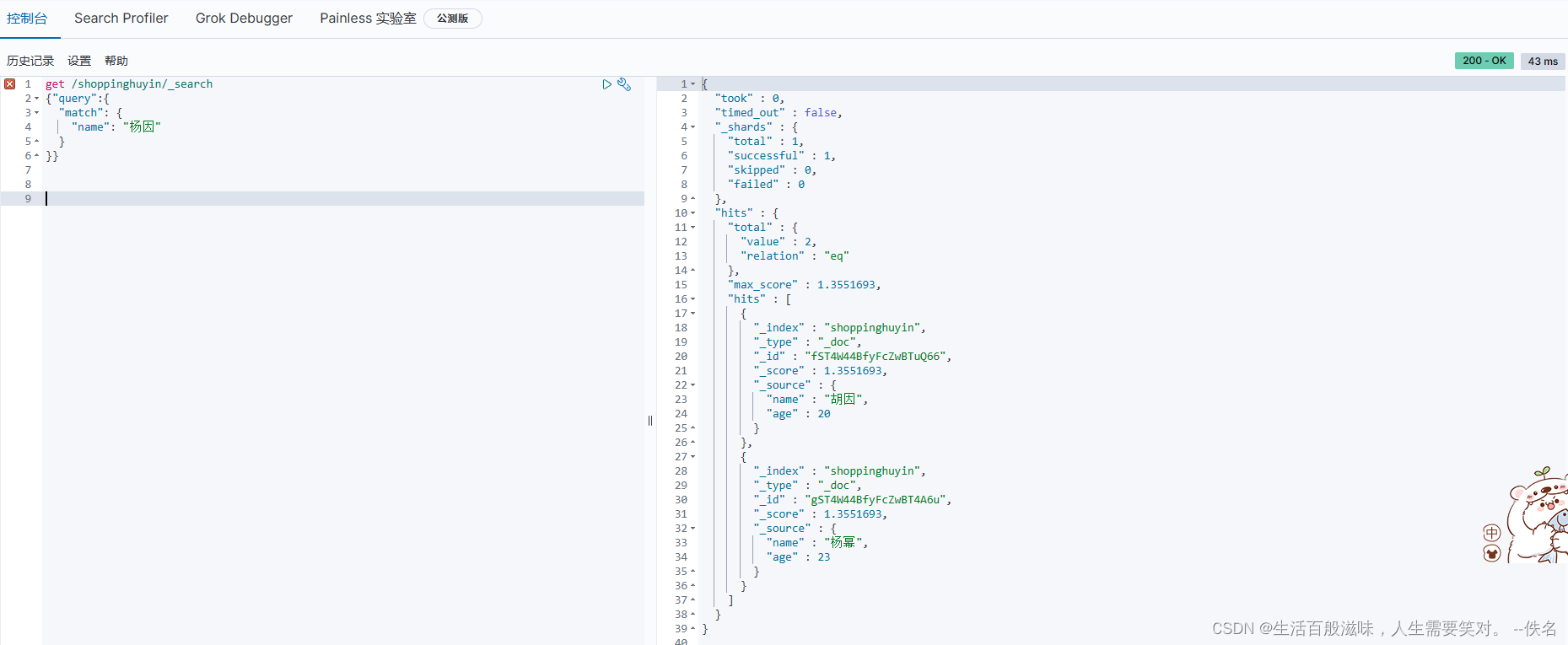
Es底层会对文本数据保存时进行拆解操作,然后保存到倒排索引,这种检索方式称为全文检索
完全匹配:match_phrase

高亮匹配:
"highlight":{ 高亮
"fields": { 字段属性
"name":{} 字段
}
}
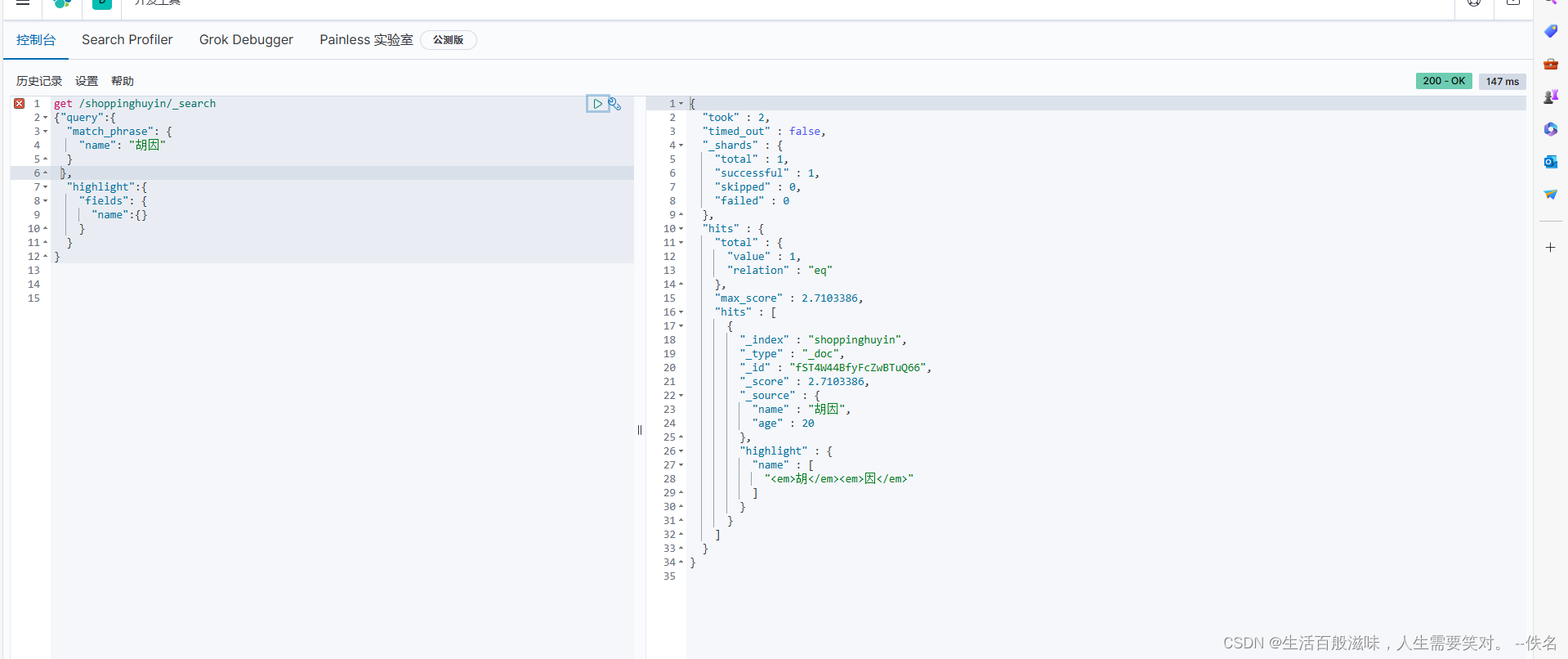
聚合函数的语法:
分组操作
{
"aggs":{ 聚合操作
"age_group":{ 别名
"terms": { 分组
"field": "age" 字段
}
}
}
}
计算平均值
{
"aggs":{
"age_avg":{
"avg": { avg 平均值
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size":0
}
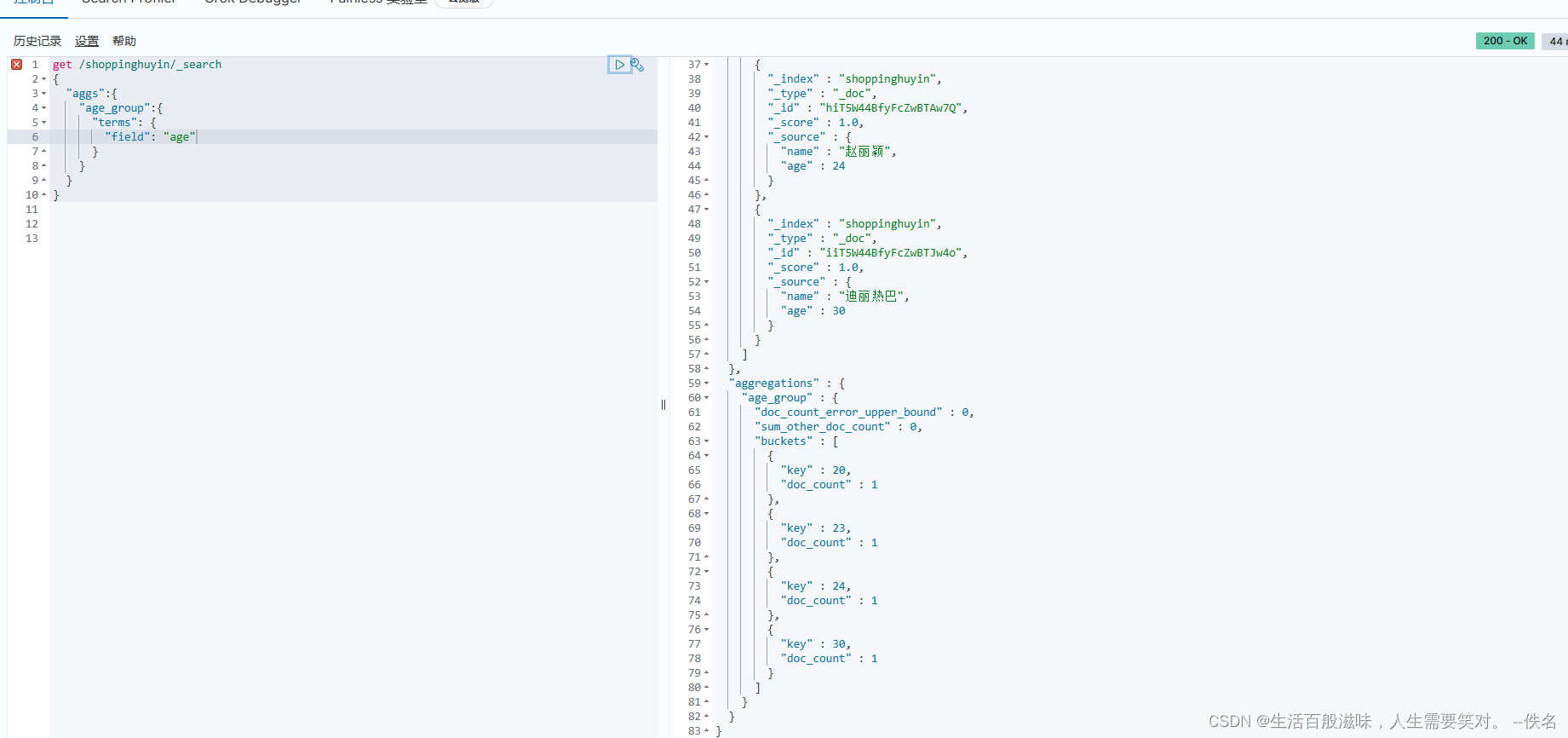
映射关系:
首先创建一个索引:put /user

创建一个映射关系:put /user/_mapping
{"properties":{ 属性
"name":{
"type":"text", type:类型 text:文本
"index":"true"
},
"age":{
"type":"keyword", type:类型 keyword:代表不能被分词
"index":"true"
},
"tel":{
"type":"keyword",
"index":"false" index:不能被索引
}
}}
获取索引信息:get /user
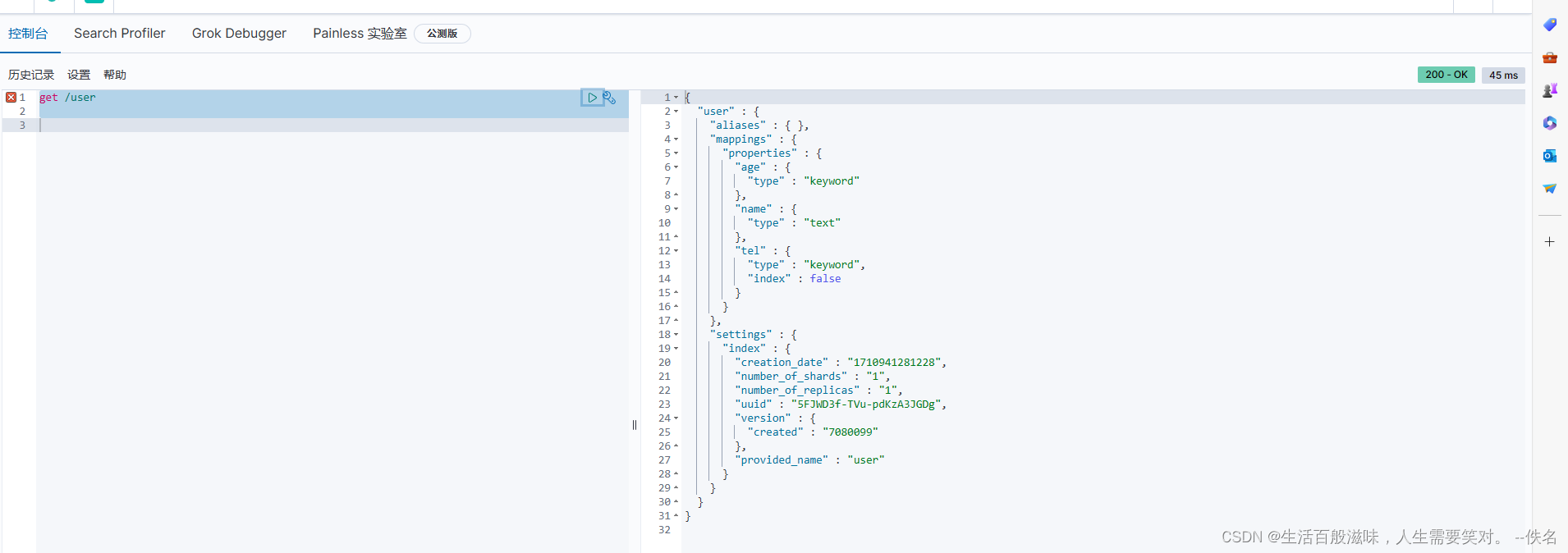
创建数据:post /user/_doc
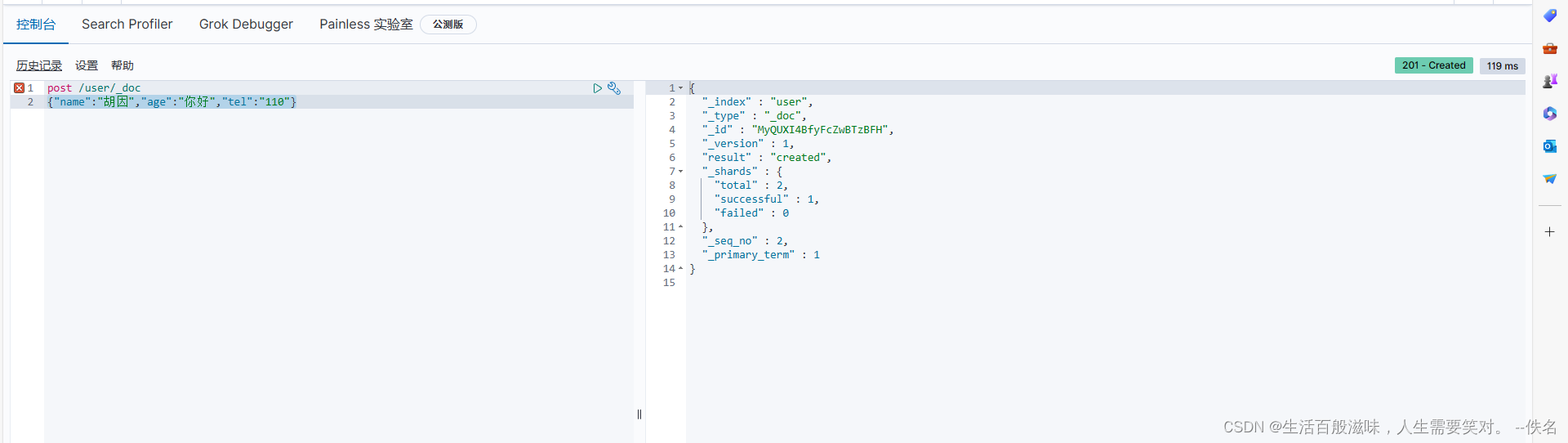
查询数据: name
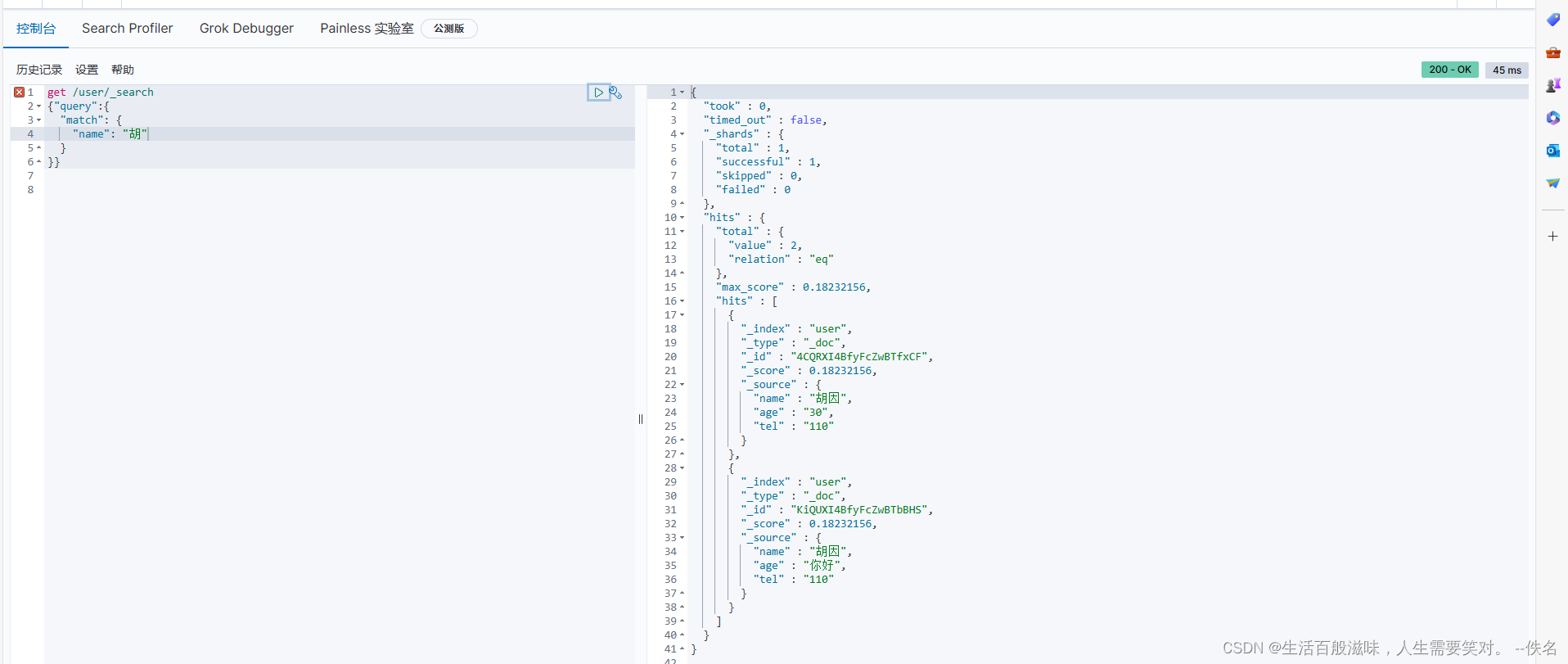
查询数据: age 因为映射的type是keyword不支持分词
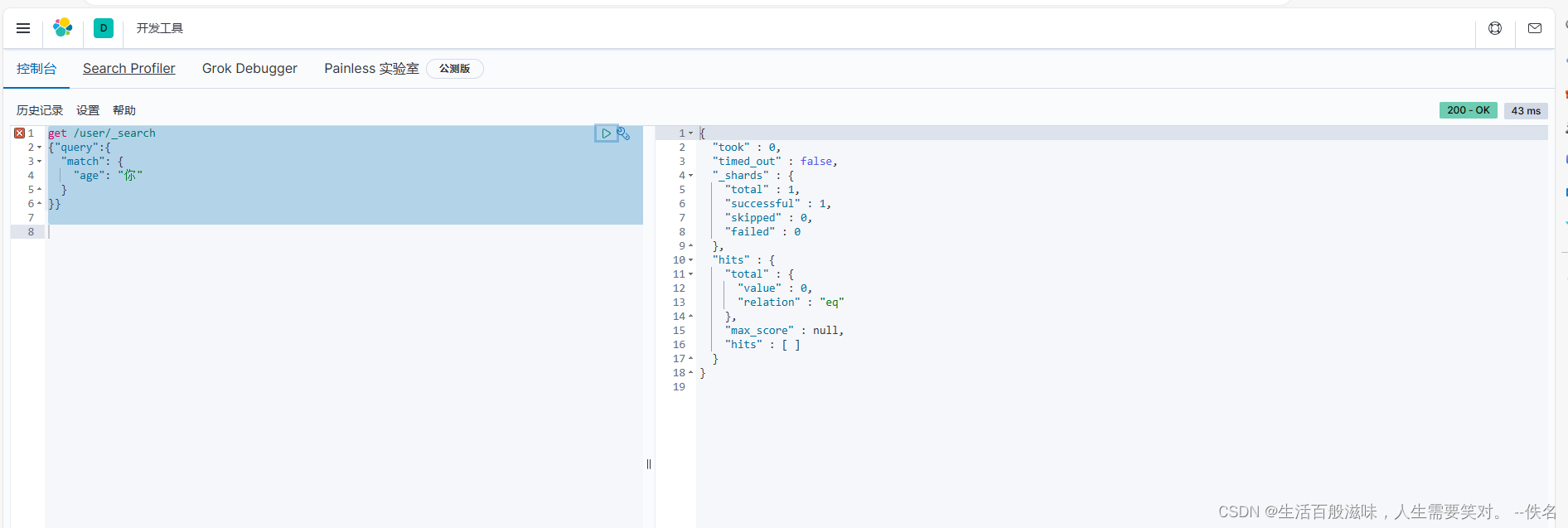
查询数据:tel index是false 不支持索引查询
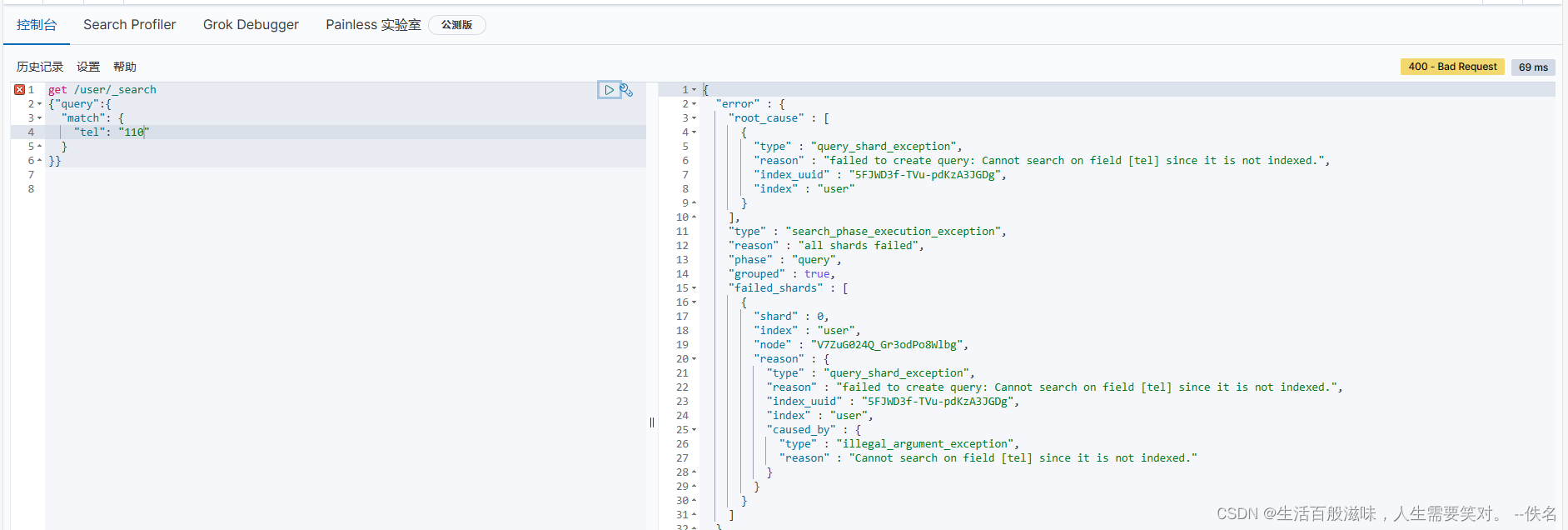
es的kibanba的语法结束,其实还有很多


)



)









)


