数学公式基础
导言区(引包)
\usepackage{amsmath} %带星号的eqution正文区
\begin{document}%数学公式初步\section{简介}\LaTeX{}将排版内容分为文本模式和数学模式。文本模式用于普通文本排版,数学模式用于数学公式排版。\section{行内公式} %有三种方式可以写行内公式\subsection{美元符号}交换律是 $a+b = b+a$,如$1+2=2+1=3$。\subsection{小括号}交换律是 \(a+b = b+a\),如\(1+2=2+1=3\)。\subsection{math环境}交换律是 \begin{math}a+b = b+a\end{math},如\begin{math}1+2=2+1=3\end{math}。\section{上下标}\subsection{上标}$3x^{20}-x+2 = 0$ %大括号最好都加上,无论是一位数字还是多位数字$3x^{3x^{20}-x+2}-x+2=0$ %也可以用已有的公式做上标处理不过要加大括号\subsection{下标}$a_0,a_1,a_2$$a_0,a_1,a_2,...,a_{100},a_{3x^{20}-x+2}$ %同理,超过一个数字也要加大括号,也可以代入公式\section{希腊字母}$\alpha$ \quad $\beta$ \quad$\gamma$ \quad$\epsilon$ \quad$\pi$ \quad$\omega$ \quad$\Gamma$ \quad$\Delta$ \quad$\Pi$ \quad$\Omega$ \quad %大写字母开始的希腊字母用于排版大写的希腊字母$\alpha^3+\beta^2+\gamma=0$ %希腊字母也可以用在通用公式中\section{数学函数}$\log$ \quad $\sin$ \quad$\cos$ \quad$\arcsin$ \quad$\arccos$ \quad$\ln$$\sin^2 x + \cos^2 x = 1$ %构成公式$y = \sin^{-1} x$ \quad $y = \log_2 x$ \quad $y = \ln x$$\sqrt{2}$ \quad $\sqrt{x^2+y^2}$ \quad $\sqrt{2+\sqrt{2}}$ \quad $\sqrt[4]{x}$ \quad %用于排版公式,"[]"用于指定开方次数\section{分式} %两种方式大约是原体积的$3/4$。大约是原体积的$\frac{3}{4}$。%第一个{}是分子,第二个是分母。$\frac{x}{x^2+x+1}$ %复杂公式$\frac{\sqrt{x-1}}{\sqrt{x+1}}$$\frac{1}{1+\frac{1}{x}}$$\sqrt{\frac{x}{x^2+x+1}}$\section{行间公式}\subsection{美元符号}交换律是$$a+b = b+a$$如$$1+2=2+1=3$$\subsection{中括号}交换律是\[a+b = b+a\]如\[1+2=2+1=3\]\subsection{displaymath环境}交换律是\begin{displaymath}a+b=b+a,\end{displaymath}如\begin{displaymath}1+2=2+1=3.\end{displaymath}\subsection{自动编号公式equation环境}交换律公式见式\ref{eq:commutative}\begin{equation}a+b=b+a \label{eq:commutative}\end{equation}\subsection{不编号公式equation*环境}交换律公式见式\ref{eq:commutative2} %此时的编号为小节编号\begin{equation*} %带星号的quation需要引入宏包:“\usepackage{amsmath}”a+b=b+a \label{eq:commutative2}\end{equation*}公式的编号与交叉引用也是自动实现的,大家在排版中要习惯采用自动化的方式处理诸如图、表、公式的编号与交叉引用。再如公式\ref{eq:pol}:\begin{equation}x^5-7x^3+4x = 0 \label{eq:pol}\end{equation}\end{document}

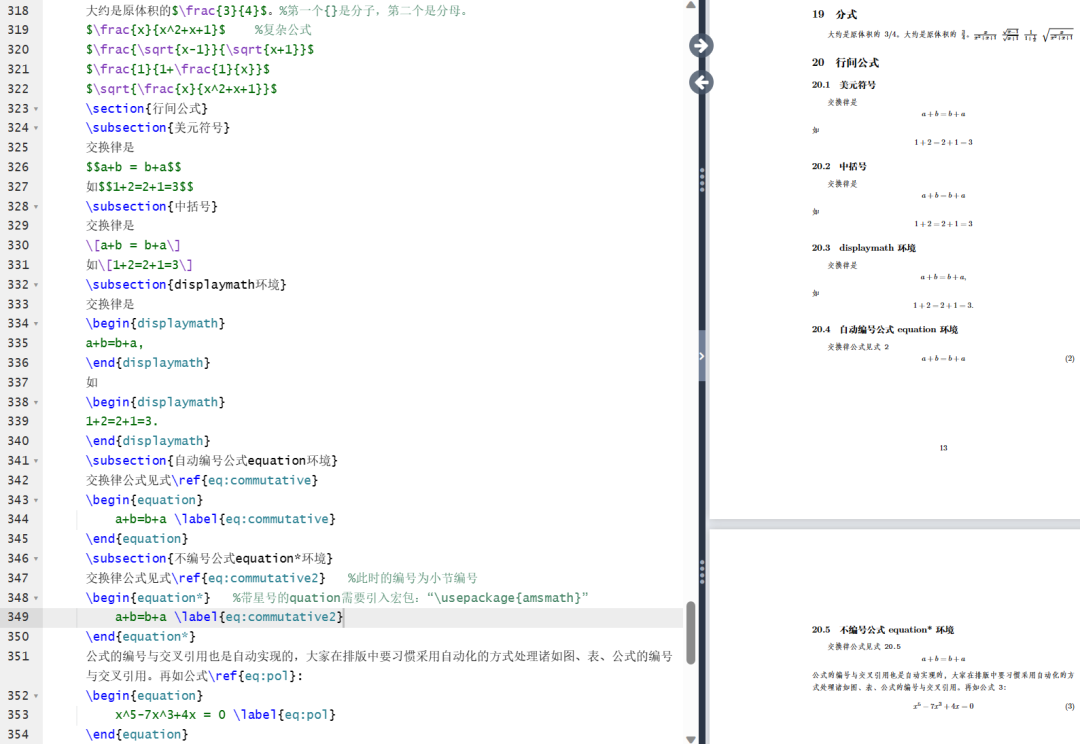
矩阵:
导言区:(自命令)
\newcommand{\adots}{\mathinner{\mkern2mu%\raisebox{0.1em}{.}\mkern2mu\raisebox{0.4em}{.}%\mkern2mu\raisebox{0.7em}{.}\mkern1mu}} %adots执行后面大括号的内容。用不同的方式排版不同的句号
正文区:
\begin{document}%矩阵%在latex中使用matrix环境实现矩阵排版,需要引入amsmath宏包\[\begin{matrix} %使用矩阵排版的matrix和使用表格排版的tabular非常相似0 & 1 \\ %用&分割列,用\\分割行1 & 0\end{matrix} \quad%pmatrix环境(矩阵两端加小括号)\begin{pmatrix}0 & -i \\i & 0\end{pmatrix} \quad\begin{bmatrix} %加中括号0 & -1 \\1 & 0\end{bmatrix} \quad\begin{Bmatrix} %加大括号1 & 0 \\0 & -1\end{Bmatrix} \quad\begin{vmatrix} %加单竖线a & b \\c & d\end{vmatrix} \quad\begin{Vmatrix} %加双竖线i & 0 \\0 & -i\end{Vmatrix} \quad\]\[A = \begin{pmatrix}a_{11}^2 & a_{12}^2 &a_{13}^2 \\ %上下标在矩阵中的使用0 & a_{22} & a_{23} \\0 & 0 & a_{33}\end{pmatrix}\]\[B = \begin{bmatrix} %矩阵中常用的省略号(横竖斜)a_{11} & \dots & a_{1n} \\\adots & \ddots & \vdots \\ %adots是自己定义出来的。当然往左斜这个省略号也可以直接用命令“\iddots”实现,不过需要导包mathdots,具体内容可见往期回顾的第一篇内容。0 & & a_{nn}\end{bmatrix}_{n \times n} %times排版乘号\]%利用矩阵的嵌套还可以实现分块矩阵 ↓↓↓\[\begin{pmatrix}\begin{matrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1\end{matrix}& \text{\Large 0} \\ %"\text{\Large 0}"表示临时切换到文本模式{\Large 0} & \begin{matrix}1 & 0 \\ 0 & -1 \end{matrix} %不加text输出的0是不一样的\end{pmatrix}\]%三角矩阵\[\begin{pmatrix}a_{11} & a_{12} \cdots & a_{1n} \\& a_{22} & \cdots & a_{2n} \\& & \ddots & \vdots \\\multicolumn{2}{c}{\raisebox{1.3ex}[0pt]{\Huge 0}}& & a_{nn} %"\multicolumn":合并多列;"\raisebox":调整高度\end{pmatrix}\]%产生跨列的省略号:\hdotsfor{<列数>}\[\begin{pmatrix}1 & \frac 12 & \dots & \frac 1n \\\hdotsfor{4} \\m & \frac m2 & \dots & \frac mn\end{pmatrix}\]%行内小矩阵(smallmatrix)环境复数 $z=(x,y)$ 也可用矩阵\begin{math}\left( %math环境下的括号手动加,也可以改成中括号等\begin{smallmatrix}x & -y \\ y & x\end{smallmatrix}\right)\end{math}来表示。%“\left”"\right"命令成对出现%array环境(类似于表格环境tabular)\[%第一行第1列\begin{array}{r|r}\frac12 & 0 \\\hline0 & -\frac abc \\ %frac命令,后面直接跟数字表示分子分母,多位数需要加花括号,frac后面不能直接跟字母,会报错,这些细节要注意。必要时用花括号进行分组,比如这里的c既不属于分母也不属于分子。\end{array}\]%利用array环境构造复杂矩阵\[\begin{array}{c@{\hspace{-5pt}}l} %@{<内容>}:添加任意内容,不占表项计数;向左移-5pt的距离\left(\begin{array}{ccc|ccc}a & \cdots & a & b & \cdots & b \\& \ddots & \vdots & \vdots & \adots \\& & a & b \\ \hline& & & c & \cdots & c \\& & & \vdots & & \vdots \\\multicolumn{3}{c|}{\raisebox{2ex}[0pt]{\Huge 0}}& c & \cdots & c\end{array}\right)&%第一行第2列\begin{array}{l}\left.\rule{0mm}{7mm}\right\}p \\ %"\left."表示与"\right\"配对,\left.什么都不输出\\\left.\rule{0mm}{7mm}\right\}q\end{array}\\[-5pt]%第二行第一列\begin{array}{cc}\underbrace{\rule{17mm}{0mm}}_m & %产生下面的横向大括号,rule指定尺寸\underbrace{\rule{17mm}{0mm}}_m\end{array}& %第二行第二列\end{array}\]\end{document}


多行公式
导言区(导包):
\usepackage{amsmath} %带星号的eqution\usepackage{amssymb}
正文区
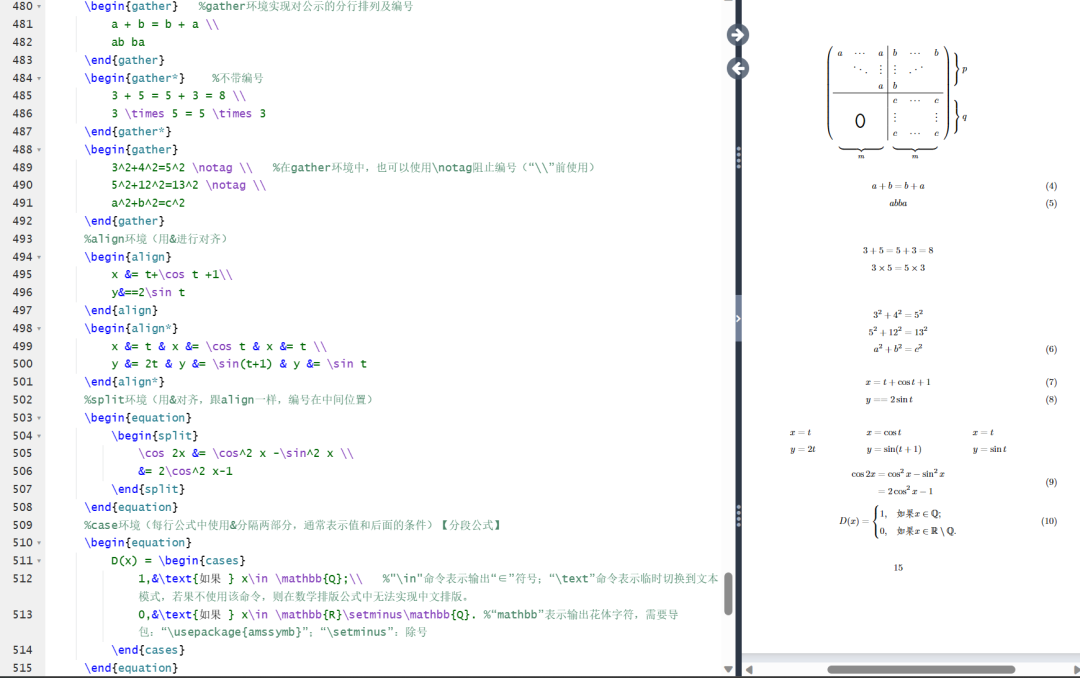
\begin{document}%多行公式%gather环境\begin{gather} %实现对公示的分行排列及编号a + b = b + a \\ab ba\end{gather}\begin{gather*} %不带编号3 + 5 = 5 + 3 = 8 \\3 \times 5 = 5 \times 3\end{gather*}\begin{gather}3^2+4^2=5^2 \notag \\ %在gather环境中,也可以使用\notag阻止编号(“\\”前使用)5^2+12^2=13^2 \notag \\a^2+b^2=c^2\end{gather}%align环境(用&进行对齐)\begin{align}x &= t+\cos t +1\\y&==2\sin t\end{align}\begin{align*}x &= t & x &= \cos t & x &= t \\y &= 2t & y &= \sin(t+1) & y &= \sin t\end{align*}%split环境(用&对齐,跟align一样,编号在中间位置)\begin{equation}\begin{split}\cos 2x &= \cos^2 x -\sin^2 x \\&= 2\cos^2 x-1\end{split}\end{equation}%case环境(每行公式中使用&分隔两部分,通常表示值和后面的条件)【分段公式】\begin{equation}D(x) = \begin{cases}1,&\text{如果 } x\in \mathbb{Q};\\ %"\in"命令表示输出“∈”符号;“\text”命令表示临时切换到文本模式,若果不使用该命令,则在数学排版公式中无法实现中文排版。0,&\text{如果 } x\in \mathbb{R}\setminus\mathbb{Q}. %“mathbb”表示输出花体字符,需要导包:“\usepackage{amssymb}”;“\setminus”:除号\end{cases}\end{equation}\end{document}


)









)

)



)
