前言
今天我们来聊聊一个即将改变我们编程习惯的新特性——ScopedValue。
有些小伙伴在工作中,一提到线程内数据传递就想到ThreadLocal,但真正用起来却遇到各种坑:内存泄漏、数据污染、性能问题等等。
其实,ScopedValue就像ThreadLocal的升级版,既保留了优点,又解决了痛点。
我们一起聊聊ScopedValue的优势和用法,希望对你会有所帮助。
一、ThreadLocal的痛点
在介绍ScopedValue之前,我们先回顾一下ThreadLocal的常见问题。
有些小伙伴可能会想:"ThreadLocal用得好好的,为什么要换?"
其实,ThreadLocal在设计上存在一些固有缺陷。
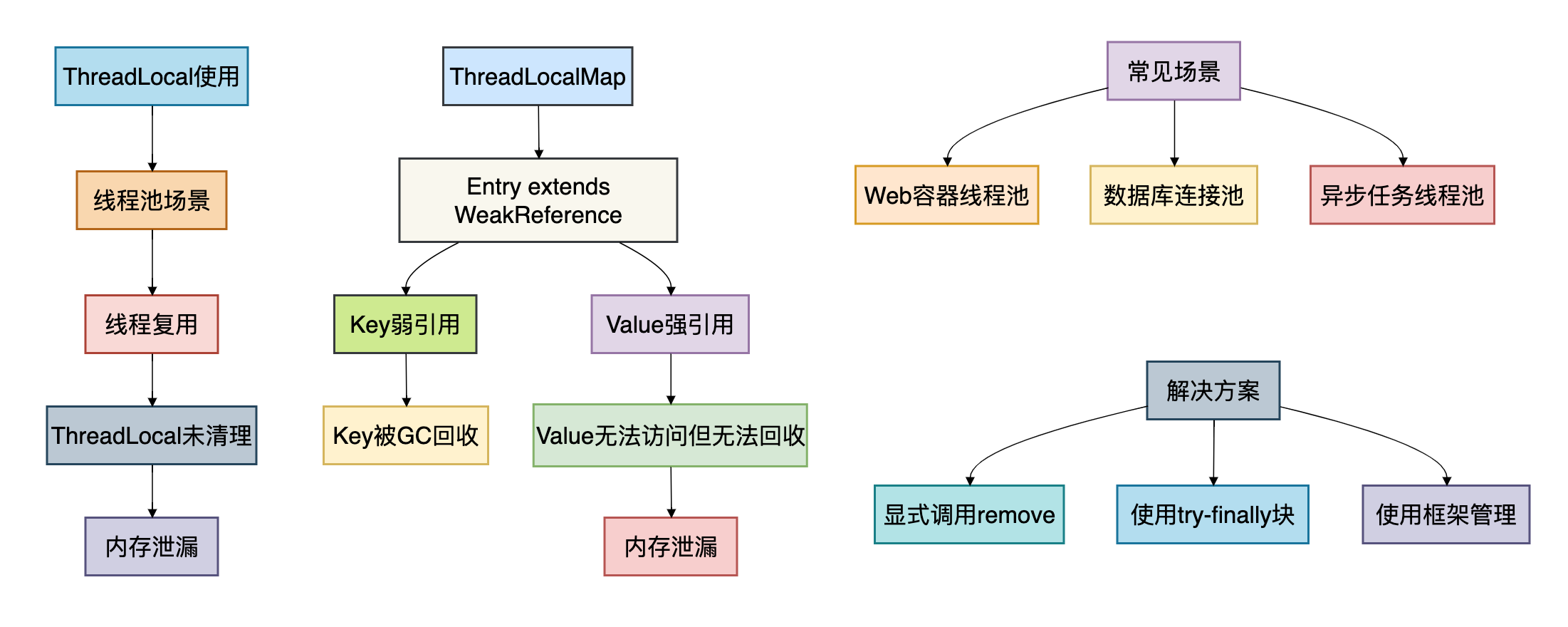
ThreadLocal的内存泄漏问题
为了更直观地理解ThreadLocal的内存泄漏问题,我画了一个内存泄漏的示意图:
ThreadLocal的典型问题代码
/*** ThreadLocal典型问题演示*/
public class ThreadLocalProblems {private static final ThreadLocal<UserContext> userContext = new ThreadLocal<>();private static final ThreadLocal<Connection> connectionHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();/*** 问题1:内存泄漏 - 忘记调用remove()*/public void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {// 设置用户上下文UserContext context = new UserContext(request.getHeader("X-User-Id"));userContext.set(context);try {// 业务处理businessService.process();// 问题:忘记调用 userContext.remove()// 在线程池中,这个线程被重用时,还会保留之前的用户信息} catch (Exception e) {// 异常处理}}/*** 问题2:数据污染 - 线程复用导致数据混乱*/public void processMultipleRequests() {// 线程池处理多个请求ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {final int userId = i;executor.submit(() -> {// 设置用户上下文userContext.set(new UserContext("user_" + userId));try {// 模拟业务处理Thread.sleep(100);// 问题:如果线程被复用,这里可能读取到错误的用户信息String currentUser = userContext.get().getUserId();System.out.println("处理用户: " + currentUser);} catch (InterruptedException e) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();} finally {// 即使调用remove,也可能因为异常跳过userContext.remove(); // 不保证一定执行}});}executor.shutdown();}/*** 问题3:继承性问题 - 子线程无法继承父线程数据*/public void parentChildThreadProblem() {userContext.set(new UserContext("parent_user"));Thread childThread = new Thread(() -> {// 这里获取不到父线程的ThreadLocal值UserContext context = userContext.get(); // nullSystem.out.println("子线程用户: " + context); // 输出null// 需要手动传递数据});childThread.start();}/*** 问题4:性能问题 - 大量ThreadLocal影响性能*/public void performanceProblem() {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {ThreadLocal<String> tl = new ThreadLocal<>();tl.set("value_" + i);String value = tl.get();tl.remove();}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("ThreadLocal操作耗时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");}
}/*** 用户上下文*/
class UserContext {private final String userId;private final long timestamp;public UserContext(String userId) {this.userId = userId;this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();}public String getUserId() {return userId;}public long getTimestamp() {return timestamp;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "UserContext{userId='" + userId + "', timestamp=" + timestamp + "}";}
}
ThreadLocal问题的根本原因
- 生命周期管理复杂:需要手动调用set/remove,容易遗漏
- 内存泄漏风险:线程池中线程复用,Value无法被GC
- 继承性差:子线程无法自动继承父线程数据
- 性能开销:ThreadLocalMap的哈希表操作有开销
有些小伙伴可能会问:"我们用InheritableThreadLocal不就能解决继承问题了吗?"
我的经验是:InheritableThreadLocal只是缓解了问题,但带来了新的复杂度,而且性能更差。
二、ScopedValue:新一代线程局部变量
ScopedValue是Java 20中引入的预览特性,在Java 21中成为正式特性。
它旨在解决ThreadLocal的痛点,提供更安全、更高效的线程内数据传递方案。
ScopedValue的核心设计理念
为了更直观地理解ScopedValue的工作原理,我画了一个ScopedValue的架构图:
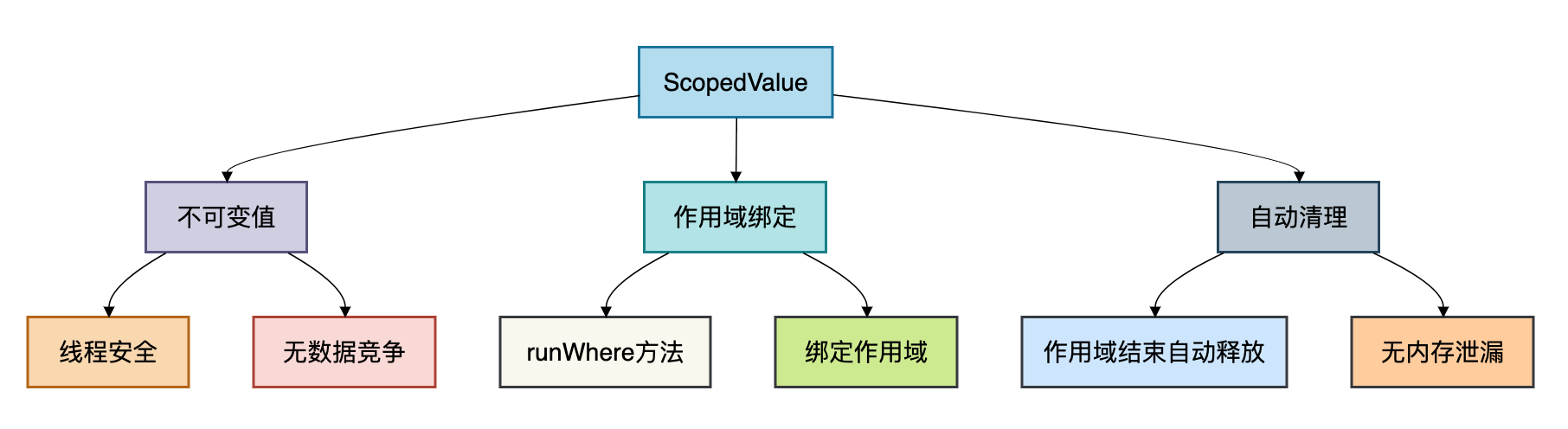
ScopedValue的核心优势:
ScopedValue基础用法
/*** ScopedValue基础用法演示*/
public class ScopedValueBasics {// 1. 定义ScopedValue(相当于ThreadLocal)private static final ScopedValue<UserContext> USER_CONTEXT = ScopedValue.newInstance();private static final ScopedValue<Connection> DB_CONNECTION = ScopedValue.newInstance();private static final ScopedValue<String> REQUEST_ID = ScopedValue.newInstance();/*** 基础用法:在作用域内使用ScopedValue*/public void basicUsage() {UserContext user = new UserContext("user_123");// 在作用域内绑定值ScopedValue.runWhere(USER_CONTEXT, user, () -> {// 在这个作用域内,USER_CONTEXT.get()返回user_123System.out.println("当前用户: " + USER_CONTEXT.get().getUserId());// 可以嵌套使用ScopedValue.runWhere(REQUEST_ID, "req_456", () -> {System.out.println("请求ID: " + REQUEST_ID.get());System.out.println("用户: " + USER_CONTEXT.get().getUserId());});// 这里REQUEST_ID已经超出作用域,获取会抛出异常});// 这里USER_CONTEXT已经超出作用域}/*** 带返回值的作用域*/public String scopedValueWithReturn() {UserContext user = new UserContext("user_789");// 使用callWhere获取返回值String result = ScopedValue.callWhere(USER_CONTEXT, user, () -> {// 业务处理String userId = USER_CONTEXT.get().getUserId();return "处理用户: " + userId;});return result;}/*** 多个ScopedValue同时使用*/public void multipleScopedValues() {UserContext user = new UserContext("user_multi");Connection conn = createConnection();// 同时绑定多个ScopedValueScopedValue.runWhere(ScopedValue.where(USER_CONTEXT, user).where(DB_CONNECTION, conn).where(REQUEST_ID, "multi_req"),() -> {// 在这个作用域内可以访问所有绑定的值processBusinessLogic();});// 作用域结束后自动清理}/*** 异常处理示例*/public void exceptionHandling() {UserContext user = new UserContext("user_exception");try {ScopedValue.runWhere(USER_CONTEXT, user, () -> {// 业务处理processBusinessLogic();// 如果抛出异常,作用域也会正常结束if (someCondition()) {throw new RuntimeException("业务异常");}});} catch (RuntimeException e) {// 异常处理System.out.println("捕获异常: " + e.getMessage());}// 即使发生异常,USER_CONTEXT也会自动清理}private Connection createConnection() {// 创建数据库连接return null;}private void processBusinessLogic() {// 业务逻辑处理UserContext user = USER_CONTEXT.get();System.out.println("处理业务逻辑,用户: " + user.getUserId());}private boolean someCondition() {return Math.random() > 0.5;}
}
三、ScopedValue vs ThreadLocal:全面对比
有些小伙伴可能还想知道ScopedValue到底比ThreadLocal强在哪里。
让我们通过详细的对比来看看。
3.1 内存管理对比
为了更直观地理解两者的内存管理差异,我画了几张图做对比。
ThreadLocal的内存模型图:
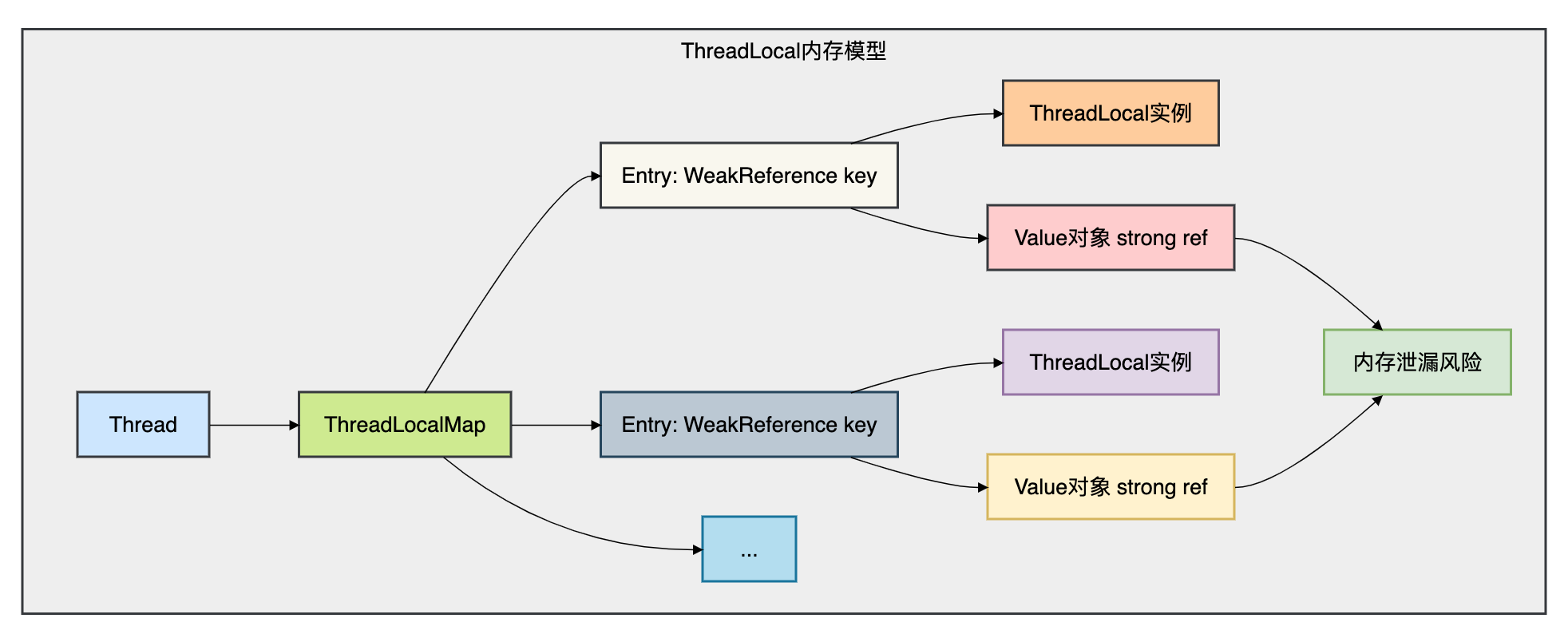
ScopedValue的内存模型图:
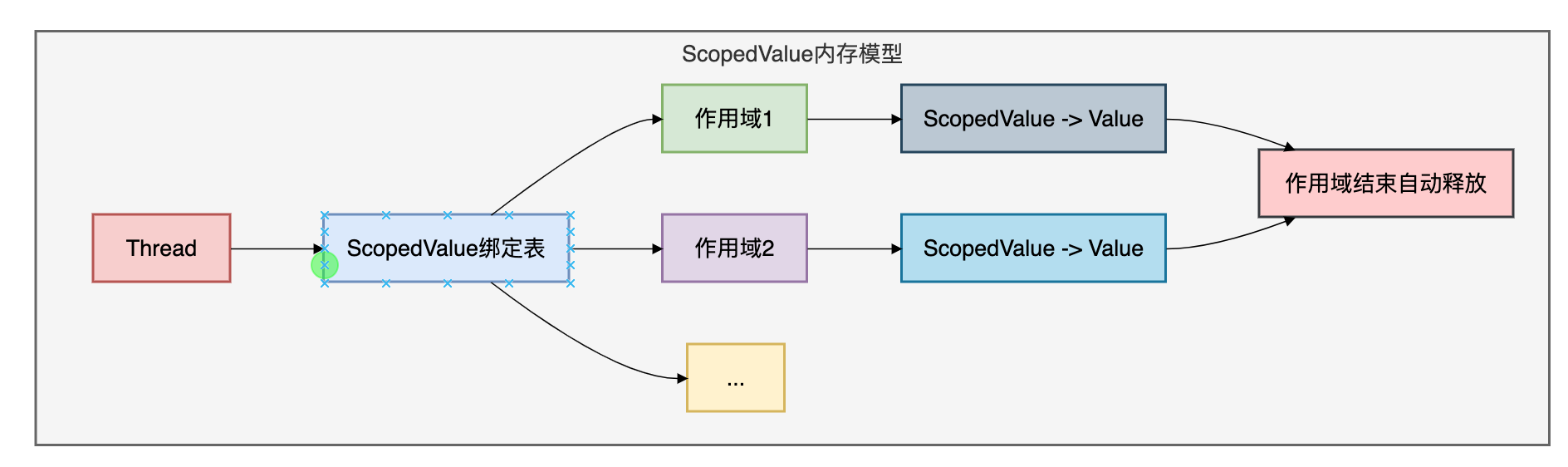
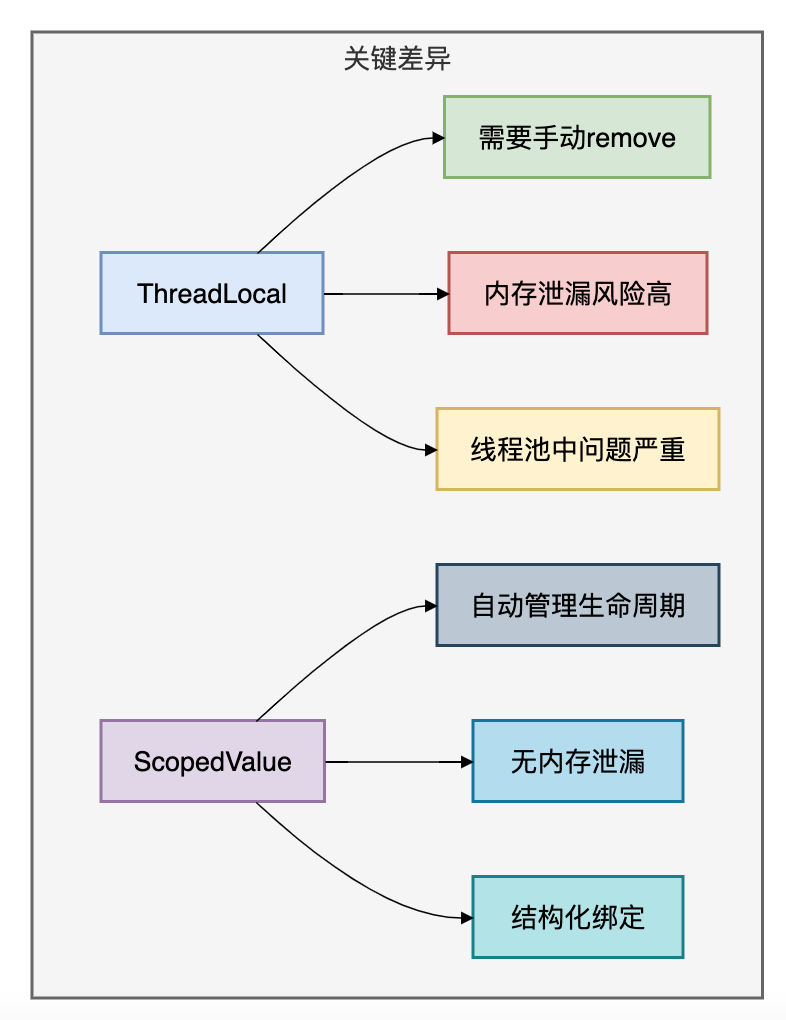
二者的关键差异如下图:
3.2 代码对比示例
/*** ThreadLocal vs ScopedValue 对比演示*/
public class ThreadLocalVsScopedValue {// ThreadLocal方式private static final ThreadLocal<UserContext> TL_USER_CONTEXT = new ThreadLocal<>();private static final ThreadLocal<Connection> TL_CONNECTION = new ThreadLocal<>();// ScopedValue方式private static final ScopedValue<UserContext> SV_USER_CONTEXT = ScopedValue.newInstance();private static final ScopedValue<Connection> SV_CONNECTION = ScopedValue.newInstance();/*** ThreadLocal方式 - 传统实现*/public void processRequestThreadLocal(HttpServletRequest request) {// 设置上下文UserContext userContext = new UserContext(request.getHeader("X-User-Id"));TL_USER_CONTEXT.set(userContext);Connection conn = null;try {// 获取数据库连接conn = dataSource.getConnection();TL_CONNECTION.set(conn);// 业务处理processBusinessLogic();} catch (SQLException e) {// 异常处理handleException(e);} finally {// 必须手动清理 - 容易忘记!TL_USER_CONTEXT.remove();TL_CONNECTION.remove();// 关闭连接if (conn != null) {try {conn.close();} catch (SQLException e) {// 日志记录}}}}/*** ScopedValue方式 - 现代实现*/public void processRequestScopedValue(HttpServletRequest request) {UserContext userContext = new UserContext(request.getHeader("X-User-Id"));// 使用try-with-resources管理连接try (Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection()) {// 在作用域内执行,自动管理生命周期ScopedValue.runWhere(ScopedValue.where(SV_USER_CONTEXT, userContext).where(SV_CONNECTION, conn),() -> {// 业务处理processBusinessLogic();});// 作用域结束后自动清理,无需手动remove} catch (SQLException e) {handleException(e);}}/*** 业务逻辑处理 - 两种方式对比*/private void processBusinessLogic() {// ThreadLocal方式 - 需要处理null值UserContext tlUser = TL_USER_CONTEXT.get();if (tlUser == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("用户上下文未设置");}Connection tlConn = TL_CONNECTION.get();if (tlConn == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("数据库连接未设置");}// ScopedValue方式 - 在作用域内保证不为nullUserContext svUser = SV_USER_CONTEXT.get(); // 不会为nullConnection svConn = SV_CONNECTION.get(); // 不会为null// 实际业务处理...System.out.println("处理用户: " + svUser.getUserId());}/*** 线程池场景对比*/public void threadPoolComparison() {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);// ThreadLocal方式 - 容易出问题for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {final int userId = i;executor.submit(() -> {TL_USER_CONTEXT.set(new UserContext("user_" + userId));try {processBusinessLogic();} finally {TL_USER_CONTEXT.remove(); // 容易忘记或异常跳过}});}// ScopedValue方式 - 更安全for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {final int userId = i;executor.submit(() -> {UserContext user = new UserContext("user_" + userId);ScopedValue.runWhere(SV_USER_CONTEXT, user, () -> {processBusinessLogic(); // 自动管理生命周期});});}executor.shutdown();}private Connection getConnectionFromTL() {return TL_CONNECTION.get();}private DataSource dataSource = null; // 模拟数据源private void handleException(SQLException e) {} // 异常处理
}
3.3 性能对比测试
/*** 性能对比测试*/
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS)
@State(Scope.Thread)
public class PerformanceComparison {private static final ThreadLocal<String> THREAD_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal<>();private static final ScopedValue<String> SCOPED_VALUE = ScopedValue.newInstance();private static final int ITERATIONS = 100000;/*** ThreadLocal性能测试*/@Benchmarkpublic void threadLocalPerformance() {for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {THREAD_LOCAL.set("value_" + i);String value = THREAD_LOCAL.get();THREAD_LOCAL.remove();}}/*** ScopedValue性能测试*/@Benchmarkpublic void scopedValuePerformance() {for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {ScopedValue.runWhere(SCOPED_VALUE, "value_" + i, () -> {String value = SCOPED_VALUE.get();// 自动清理,无需remove});}}/*** 实际场景性能测试*/public void realScenarioTest() {long tlStart = System.nanoTime();// ThreadLocal场景THREAD_LOCAL.set("initial_value");for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {String current = THREAD_LOCAL.get();THREAD_LOCAL.set(current + "_" + i);}THREAD_LOCAL.remove();long tlEnd = System.nanoTime();// ScopedValue场景long svStart = System.nanoTime();ScopedValue.runWhere(SCOPED_VALUE, "initial_value", () -> {String current = SCOPED_VALUE.get();for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {// ScopedValue是不可变的,需要重新绑定String newValue = current + "_" + i;ScopedValue.runWhere(SCOPED_VALUE, newValue, () -> {// 嵌套作用域String nestedValue = SCOPED_VALUE.get();});}});long svEnd = System.nanoTime();System.out.printf("ThreadLocal耗时: %d ns%n", tlEnd - tlStart);System.out.printf("ScopedValue耗时: %d ns%n", svEnd - svStart);}
}
四、ScopedValue高级特性
有些小伙伴掌握了基础用法后,还想了解更高级的特性。
ScopedValue确实提供了很多强大的功能。
4.1 结构化并发支持
ScopedValue与虚拟线程和结构化并发完美配合:
/*** ScopedValue与结构化并发*/
public class StructuredConcurrencyExample {private static final ScopedValue<UserContext> USER_CONTEXT = ScopedValue.newInstance();private static final ScopedValue<RequestInfo> REQUEST_INFO = ScopedValue.newInstance();/*** 结构化并发中的ScopedValue使用*/public void structuredConcurrencyWithScopedValue() throws Exception {UserContext user = new UserContext("structured_user");RequestInfo request = new RequestInfo("req_123", System.currentTimeMillis());try (var scope = new StructuredTaskScope.ShutdownOnFailure()) {ScopedValue.runWhere(ScopedValue.where(USER_CONTEXT, user).where(REQUEST_INFO, request),() -> {// 在作用域内提交子任务Future<String> userTask = scope.fork(this::fetchUserData);Future<String> orderTask = scope.fork(this::fetchOrderData);Future<String> paymentTask = scope.fork(this::fetchPaymentData);try {// 等待所有任务完成scope.join();scope.throwIfFailed();// 处理结果String userData = userTask.resultNow();String orderData = orderTask.resultNow();String paymentData = paymentTask.resultNow();System.out.println("聚合结果: " + userData + ", " + orderData + ", " + paymentData);} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();throw new RuntimeException("任务执行失败", e);}});}}private String fetchUserData() {// 可以访问ScopedValue,无需参数传递UserContext user = USER_CONTEXT.get();RequestInfo request = REQUEST_INFO.get();return "用户数据: " + user.getUserId() + ", 请求: " + request.getRequestId();}private String fetchOrderData() {UserContext user = USER_CONTEXT.get();return "订单数据: " + user.getUserId();}private String fetchPaymentData() {UserContext user = USER_CONTEXT.get();return "支付数据: " + user.getUserId();}
}class RequestInfo {private final String requestId;private final long timestamp;public RequestInfo(String requestId, long timestamp) {this.requestId = requestId;this.timestamp = timestamp;}public String getRequestId() { return requestId; }public long getTimestamp() { return timestamp; }
}
4.2 继承和嵌套作用域
/*** ScopedValue继承和嵌套*/
public class ScopedValueInheritance {private static final ScopedValue<String> PARENT_VALUE = ScopedValue.newInstance();private static final ScopedValue<String> CHILD_VALUE = ScopedValue.newInstance();/*** 作用域嵌套*/public void nestedScopes() {ScopedValue.runWhere(PARENT_VALUE, "parent_value", () -> {System.out.println("外层作用域: " + PARENT_VALUE.get());// 内层作用域可以访问外层值ScopedValue.runWhere(CHILD_VALUE, "child_value", () -> {System.out.println("内层作用域 - 父值: " + PARENT_VALUE.get());System.out.println("内层作用域 - 子值: " + CHILD_VALUE.get());// 可以重新绑定父值(遮蔽)ScopedValue.runWhere(PARENT_VALUE, "shadowed_parent", () -> {System.out.println("遮蔽作用域 - 父值: " + PARENT_VALUE.get());System.out.println("遮蔽作用域 - 子值: " + CHILD_VALUE.get());});// 恢复原来的父值System.out.println("恢复作用域 - 父值: " + PARENT_VALUE.get());});// 子值已超出作用域try {System.out.println(CHILD_VALUE.get()); // 抛出异常} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("子值已超出作用域: " + e.getMessage());}});}/*** 虚拟线程中的继承*/public void virtualThreadInheritance() throws Exception {ScopedValue.runWhere(PARENT_VALUE, "virtual_parent", () -> {try (var scope = new StructuredTaskScope.ShutdownOnFailure()) {// 虚拟线程自动继承ScopedValuefor (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {final int taskId = i;scope.fork(() -> {// 可以访问父线程的ScopedValueString parentVal = PARENT_VALUE.get();return "任务" + taskId + " - 父值: " + parentVal;});}scope.join();scope.throwIfFailed();}});}/*** 条件绑定*/public void conditionalBinding() {String condition = Math.random() > 0.5 ? "case_a" : "case_b";ScopedValue.runWhere(PARENT_VALUE, condition, () -> {String value = PARENT_VALUE.get();if ("case_a".equals(value)) {System.out.println("处理情况A");} else {System.out.println("处理情况B");}});}
}
4.3 错误处理和调试
/*** ScopedValue错误处理和调试*/
public class ScopedValueErrorHandling {private static final ScopedValue<String> MAIN_VALUE = ScopedValue.newInstance();private static final ScopedValue<Integer> COUNT_VALUE = ScopedValue.newInstance();/*** 异常处理*/public void exceptionHandling() {try {ScopedValue.runWhere(MAIN_VALUE, "test_value", () -> {// 业务逻辑processWithError();});} catch (RuntimeException e) {System.out.println("捕获异常: " + e.getMessage());// ScopedValue已自动清理,无需额外处理}// 验证值已清理try {String value = MAIN_VALUE.get();System.out.println("不应该执行到这里: " + value);} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("值已正确清理: " + e.getMessage());}}/*** 调试信息*/public void debugInformation() {ScopedValue.runWhere(ScopedValue.where(MAIN_VALUE, "debug_value").where(COUNT_VALUE, 42),() -> {// 获取当前绑定的所有ScopedValueSystem.out.println("当前作用域绑定:");System.out.println("MAIN_VALUE: " + MAIN_VALUE.get());System.out.println("COUNT_VALUE: " + COUNT_VALUE.get());// 模拟复杂调试debugComplexScenario();});}/*** 资源清理保证*/public void resourceCleanupGuarantee() {List<String> cleanupLog = new ArrayList<>();ScopedValue.runWhere(MAIN_VALUE, "resource_value", () -> {// 注册清理钩子Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> {cleanupLog.add("资源清理完成");}));// 即使这里发生异常,ScopedValue也会清理if (Math.random() > 0.5) {throw new RuntimeException("模拟异常");}});// 检查清理情况System.out.println("清理日志: " + cleanupLog);}private void processWithError() {throw new RuntimeException("业务处理异常");}private void debugComplexScenario() {// 复杂的调试场景ScopedValue.runWhere(COUNT_VALUE, COUNT_VALUE.get() + 1, () -> {System.out.println("嵌套调试 - COUNT_VALUE: " + COUNT_VALUE.get());});}
}
五、实战案例
有些小伙伴可能还想看更复杂的实战案例。
让我们用一个Web应用中的用户上下文管理来展示ScopedValue在真实项目中的应用。
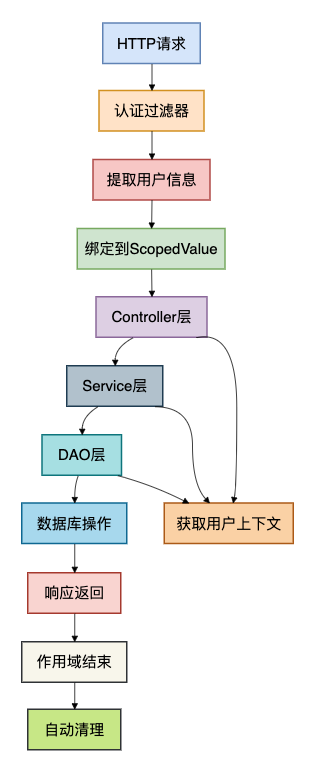
为了更直观地理解Web应用中ScopedValue的应用,我画了一个请求处理流程的架构图:
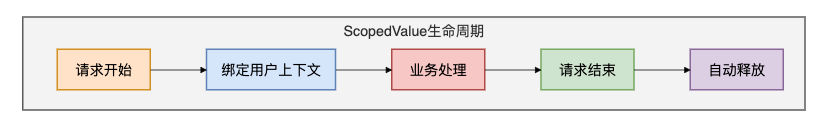
ScopedValue的生命周期如下图所示:
优势如下图所示:
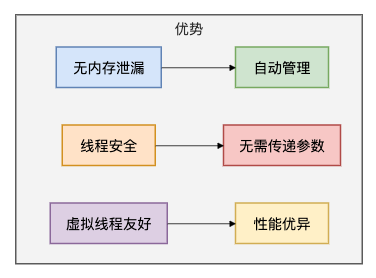
5.1 定义Web应用中的ScopedValue
/*** Web应用ScopedValue定义*/
public class WebScopedValues {// 用户上下文public static final ScopedValue<UserContext> USER_CONTEXT = ScopedValue.newInstance();// 请求信息public static final ScopedValue<RequestInfo> REQUEST_INFO = ScopedValue.newInstance();// 数据库连接(可选)public static final ScopedValue<Connection> DB_CONNECTION = ScopedValue.newInstance();// 追踪IDpublic static final ScopedValue<String> TRACE_ID = ScopedValue.newInstance();
}/*** 用户上下文详细信息*/
class UserContext {private final String userId;private final String username;private final List<String> roles;private final Map<String, Object> attributes;private final Locale locale;public UserContext(String userId, String username, List<String> roles, Map<String, Object> attributes, Locale locale) {this.userId = userId;this.username = username;this.roles = Collections.unmodifiableList(new ArrayList<>(roles));this.attributes = Collections.unmodifiableMap(new HashMap<>(attributes));this.locale = locale;}// Getter方法public String getUserId() { return userId; }public String getUsername() { return username; }public List<String> getRoles() { return roles; }public Map<String, Object> getAttributes() { return attributes; }public Locale getLocale() { return locale; }public boolean hasRole(String role) {return roles.contains(role);}public Object getAttribute(String key) {return attributes.get(key);}
}/*** 请求信息*/
class RequestInfo {private final String requestId;private final String method;private final String path;private final String clientIp;private final Map<String, String> headers;public RequestInfo(String requestId, String method, String path, String clientIp, Map<String, String> headers) {this.requestId = requestId;this.method = method;this.path = path;this.clientIp = clientIp;this.headers = Collections.unmodifiableMap(new HashMap<>(headers));}// Getter方法public String getRequestId() { return requestId; }public String getMethod() { return method; }public String getPath() { return path; }public String getClientIp() { return clientIp; }public Map<String, String> getHeaders() { return headers; }
}
5.2 过滤器实现
/*** 认证过滤器 - 使用ScopedValue*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class AuthenticationFilter implements Filter {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@Autowiredprivate JwtTokenProvider tokenProvider;@Overridepublic void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {HttpServletRequest httpRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request;HttpServletResponse httpResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response;// 生成请求IDString requestId = generateRequestId();// 提取请求信息RequestInfo requestInfo = extractRequestInfo(httpRequest, requestId);// 认证用户UserContext userContext = authenticateUser(httpRequest);// 在作用域内执行请求处理ScopedValue.runWhere(ScopedValue.where(WebScopedValues.REQUEST_INFO, requestInfo).where(WebScopedValues.USER_CONTEXT, userContext).where(WebScopedValues.TRACE_ID, requestId),() -> {try {chain.doFilter(request, response);} catch (Exception e) {log.error("请求处理异常", e);throw new RuntimeException("过滤器异常", e);}});// 作用域结束后自动清理所有ScopedValuelog.info("请求处理完成: {}", requestId);}private String generateRequestId() {return "req_" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "_" + ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1000, 9999);}private RequestInfo extractRequestInfo(HttpServletRequest request, String requestId) {Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<>();Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames();while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()) {String headerName = headerNames.nextElement();headers.put(headerName, request.getHeader(headerName));}return new RequestInfo(requestId,request.getMethod(),request.getRequestURI(),request.getRemoteAddr(),headers);}private UserContext authenticateUser(HttpServletRequest request) {String authHeader = request.getHeader("Authorization");if (authHeader != null && authHeader.startsWith("Bearer ")) {String token = authHeader.substring(7);return tokenProvider.validateToken(token);}// 返回匿名用户return new UserContext("anonymous","Anonymous User",List.of("GUEST"),Map.of("source", "web"),request.getLocale());}
}
5.3 业务层使用
/*** 用户服务 - 使用ScopedValue*/
@Service
@Slf4j
@Transactional
public class UserService {@Autowiredprivate UserRepository userRepository;@Autowiredprivate OrderService orderService;/*** 获取当前用户信息*/public UserProfile getCurrentUserProfile() {UserContext userContext = WebScopedValues.USER_CONTEXT.get();RequestInfo requestInfo = WebScopedValues.REQUEST_INFO.get();String traceId = WebScopedValues.TRACE_ID.get();log.info("[{}] 获取用户资料: {}", traceId, userContext.getUserId());// 根据用户ID查询用户信息User user = userRepository.findById(userContext.getUserId()).orElseThrow(() -> new UserNotFoundException("用户不存在: " + userContext.getUserId()));// 构建用户资料return UserProfile.builder().userId(user.getId()).username(user.getUsername()).email(user.getEmail()).roles(userContext.getRoles()).locale(userContext.getLocale()).lastLogin(user.getLastLoginTime()).build();}/*** 更新用户信息*/public void updateUserProfile(UpdateProfileRequest request) {UserContext userContext = WebScopedValues.USER_CONTEXT.get();String traceId = WebScopedValues.TRACE_ID.get();log.info("[{}] 更新用户资料: {}", traceId, userContext.getUserId());// 验证权限if (!userContext.getUserId().equals(request.getUserId())) {throw new PermissionDeniedException("无权更新其他用户资料");}// 更新用户信息User user = userRepository.findById(request.getUserId()).orElseThrow(() -> new UserNotFoundException("用户不存在: " + request.getUserId()));user.setEmail(request.getEmail());user.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());userRepository.save(user);log.info("[{}] 用户资料更新成功: {}", traceId, userContext.getUserId());}/*** 获取用户订单列表*/public List<Order> getUserOrders() {UserContext userContext = WebScopedValues.USER_CONTEXT.get();// 调用订单服务,无需传递用户IDreturn orderService.getUserOrders();}
}/*** 订单服务*/
@Service
@Slf4j
@Transactional
public class OrderService {@Autowiredprivate OrderRepository orderRepository;public List<Order> getUserOrders() {UserContext userContext = WebScopedValues.USER_CONTEXT.get();String traceId = WebScopedValues.TRACE_ID.get();log.info("[{}] 查询用户订单: {}", traceId, userContext.getUserId());// 直接从ScopedValue获取用户ID,无需参数传递return orderRepository.findByUserId(userContext.getUserId());}/*** 创建订单*/public Order createOrder(CreateOrderRequest request) {UserContext userContext = WebScopedValues.USER_CONTEXT.get();String traceId = WebScopedValues.TRACE_ID.get();log.info("[{}] 创建订单: 用户={}", traceId, userContext.getUserId());// 创建订单Order order = new Order();order.setOrderId(generateOrderId());order.setUserId(userContext.getUserId());order.setAmount(request.getTotalAmount());order.setStatus(OrderStatus.CREATED);order.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());Order savedOrder = orderRepository.save(order);log.info("[{}] 订单创建成功: {}", traceId, savedOrder.getOrderId());return savedOrder;}private String generateOrderId() {return "ORD" + System.currentTimeMillis() + ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1000, 9999);}
}
5.4 Controller层
/*** 用户控制器 - 使用ScopedValue*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
@Slf4j
public class UserController {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;/*** 获取当前用户资料*/@GetMapping("/profile")public ResponseEntity<UserProfile> getCurrentUserProfile() {// 无需传递用户ID,直接从ScopedValue获取UserProfile profile = userService.getCurrentUserProfile();return ResponseEntity.ok(profile);}/*** 更新用户资料*/@PutMapping("/profile")public ResponseEntity<Void> updateUserProfile(@RequestBody @Valid UpdateProfileRequest request) {userService.updateUserProfile(request);return ResponseEntity.ok().build();}/*** 获取用户订单*/@GetMapping("/orders")public ResponseEntity<List<Order>> getUserOrders() {List<Order> orders = userService.getUserOrders();return ResponseEntity.ok(orders);}/*** 异常处理*/@ExceptionHandler({UserNotFoundException.class, PermissionDeniedException.class})public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleUserExceptions(RuntimeException e) {// 可以从ScopedValue获取请求信息用于日志String traceId = WebScopedValues.TRACE_ID.get();log.error("[{}] 用户操作异常: {}", traceId, e.getMessage());ErrorResponse error = new ErrorResponse(e.getClass().getSimpleName(),e.getMessage(),traceId);return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).body(error);}
}/*** 错误响应*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class ErrorResponse {private String error;private String message;private String traceId;private long timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
六、迁移指南:从ThreadLocal到ScopedValue
有些小伙伴可能担心迁移成本,其实从ThreadLocal迁移到ScopedValue并不复杂。
6.1 迁移步骤
/*** ThreadLocal到ScopedValue迁移指南*/
public class MigrationGuide {// ThreadLocal定义(旧方式)private static final ThreadLocal<UserContext> TL_USER = new ThreadLocal<>();private static final ThreadLocal<Connection> TL_CONN = new ThreadLocal<>();private static final ThreadLocal<String> TL_TRACE = new ThreadLocal<>();// ScopedValue定义(新方式)private static final ScopedValue<UserContext> SV_USER = ScopedValue.newInstance();private static final ScopedValue<Connection> SV_CONN = ScopedValue.newInstance();private static final ScopedValue<String> SV_TRACE = ScopedValue.newInstance();/*** 迁移前:ThreadLocal方式*/public void beforeMigration() {// 设置值TL_USER.set(new UserContext("user_old"));TL_TRACE.set("trace_old");Connection conn = null;try {conn = createConnection();TL_CONN.set(conn);// 业务处理processBusinessOld();} catch (Exception e) {// 异常处理} finally {// 必须手动清理TL_USER.remove();TL_TRACE.remove();TL_CONN.remove();if (conn != null) {closeConnection(conn);}}}/*** 迁移后:ScopedValue方式*/public void afterMigration() {UserContext user = new UserContext("user_new");String trace = "trace_new";// 使用try-with-resources管理连接try (Connection conn = createConnection()) {// 在作用域内执行ScopedValue.runWhere(ScopedValue.where(SV_USER, user).where(SV_TRACE, trace).where(SV_CONN, conn),() -> {// 业务处理processBusinessNew();});// 自动清理,无需finally块} catch (Exception e) {// 异常处理}}/*** 业务处理 - 旧方式*/private void processBusinessOld() {// 需要处理null值UserContext user = TL_USER.get();if (user == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("用户上下文未设置");}Connection conn = TL_CONN.get();if (conn == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("数据库连接未设置");}String trace = TL_TRACE.get();// 业务逻辑...System.out.println("处理用户: " + user.getUserId() + ", 追踪: " + trace);}/*** 业务处理 - 新方式*/private void processBusinessNew() {// 在作用域内保证不为nullUserContext user = SV_USER.get();Connection conn = SV_CONN.get();String trace = SV_TRACE.get();// 业务逻辑...System.out.println("处理用户: " + user.getUserId() + ", 追踪: " + trace);}/*** 复杂迁移场景:嵌套ThreadLocal*/public void complexMigration() {// 旧方式:嵌套ThreadLocalTL_USER.set(new UserContext("outer_user"));try {// 内层逻辑TL_USER.set(new UserContext("inner_user"));try {processBusinessOld();} finally {// 恢复外层值TL_USER.set(new UserContext("outer_user"));}} finally {TL_USER.remove();}// 新方式:嵌套ScopedValueScopedValue.runWhere(SV_USER, new UserContext("outer_user"), () -> {ScopedValue.runWhere(SV_USER, new UserContext("inner_user"), () -> {processBusinessNew(); // 使用内层值});// 自动恢复外层值processBusinessNew(); // 使用外层值});}private Connection createConnection() {// 创建连接return null;}private void closeConnection(Connection conn) {// 关闭连接}
}
6.2 兼容性处理
/*** 兼容性处理 - 逐步迁移*/
public class CompatibilityLayer {// 新代码使用ScopedValueprivate static final ScopedValue<UserContext> SV_USER = ScopedValue.newInstance();// 旧代码可能还在使用ThreadLocalprivate static final ThreadLocal<UserContext> TL_USER = new ThreadLocal<>();/*** 桥接模式:同时支持两种方式*/public void bridgePattern() {UserContext user = new UserContext("bridge_user");// 在新作用域内执行ScopedValue.runWhere(SV_USER, user, () -> {// 同时设置ThreadLocal以兼容旧代码TL_USER.set(user);try {// 执行业务逻辑(新旧代码都可以工作)processMixedBusiness();} finally {// 清理ThreadLocalTL_USER.remove();}});}/*** 适配器:让旧代码使用ScopedValue*/public static class ThreadLocalAdapter {private final ScopedValue<UserContext> scopedValue;public ThreadLocalAdapter(ScopedValue<UserContext> scopedValue) {this.scopedValue = scopedValue;}public void set(UserContext user) {// 对于set操作,需要在适当的作用域调用throw new UnsupportedOperationException("请使用ScopedValue.runWhere");}public UserContext get() {try {return scopedValue.get();} catch (Exception e) {// 如果不在作用域内,返回null(模拟ThreadLocal行为)return null;}}public void remove() {// 无需操作,ScopedValue自动管理}}/*** 混合业务处理*/private void processMixedBusiness() {// 新代码使用ScopedValueUserContext svUser = SV_USER.get();System.out.println("ScopedValue用户: " + svUser.getUserId());// 旧代码使用ThreadLocal(通过桥接设置)UserContext tlUser = TL_USER.get();System.out.println("ThreadLocal用户: " + tlUser.getUserId());// 两者应该相同assert svUser == tlUser;}/*** 逐步迁移策略*/public void gradualMigrationStrategy() {// 阶段1:引入ScopedValue,与ThreadLocal共存// 阶段2:新代码使用ScopedValue,旧代码逐步迁移// 阶段3:移除ThreadLocal,完全使用ScopedValueSystem.out.println("建议的迁移阶段:");System.out.println("1. 引入ScopedValue,建立桥接");System.out.println("2. 新功能使用ScopedValue");System.out.println("3. 逐步迁移旧代码");System.out.println("4. 移除ThreadLocal相关代码");System.out.println("5. 清理桥接层");}
}
总结
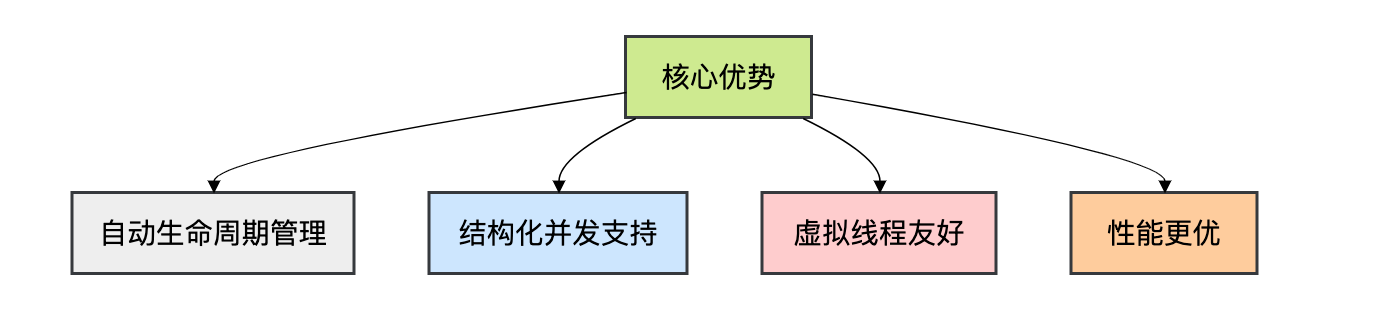
经过上面的深度剖析,我们来总结一下ScopedValue的核心优势。
核心优势
- 内存安全:自动生命周期管理,彻底解决内存泄漏
- 使用简单:结构化绑定,无需手动清理
- 性能优异:专为虚拟线程优化,性能更好
- 并发友好:完美支持结构化并发和虚拟线程
迁移决策指南
有些小伙伴在迁移时可能犹豫不决,我总结了一个决策指南:
ThreadLocal vs ScopedValue 选择口诀
- 新项目:直接使用ScopedValue,享受现代特性
- 老项目:逐步迁移,先在新模块使用
- 性能敏感:ScopedValue在虚拟线程中表现更佳
- 内存敏感:ScopedValue无内存泄漏风险
- 团队技能:ThreadLocal更普及,ScopedValue需要学习
技术对比
| 特性 | ThreadLocal | ScopedValue |
|---|---|---|
| 内存管理 | 手动remove | 自动管理 |
| 内存泄漏 | 高风险 | 无风险 |
| 使用复杂度 | 高(需要try-finally) | 低(结构化绑定) |
| 性能 | 较好 | 更优(虚拟线程) |
| 继承性 | 需要InheritableThreadLocal | 自动继承 |
| 虚拟线程支持 | 有问题 | 完美支持 |
最后的建议
ScopedValue是Java并发编程的重要进步,我建议大家:
- 学习掌握:尽快学习掌握ScopedValue的使用
- 新项目首选:在新项目中优先使用ScopedValue
- 逐步迁移:在老项目中制定合理的迁移计划
- 关注生态:关注相关框架对ScopedValue的支持
最后说一句(求关注,别白嫖我)
如果这篇文章对您有所帮助,或者有所启发的话,帮忙关注一下我的同名公众号:苏三说技术,您的支持是我坚持写作最大的动力。
求一键三连:点赞、转发、在看。
关注公众号:【苏三说技术】,在公众号中回复:进大厂,可以免费获取我最近整理的10万字的面试宝典,好多小伙伴靠这个宝典拿到了多家大厂的offer。
更多项目实战在我的技术网站:http://www.susan.net.cn/project






)









 A+B+C+D)


