条件测试
JUnit5支持条件注解,根据布尔值判断是否执行测试。
自定义条件
@EnabledIf和@DisabledIf注解用来设置自定义条件,示例:
-
@Test -
@EnabledIf("customCondition") -
void enabled() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@DisabledIf("customCondition") -
void disabled() { -
// ... -
} -
boolean customCondition() { -
return true; -
}
其中customCondition()方法用来返回布尔值,它可以接受一个ExtensionContext类型的参数。如果定义在测试类外部,那么需要是static方法。
内置条件
JUnit5的org.junit.jupiter.api.condition包中内置了一些条件注解。
操作系统条件
@EnabledOnOs和DisabledOnOs,示例:
-
@Test -
@EnabledOnOs(MAC) -
void onlyOnMacOs() { -
// ... -
} -
@TestOnMac -
void testOnMac() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@EnabledOnOs({ LINUX, MAC }) -
void onLinuxOrMac() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@DisabledOnOs(WINDOWS) -
void notOnWindows() { -
// ... -
} -
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) -
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) -
@Test -
@EnabledOnOs(MAC) -
@interface TestOnMac { -
}
![]()
JRE条件
@EnabledOnJre和@DisabledOnJre用于指定版本,@EnabledForJreRange和@DisabledForJreRange用于指定版本范围,示例:
-
@Test -
@EnabledOnJre(JAVA_8) -
void onlyOnJava8() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@EnabledOnJre({ JAVA_9, JAVA_10 }) -
void onJava9Or10() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@EnabledForJreRange(min = JAVA_9, max = JAVA_11) -
void fromJava9to11() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@EnabledForJreRange(min = JAVA_9) -
void fromJava9toCurrentJavaFeatureNumber() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@EnabledForJreRange(max = JAVA_11) -
void fromJava8To11() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@DisabledOnJre(JAVA_9) -
void notOnJava9() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@DisabledForJreRange(min = JAVA_9, max = JAVA_11) -
void notFromJava9to11() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@DisabledForJreRange(min = JAVA_9) -
void notFromJava9toCurrentJavaFeatureNumber() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@DisabledForJreRange(max = JAVA_11) -
void notFromJava8to11() { -
// ... -
}
![]()
JVM系统属性条件
@EnabledIfSystemProperty和@DisabledIfSystemProperty,示例:
-
@Test -
@EnabledIfSystemProperty(named = "os.arch", matches = ".*64.*") -
void onlyOn64BitArchitectures() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@DisabledIfSystemProperty(named = "ci-server", matches = "true") -
void notOnCiServer() { -
// ... -
}
环境变量条件
@EnabledIfEnvironmentVariable和@DisabledIfEnvironmentVariable,示例:
-
@Test -
@EnabledIfEnvironmentVariable(named = "ENV", matches = "staging-server") -
void onlyOnStagingServer() { -
// ... -
} -
@Test -
@DisabledIfEnvironmentVariable(named = "ENV", matches = ".*development.*") -
void notOnDeveloperWorkstation() { -
// ... -
}
-
现在我也找了很多测试的朋友,做了一个分享技术的交流群,共享了很多我们收集的技术文档和视频教程。 -
如果你不想再体验自学时找不到资源,没人解答问题,坚持几天便放弃的感受 -
可以加入我们一起交流。而且还有很多在自动化,性能,安全,测试开发等等方面有一定建树的技术大牛 -
分享他们的经验,还会分享很多直播讲座和技术沙龙 -
可以免费学习!划重点!开源的!!! -
qq群号:110685036
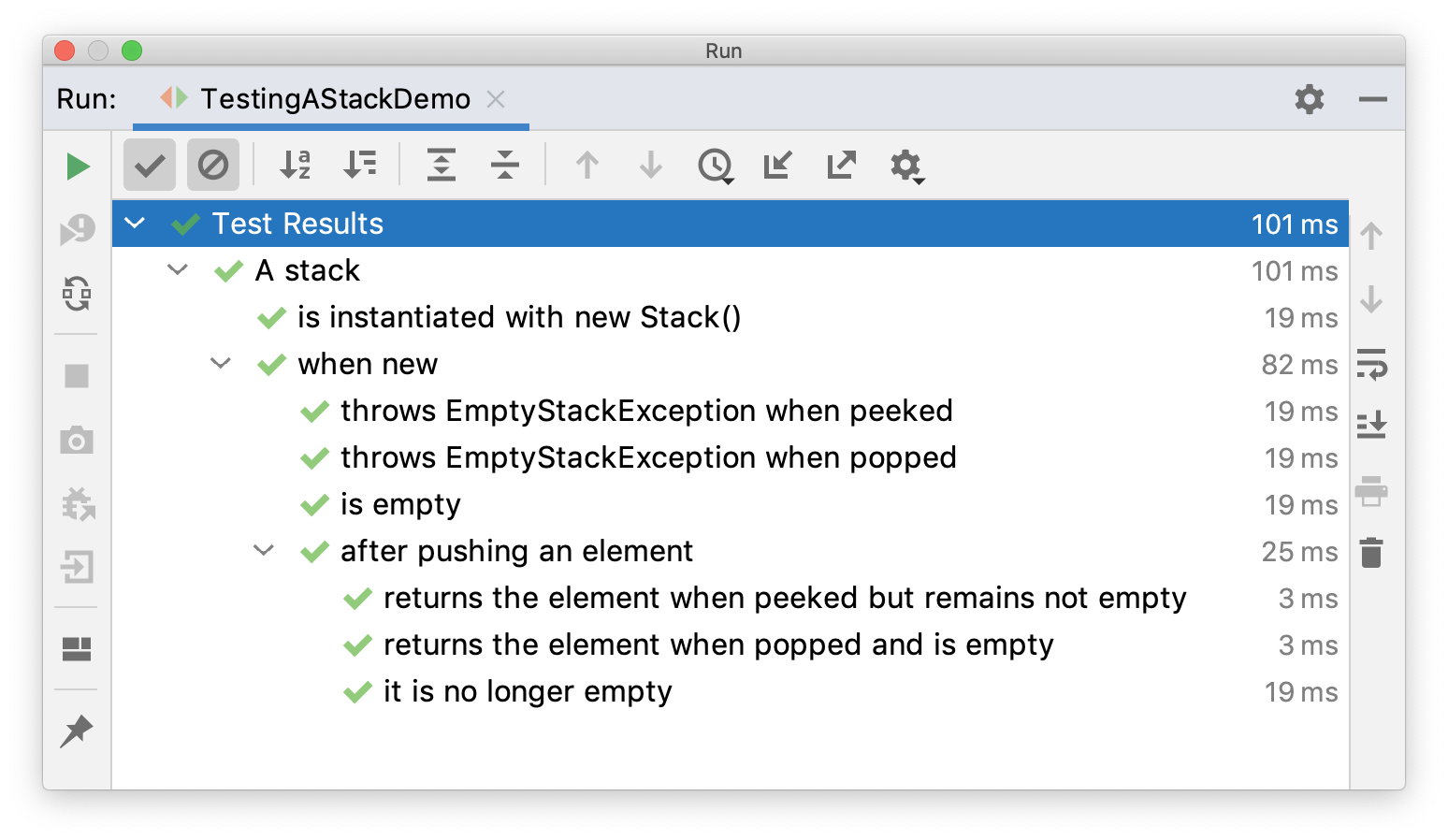
嵌套测试
嵌套测试可以帮助我们对测试结构进行分层。借助于Java嵌套类的语法,JUnit5可以通过@Nested注解,实现嵌套测试,示例:
-
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals; -
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertFalse; -
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertThrows; -
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue; -
import java.util.EmptyStackException; -
import java.util.Stack; -
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach; -
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName; -
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Nested; -
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; -
@DisplayName("A stack") -
class TestingAStackDemo { -
Stack<Object> stack; -
@Test -
@DisplayName("is instantiated with new Stack()") -
void isInstantiatedWithNew() { -
new Stack<>(); -
} -
@Nested -
@DisplayName("when new") -
class WhenNew { -
@BeforeEach -
void createNewStack() { -
stack = new Stack<>(); -
} -
@Test -
@DisplayName("is empty") -
void isEmpty() { -
assertTrue(stack.isEmpty()); -
} -
@Test -
@DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when popped") -
void throwsExceptionWhenPopped() { -
assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::pop); -
} -
@Test -
@DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when peeked") -
void throwsExceptionWhenPeeked() { -
assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::peek); -
} -
@Nested -
@DisplayName("after pushing an element") -
class AfterPushing { -
String anElement = "an element"; -
@BeforeEach -
void pushAnElement() { -
stack.push(anElement); -
} -
@Test -
@DisplayName("it is no longer empty") -
void isNotEmpty() { -
assertFalse(stack.isEmpty()); -
} -
@Test -
@DisplayName("returns the element when popped and is empty") -
void returnElementWhenPopped() { -
assertEquals(anElement, stack.pop()); -
assertTrue(stack.isEmpty()); -
} -
@Test -
@DisplayName("returns the element when peeked but remains not empty") -
void returnElementWhenPeeked() { -
assertEquals(anElement, stack.peek()); -
assertFalse(stack.isEmpty()); -
} -
} -
} -
}
![]()
外部测试类通过@BeforeEach向内部测试类传递变量。
执行后结果:
重复测试
@RepeatedTest注解能控制测试方法的重复执行次数,示例:
-
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals; -
import java.util.logging.Logger; -
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach; -
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName; -
import org.junit.jupiter.api.RepeatedTest; -
import org.junit.jupiter.api.RepetitionInfo; -
import org.junit.jupiter.api.TestInfo; -
class RepeatedTestsDemo { -
private Logger logger = // ... -
@BeforeEach -
void beforeEach(TestInfo testInfo, RepetitionInfo repetitionInfo) { -
int currentRepetition = repetitionInfo.getCurrentRepetition(); -
int totalRepetitions = repetitionInfo.getTotalRepetitions(); -
String methodName = testInfo.getTestMethod().get().getName(); -
logger.info(String.format("About to execute repetition %d of %d for %s", // -
currentRepetition, totalRepetitions, methodName)); -
} -
@RepeatedTest(10) -
void repeatedTest() { -
// ... -
} -
@RepeatedTest(5) -
void repeatedTestWithRepetitionInfo(RepetitionInfo repetitionInfo) { -
assertEquals(5, repetitionInfo.getTotalRepetitions()); -
} -
@RepeatedTest(value = 1, name = "{displayName} {currentRepetition}/{totalRepetitions}") -
@DisplayName("Repeat!") -
void customDisplayName(TestInfo testInfo) { -
assertEquals("Repeat! 1/1", testInfo.getDisplayName()); -
} -
@RepeatedTest(value = 1, name = RepeatedTest.LONG_DISPLAY_NAME) -
@DisplayName("Details...") -
void customDisplayNameWithLongPattern(TestInfo testInfo) { -
assertEquals("Details... :: repetition 1 of 1", testInfo.getDisplayName()); -
} -
@RepeatedTest(value = 5, name = "Wiederholung {currentRepetition} von {totalRepetitions}") -
void repeatedTestInGerman() { -
// ... -
} -
}
![]()
其中name可以用来自定义重复测试的显示名字,{currentRepetition}和{totalRepetitions}是当前次数和总共次数的变量。
执行结果:
-
├─ RepeatedTestsDemo ✔ -
│ ├─ repeatedTest() ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 1 of 10 ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 2 of 10 ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 3 of 10 ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 4 of 10 ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 5 of 10 ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 6 of 10 ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 7 of 10 ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 8 of 10 ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 9 of 10 ✔ -
│ │ └─ repetition 10 of 10 ✔ -
│ ├─ repeatedTestWithRepetitionInfo(RepetitionInfo) ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 1 of 5 ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 2 of 5 ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 3 of 5 ✔ -
│ │ ├─ repetition 4 of 5 ✔ -
│ │ └─ repetition 5 of 5 ✔ -
│ ├─ Repeat! ✔ -
│ │ └─ Repeat! 1/1 ✔ -
│ ├─ Details... ✔ -
│ │ └─ Details... :: repetition 1 of 1 ✔ -
│ └─ repeatedTestInGerman() ✔ -
│ ├─ Wiederholung 1 von 5 ✔ -
│ ├─ Wiederholung 2 von 5 ✔ -
│ ├─ Wiederholung 3 von 5 ✔ -
│ ├─ Wiederholung 4 von 5 ✔ -
│ └─ Wiederholung 5 von 5 ✔
![]()
小结
本文分别对JUnit5的条件测试、嵌套测试、重复测试进行了介绍,它们可以使得测试更加灵活和富有层次。除了这些,JUnit5还支持另一个重要且常见的测试:参数化测试。



















