【0】README
0.1)本文部分内容转自 http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3638493.html, 旨在理解 优先队列——斜堆 的基础知识;
0.2) for original source code , please visit https://github.com/pacosonTang/dataStructure-algorithmAnalysis/tree/master/chapter6/p150_skew_heap
【1】优先队列——斜堆相关
1.0)斜堆定义: 斜堆是具有堆序性的二叉树, 与左式堆的差别在于没有零路径属性,故merge操作后,不需要考虑左右子堆的零路径大小,而是无条件交换左右子堆;(干货——斜堆定义)
1.1)定义:斜堆(Skew heap)也叫自适应堆(self-adjusting heap),它是左式堆的一个变种。和左式堆一样,它通常也用于实现优先队列。它的合并操作的时间复杂度也是O(log n)。
1.2)相比于左倾堆,斜堆的节点没有”零距离”这个属性: 除此之外,它们斜堆的合并操作也不同。
1.3)斜堆的合并操作算法如下:
- case1) 如果一个空斜堆与一个非空斜堆合并,返回非空斜堆。
- case2) 如果两个斜堆都非空,那么比较两个根节点,取较小堆的根节点为新的根节点。将”较小堆的根节点的右孩子”和”较大堆”进行合并。
- case3) 合并后,交换新堆根节点的左孩子和右孩子。
Attention)
- A1)第3步是斜堆和左式堆的合并操作差别的关键所在,如果是左式堆,则合并后要比较左右孩子的零距离大小,若右孩子的零距离 > 左孩子的零距离,则交换左右孩子;最后,在设置根的零距离。
- A2) 下面是一个关于斜堆的干货荔枝:
【2】source code + printing results
2.1)source code at a glance
#include "skew_heap.h" // swap the left and the right in priority queue.
void swap(PriorityQueue h1)
{PriorityQueue temp;temp = h1->left;h1->left = h1->right;h1->right = temp;
}// analog print directories and files name in the BinaryTree, which involves postorder traversal.
void printPreorder(int depth, TreeNode root)
{ int i;if(root) { for(i = 0; i < depth; i++)printf(" "); printf("%d\n", root->value);printPreorder(depth + 1, root->left); // Attention: there's difference between traversing binary tree and common tree.printPreorder(depth + 1, root->right);}else {for(i = 0; i < depth; i++)printf(" "); printf("NULL\n");}
}// insert an element with value into the priority queue.
PriorityQueue insert(ElementType value, PriorityQueue pq)
{TreeNode node; node = (TreeNode)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));if(!node){Error("failed inserting, for out of space !");return pq;}node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL; node->value = value; if(pq == NULL) // means that just only creating a node with value.{return node;}else{return merge(node, pq); }
}// return the minimal between a and b.
int minimal(int a, int b)
{return a > b ? b : a;
}// merge the priority queue h1 and h2.
PriorityQueue merge(PriorityQueue h1, PriorityQueue h2)
{ if(h1 == NULL){return h2;}else if(h2 == NULL){return h1;} if(h1->value > h2->value){return innerMerge(h2, h1);}else{return innerMerge(h1, h2);}
}// merge the priority queue h1 and h2.
PriorityQueue innerMerge(PriorityQueue h1, PriorityQueue h2)
{ if(h1->left == NULL){h1->left = h2;}else{h1->right = merge(h1->right, h2);swap(h1); } return h1;
} int main()
{PriorityQueue h1;PriorityQueue h2; int data[] = {21, 10, 23, 14, 3, 26, 17, 8}; int data2[] = {18, 7, 37, 6, 24, 33, 12, 18}; int i;h1 = insert(data[0], NULL);for(i=1; i<8; i++){h1 = insert(data[i], h1);}printf("\n=== after the leftist heap h1 is merged===\n");printPreorder(1, h1);h2 = insert(data2[0], NULL);for(i=1; i<8; i++){h2 = insert(data2[i], h2);}printf("\n=== after the leftist heap h2 is merged===\n");printPreorder(1, h2);h1 = merge(h1, h2);printf("\n=== after both h1 and h2 are merged===\n");printPreorder(1, h1); return 0;
}2.2) printing results
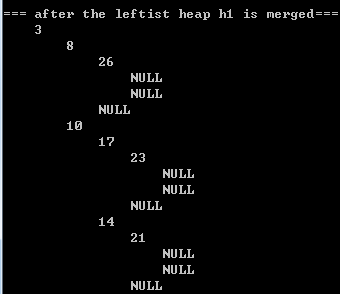 | 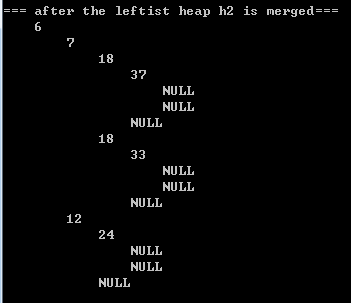 | 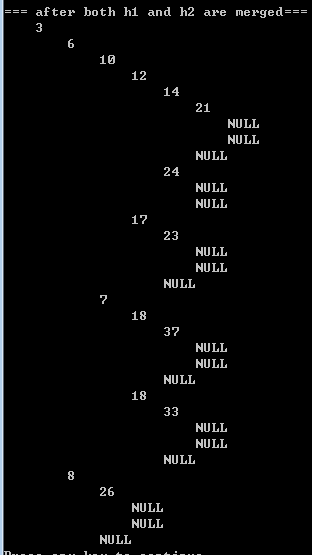 |




)



)









)

