文章目录
- `grep --help`
- 英文
- 中文
- 使用示例
- `-E, --extended-regexp`:此选项表示模式为扩展正则表达式。
- `-F, --fixed-strings`:此选项表示模式被视为固定字符串而不是正则表达式。
- `-G, --basic-regexp`:此选项表示模式为基础正则表达式。这是默认的模式类型。
- `-P, --perl-regexp`:此选项表示模式为 Perl 正则表达式。这种类型的正则表达式更加强大和灵活。
- `-e, --regexp=PATTERNS`:此选项允许你指定用于匹配的模式。当你的模式以“-”开头时,或者当你有多个模式需要匹配时,这个选项特别有用。
- `-f, --file=FILE`:此选项允许你从文件中读取模式。
- `-i, --ignore-case`:此选项使得匹配时忽略大小写。
- `-w, --word-regexp`:此选项将模式视为单词,只有整个单词与模式匹配才算成功。
- `-x, --line-regexp`:此选项表示整行必须与模式完全匹配才算成功。
- `-z, --null-data`:此选项将使得数据行以0字节而非换行符结束。
- `-s, --no-messages`:此选项会抑制错误信息。
- `-v, --invert-match`:此选项会反转匹配,选择不匹配模式的行。
- `-V, --version`:此选项会显示版本信息并退出。
- `-m, --max-count=NUM`:此选项会在找到指定数量的匹配行后停止搜索。
- `-b, --byte-offset`:此选项会在输出行前打印该行在输入文件中的字节偏移量。
- `-n, --line-number`:此选项会在输出行前打印行号。
- `-H, --with-filename`:此选项会在输出行前打印文件名。这在搜索多个文件时非常有用。
- `-h, --no-filename`:此选项会在输出行前不打印文件名。这是默认的行为,当只搜索一个文件时。
- `-o, --only-matching`:此选项会只显示匹配的部分,而非整行。
- `-q, --quiet, --silent`:此选项会抑制所有正常的输出。它通常与其他命令一起使用,例如 `if` 语句,来检查某个模式是否存在。
- `-L, --files-without-match`:此选项会打印出没有匹配到模式的文件名。
- `-l, --files-with-matches`:此选项会打印出至少匹配到一次模式的文件名。
- `-c, --count`:此选项会打印每个文件中匹配到模式的行数。
- `-r, --recursive` 或 `-R, --dereference-recursive`:此选项会使得 `grep` 在目录以及其子目录中搜索文件。`-R` 选项还会跟踪符号链接。
grep --help
grep 是一个强大的文本搜索工具,它使用正则表达式来搜索与模式匹配的行,并打印出来。下面是使用文档的英文和中文翻译。
英文
root@ky:/userdata/testKYAI/kyai# grep --help
Usage: grep [OPTION]... PATTERNS [FILE]...
Search for PATTERNS in each FILE.
Example: grep -i 'hello world' menu.h main.c
PATTERNS can contain multiple patterns separated by newlines.Pattern selection and interpretation:-E, --extended-regexp PATTERNS are extended regular expressions-F, --fixed-strings PATTERNS are strings-G, --basic-regexp PATTERNS are basic regular expressions-P, --perl-regexp PATTERNS are Perl regular expressions-e, --regexp=PATTERNS use PATTERNS for matching-f, --file=FILE take PATTERNS from FILE-i, --ignore-case ignore case distinctions in patterns and data--no-ignore-case do not ignore case distinctions (default)-w, --word-regexp match only whole words-x, --line-regexp match only whole lines-z, --null-data a data line ends in 0 byte, not newlineMiscellaneous:-s, --no-messages suppress error messages-v, --invert-match select non-matching lines-V, --version display version information and exit--help display this help text and exitOutput control:-m, --max-count=NUM stop after NUM selected lines-b, --byte-offset print the byte offset with output lines-n, --line-number print line number with output lines--line-buffered flush output on every line-H, --with-filename print file name with output lines-h, --no-filename suppress the file name prefix on output--label=LABEL use LABEL as the standard input file name prefix-o, --only-matching show only nonempty parts of lines that match-q, --quiet, --silent suppress all normal output--binary-files=TYPE assume that binary files are TYPE;TYPE is 'binary', 'text', or 'without-match'-a, --text equivalent to --binary-files=text-I equivalent to --binary-files=without-match-d, --directories=ACTION how to handle directories;ACTION is 'read', 'recurse', or 'skip'-D, --devices=ACTION how to handle devices, FIFOs and sockets;ACTION is 'read' or 'skip'-r, --recursive like --directories=recurse-R, --dereference-recursive likewise, but follow all symlinks--include=GLOB search only files that match GLOB (a file pattern)--exclude=GLOB skip files that match GLOB--exclude-from=FILE skip files that match any file pattern from FILE--exclude-dir=GLOB skip directories that match GLOB-L, --files-without-match print only names of FILEs with no selected lines-l, --files-with-matches print only names of FILEs with selected lines-c, --count print only a count of selected lines per FILE-T, --initial-tab make tabs line up (if needed)-Z, --null print 0 byte after FILE nameContext control:-B, --before-context=NUM print NUM lines of leading context-A, --after-context=NUM print NUM lines of trailing context-C, --context=NUM print NUM lines of output context-NUM same as --context=NUM--color[=WHEN],--colour[=WHEN] use markers to highlight the matching strings;WHEN is 'always', 'never', or 'auto'-U, --binary do not strip CR characters at EOL (MSDOS/Windows)When FILE is '-', read standard input. With no FILE, read '.' if
recursive, '-' otherwise. With fewer than two FILEs, assume -h.
Exit status is 0 if any line (or file if -L) is selected, 1 otherwise;
if any error occurs and -q is not given, the exit status is 2.Report bugs to: bug-grep@gnu.org
GNU grep home page: <http://www.gnu.org/software/grep/>
General help using GNU software: <https://www.gnu.org/gethelp/>
中文
root@ky:/userdata/testKYAI/kyai# grep --help
用法:grep [选项]... 模式 [文件]...
在每个文件中搜索模式。
示例:grep -i 'hello world' menu.h main.c
模式可以包含由换行符分隔的多个模式。模式选择和解释:-E, --extended-regexp 模式是扩展正则表达式-F, --fixed-strings 模式是字符串-G, --basic-regexp 模式是基础正则表达式-P, --perl-regexp 模式是Perl正则表达式-e, --regexp=模式 使用模式进行匹配-f, --file=文件 从文件获取模式-i, --ignore-case 忽略模式和数据中的大小写区别--no-ignore-case 不忽略大小写区别(默认)-w, --word-regexp 只匹配整个单词-x, --line-regexp 只匹配整行-z, --null-data 数据行以0字节结束,而非新行杂项:-s, --no-messages 抑制错误消息-v, --invert-match 选择不匹配的行-V, --version 显示版本信息并退出--help 显示此帮助文本并退出输出控制:-m, --max-count=NUM 在选定的行后停止NUM-b, --byte-offset 与输出行一起打印字节偏移量-n, --line-number 与输出行一起打印行号--line-buffered 每行刷新输出-H, --with-filename 与输出行一起打印文件名-h, --no-filename 在输出时抑制文件名前缀--label=标签 使用标签作为标准输入文件名前缀-o, --only-matching 只显示匹配行的非空部分-q, --quiet, --silent 抑制所有正常输出--binary-files=类型 假设二进制文件是类型;类型是'binary', 'text', 或 'without-match'-a, --text 等同于 --binary-files=text-I 等同于 --binary-files=without-match-d, --directories=动作 如何处理目录;动作是'read', 'recurse', 或 'skip'-D, --devices=动作 如何处理设备、FIFOs 和套接字;动作是'read' 或 'skip'-r, --recursive 像 --directories=recurse-R, --dereference-recursive 同样,但是跟踪所有符号链接--include=GLOB 只搜索匹配GLOB的文件(一个文件模式)--exclude=GLOB 跳过匹配GLOB的文件--exclude-from=FILE 跳过与文件中的任何文件模式匹配的文件--exclude-dir=GLOB 跳过匹配GLOB的目录-L, --files-without-match 只打印没有选定行的FILEs的名称-l, --files-with-matches 只打印有选定行的FILEs的名称-c, --count 每个文件只打印选定行的数量-T, --initial-tab 让制表符对齐(如果需要)-Z, --null 在文件名后打印0字节上下文控制:-B, --before-context=NUM 打印前NUM行的上下文-A, --after-context=NUM 打印后NUM行的上下文-C, --context=NUM 打印NUM行的输出上下文-NUM 同 --context=NUM--color[=WHEN],--colour[=WHEN] 使用标记来突出显示匹配的字符串;WHEN是 'always', 'never', 或 'auto'-U, --binary 不在EOL(MSDOS/Windows)剥离CR字符当文件为'-'时,读取标准输入。如果没有文件,如果是递归的,则读取'.',否则读取'-'。如果文件少于两个,假设-h。
如果选择了任何行(或者如果-L则为文件),退出状态为0,否则为1;如果发生任何错误并且未给出-q,则退出状态为2。报告错误至:bug-grep@gnu.org
GNU grep主页:<http://www.gnu.org/software/grep/>
使用GNU软件的一般帮助:<https://www.gnu.org/gethelp/>
使用示例
-E, --extended-regexp:此选项表示模式为扩展正则表达式。
-E, --extended-regexp 是 grep 命令的一个选项,它告诉 grep 使用扩展正则表达式进行匹配。
在默认情况下,grep 使用基本正则表达式 (Basic Regular Expression, BRE)。而 -E 选项使得 grep 使用扩展正则表达式 (Extended Regular Expression, ERE)。
扩展正则表达式提供了更多的功能和灵活性。例如,你可以使用 | 字符来表示 “或” 运算,无需转义。在基本正则表达式中,你需要使用 \| 来表示 “或” 运算。
这是一些示例:
-
匹配 “abc” 或 “def”:
echo -e "abc\ndef" | grep -E 'abc|def'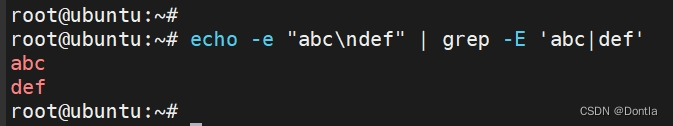
-
匹配重复的单词(注意这里使用了括号和加号,这两个符号在基本正则表达式中都需要转义):
echo "hello hello" | grep -E '(\b.+\b) \1'这个命令是在查找重复的单词。让我们分解一下这个命令:
-
echo "hello hello":这个命令会输出字符串 “hello hello”。 -
|:管道符号,它把前一个命令的输出作为后一个命令的输入。 -
grep -E '(\b.+\b) \1':这个命令使用了扩展正则表达式来搜索模式。-
\b是一个单词边界。这意味着模式必须出现在单词的开始或结束位置。 -
.匹配任何字符(除了换行符)。 -
+表示前面的元素可以出现一次或多次。因此,.+匹配任意长度的单词。 -
(\b.+\b)这个括号表示一个捕获组,它可以捕获匹配的文本以便稍后引用。在这里,它捕获了一个完整的单词,如:hello。 -
\1是一个反向引用,它引用了第一个捕获组的内容。在这里,它引用了前面捕获的单词。
-
所以,这个正则表达式的含义是:找到一个单词(由
\b.+\b定义),然后找到一个空格,再找到和第一个单词完全相同的单词(由\1
定义)。如果输入的字符串满足这个条件,那么grep命令就会把这个字符串打印出来。在你给出的例子中,
"hello hello"符合这个条件,因为 “hello” 是一个单词,然后是一个空格,然后又是
“hello”。所以grep命令会把整个字符串 “hello hello” 打印出来。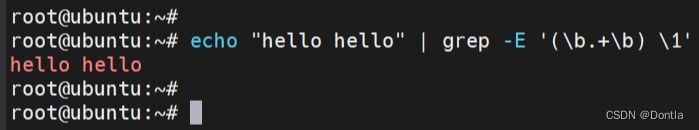
-
-
.+和.*的区别
在正则表达式中,+和*都是数量词,用于指定前面的字符或组可以出现的次数。但它们有一个关键的区别:-
*表示前面的字符或组可以出现零次或多次。也就是说,即使前面的字符或组完全没有出现,匹配也会成功。 -
+表示前面的字符或组必须至少出现一次。如果前面的字符或组没有出现,匹配就会失败。
因此,当你将
.(匹配任意单个字符)与这两个数量词结合时:-
.*会匹配任意数量的任意字符,包括没有字符的情况(也就是空字符串)。 -
.+会匹配一个或更多的任意字符,但不会匹配空字符串。
举个例子,假设我们有以下的输入:
abcdef在这里,我们有三行:一行是 “abc”,一行是空行,一行是 “def”。
如果我们运行
grep -E '.*',所有的三行都会被匹配,因为.*可以匹配任意字符(包括没有字符的情况)。但是,如果我们运行
grep -E '.+',只有 “abc” 和 “def” 这两行会被匹配,因为.+必须匹配至少一个字符,所以它无法匹配空行。 -
-F, --fixed-strings:此选项表示模式被视为固定字符串而不是正则表达式。
echo -e "abc.def\nabc-def" | grep -F 'abc.def'
-G, --basic-regexp:此选项表示模式为基础正则表达式。这是默认的模式类型。
echo -e "abc\ndef" | grep -G 'abc'
-P, --perl-regexp:此选项表示模式为 Perl 正则表达式。这种类型的正则表达式更加强大和灵活。
echo -e "abc\ndef" | grep -P 'abc'
-e, --regexp=PATTERNS:此选项允许你指定用于匹配的模式。当你的模式以“-”开头时,或者当你有多个模式需要匹配时,这个选项特别有用。
grep -e '-abc' -e 'def' filename
-f, --file=FILE:此选项允许你从文件中读取模式。
grep -f patterns.txt filename
-i, --ignore-case:此选项使得匹配时忽略大小写。
echo -e "Abc\ndef" | grep -i 'abc'
-w, --word-regexp:此选项将模式视为单词,只有整个单词与模式匹配才算成功。
echo -e "abc def\nabcdef" | grep -w 'abc'
-x, --line-regexp:此选项表示整行必须与模式完全匹配才算成功。
echo -e "abc\ndef abc" | grep -x 'abc'
-z, --null-data:此选项将使得数据行以0字节而非换行符结束。
printf 'abc\0def' | grep -z 'abc'
-s, --no-messages:此选项会抑制错误信息。
grep -s 'abc' non_existent_file
-v, --invert-match:此选项会反转匹配,选择不匹配模式的行。
echo -e "abc\ndef" | grep -v 'abc'
-V, --version:此选项会显示版本信息并退出。
grep --version
-m, --max-count=NUM:此选项会在找到指定数量的匹配行后停止搜索。
echo -e "abc\nabc\ndef" | grep -m 1 'abc'
-b, --byte-offset:此选项会在输出行前打印该行在输入文件中的字节偏移量。
echo -e "abc\ndef" | grep -b 'def'
-n, --line-number:此选项会在输出行前打印行号。
echo -e "abc\ndef" | grep -n 'def'
-H, --with-filename:此选项会在输出行前打印文件名。这在搜索多个文件时非常有用。
grep -H 'pattern' file1 file2
-h, --no-filename:此选项会在输出行前不打印文件名。这是默认的行为,当只搜索一个文件时。
grep -h 'pattern' file
-o, --only-matching:此选项会只显示匹配的部分,而非整行。
echo "abc def" | grep -o 'abc'
-q, --quiet, --silent:此选项会抑制所有正常的输出。它通常与其他命令一起使用,例如 if 语句,来检查某个模式是否存在。
if echo "abc def" | grep -q 'abc'; then echo 'Pattern found!'; fi
-L, --files-without-match:此选项会打印出没有匹配到模式的文件名。
grep -L 'pattern' file1 file2
-l, --files-with-matches:此选项会打印出至少匹配到一次模式的文件名。
grep -l 'pattern' file1 file2
-c, --count:此选项会打印每个文件中匹配到模式的行数。
grep -c 'pattern' file
-r, --recursive 或 -R, --dereference-recursive:此选项会使得 grep 在目录以及其子目录中搜索文件。-R 选项还会跟踪符号链接。
grep -r 'pattern' directory

 -- 上部分)









)







