这里写目录标题
- 1 流程
- 1 预处理
- 2 跟踪
- 2 代码
参考:sort代码 https://github.com/abewley/sort
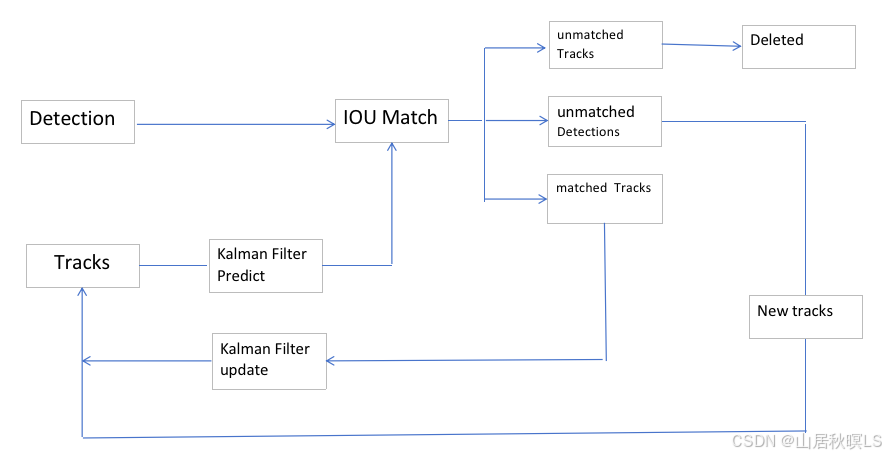
1 流程
1 预处理
1.1 获取离线检测数据。1.2 实例化跟踪器。
2 跟踪
2.1 轨迹处理。根据上一帧的轨迹预测当前帧的轨迹,剔除到当前轨迹中为空的轨迹得到当前有效轨迹。
2.2 匹配。用匈牙利算法对有效轨迹和检测框匹配,得到匹配id、新检测id、未匹配ida. 如果跟踪器的个数为零,即第一帧图像,返回值为0的匹配id、新检测id、值为0的未匹配id。b. 如果跟踪器的个数为不为0,则计算检测框与当前轨迹的iou,如果iou不为空,得到iou大于阈值的掩码矩阵,判断掩码矩阵每行是否跟每列是一一对应,如果是则不需要匈牙利算法匹配;反之,用匈牙利算法得到匹配的检测框和轨迹的索引。c. 根据匹配索引得到新检测的框的id和为匹配的轨迹的id。d.根据iou再筛选一次。
2.3 更新轨迹。a. 对匹配上的轨迹,根据匹配id得到当前帧的最优估计。b. 添加新的检测。对于没有被匹配上的检测框生成新的跟踪器,并添加到轨迹中。c. 筛选轨迹。
2 代码
""" sort代码 https://github.com/abewley/sortSORT: A Simple, Online and Realtime TrackerCopyright (C) 2016-2020 Alex Bewley alex@bewley.aiThis program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modifyit under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published bythe Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or(at your option) any later version.This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty ofMERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See theGNU General Public License for more details.You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public Licensealong with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.-i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
filterpy==1.4.5
scikit-image==0.14.0
lap==0.4.0
numba==0.38.1
scikit-learn==0.19.1
"""
from __future__ import print_functionimport os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
from skimage import ioimport glob
import time
import argparse
from filterpy.kalman import KalmanFilternp.random.seed(0)def linear_assignment(cost_matrix):try:import lap_, x, y = lap.lapjv(cost_matrix, extend_cost=True)return np.array([[y[i],i] for i in x if i >= 0])except ImportError:from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignmentx, y = linear_sum_assignment(cost_matrix)return np.array(list(zip(x, y)))def iou_batch(bb_test, bb_gt):"""From SORT: Computes IOU between two bboxes in the form [x1,y1,x2,y2]"""bb_gt = np.expand_dims(bb_gt, 0)bb_test = np.expand_dims(bb_test, 1)xx1 = np.maximum(bb_test[..., 0], bb_gt[..., 0])yy1 = np.maximum(bb_test[..., 1], bb_gt[..., 1])xx2 = np.minimum(bb_test[..., 2], bb_gt[..., 2])yy2 = np.minimum(bb_test[..., 3], bb_gt[..., 3])w = np.maximum(0., xx2 - xx1)h = np.maximum(0., yy2 - yy1)wh = w * ho = wh / ((bb_test[..., 2] - bb_test[..., 0]) * (bb_test[..., 3] - bb_test[..., 1]) + (bb_gt[..., 2] - bb_gt[..., 0]) * (bb_gt[..., 3] - bb_gt[..., 1]) - wh) return(o) def convert_bbox_to_z(bbox):"""Takes a bounding box in the form [x1,y1,x2,y2] and returns z in the form[x,y,s,r] where x,y is the centre of the box and s is the scale/area and r isthe aspect ratio"""w = bbox[2] - bbox[0]h = bbox[3] - bbox[1]x = bbox[0] + w/2.y = bbox[1] + h/2.s = w * h #scale is just arear = w / float(h)return np.array([x, y, s, r]).reshape((4, 1))def convert_x_to_bbox(x,score=None):"""Takes a bounding box in the centre form [x,y,s,r] and returns it in the form[x1,y1,x2,y2] where x1,y1 is the top left and x2,y2 is the bottom right"""w = np.sqrt(x[2] * x[3])h = x[2] / wif(score==None):return np.array([x[0]-w/2.,x[1]-h/2.,x[0]+w/2.,x[1]+h/2.]).reshape((1,4))else:return np.array([x[0]-w/2.,x[1]-h/2.,x[0]+w/2.,x[1]+h/2.,score]).reshape((1,5))class KalmanBoxTracker(object):"""This class represents the internal state of individual tracked objects observed as bbox."""count = 0def __init__(self,bbox):"""Initialises a tracker using initial bounding box."""#define constant velocity modelself.kf = KalmanFilter(dim_x=7, dim_z=4) self.kf.F = np.array([[1,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0,0,1,0],[0,0,1,0,0,0,1],[0,0,0,1,0,0,0], [0,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,1]])self.kf.H = np.array([[1,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,1,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0,0,0]])self.kf.R[2:,2:] *= 10.self.kf.P[4:,4:] *= 1000. #give high uncertainty to the unobservable initial velocitiesself.kf.P *= 10.self.kf.Q[-1,-1] *= 0.01self.kf.Q[4:,4:] *= 0.01self.kf.x[:4] = convert_bbox_to_z(bbox)self.time_since_update = 0self.id = KalmanBoxTracker.countKalmanBoxTracker.count += 1self.history = []self.hits = 0self.hit_streak = 0self.age = 0def update(self,bbox):"""Updates the state vector with observed bbox."""self.time_since_update = 0self.history = []self.hits += 1self.hit_streak += 1 # 连续匹配并更新的次数self.kf.update(convert_bbox_to_z(bbox))def predict(self):"""Advances the state vector and returns the predicted bounding box estimate."""if((self.kf.x[6]+self.kf.x[2])<=0):self.kf.x[6] *= 0.0self.kf.predict()self.age += 1if(self.time_since_update>0): # 上一次更新距离现在的时间self.hit_streak = 0 # 匹配次数归0self.time_since_update += 1 # 轨迹只预测没有匹配的的次数➕1self.history.append(convert_x_to_bbox(self.kf.x))return self.history[-1]def get_state(self):"""Returns the current bounding box estimate."""return convert_x_to_bbox(self.kf.x)def associate_detections_to_trackers(detections,trackers,iou_threshold = 0.3):"""Assigns detections to tracked object (both represented as bounding boxes)Returns 3 lists of matches, unmatched_detections and unmatched_trackers"""if(len(trackers)==0):return np.empty((0,2),dtype=int), np.arange(len(detections)), np.empty((0,5),dtype=int)iou_matrix = iou_batch(detections, trackers)if min(iou_matrix.shape) > 0:a = (iou_matrix > iou_threshold).astype(np.int32)if a.sum(1).max() == 1 and a.sum(0).max() == 1:matched_indices = np.stack(np.where(a), axis=1) # 如果正好是一个检测与一个轨迹匹配,则找出匹配的索引else:matched_indices = linear_assignment(-iou_matrix) # 匈牙利匹配,matched_indices存储的是每个检测框对应的轨迹,第一列存储的是检测框的id;第二列存储的是检测框匹配的轨迹idelse:matched_indices = np.empty(shape=(0,2)) unmatched_detections = [] # 寻找没有被匹配上的检测框for d, det in enumerate(detections): # 这一步写的麻烦,不用枚举if(d not in matched_indices[:,0]):unmatched_detections.append(d)unmatched_trackers = [] # 寻找没有被匹配上的轨迹for t, trk in enumerate(trackers):if(t not in matched_indices[:,1]):unmatched_trackers.append(t)#filter out matched with low IOUmatches = [] # 寻找被匹配上的检测框的idfor m in matched_indices: # 根据iou再进行一次筛选if(iou_matrix[m[0], m[1]]<iou_threshold):unmatched_detections.append(m[0])unmatched_trackers.append(m[1])else:matches.append(m.reshape(1,2))if(len(matches)==0):matches = np.empty((0,2),dtype=int)else:matches = np.concatenate(matches,axis=0)return matches, np.array(unmatched_detections), np.array(unmatched_trackers)class Sort(object):def __init__(self, max_age=1, min_hits=3, iou_threshold=0.3):"""Sets key parameters for SORT"""self.max_age = max_ageself.min_hits = min_hitsself.iou_threshold = iou_thresholdself.trackers = []self.frame_count = 0def update(self, dets=np.empty((0, 5))):"""Params:dets - a numpy array of detections in the format [[x1,y1,x2,y2,score],[x1,y1,x2,y2,score],...]Requires: this method must be called once for each frame even with empty detections (use np.empty((0, 5)) for frames without detections).Returns the a similar array, where the last column is the object ID.NOTE: The number of objects returned may differ from the number of detections provided."""self.frame_count += 1# get predicted locations from existing trackers.trks = np.zeros((len(self.trackers), 5)) # 存储筛选后的轨迹。第一帧shape=(0, 5);to_del = [] # 没有匹配的轨迹ret = [] # 存放检测所有合格的轨迹for t, trk in enumerate(trks):pos = self.trackers[t].predict()[0] # 根据上一帧的轨迹当前帧的轨迹.trk[:] = [pos[0], pos[1], pos[2], pos[3], 0]if np.any(np.isnan(pos)):to_del.append(t)trks = np.ma.compress_rows(np.ma.masked_invalid(trks)) # 剔除当前无效轨迹for t in reversed(to_del):self.trackers.pop(t) # 剔除上一帧中的无效轨迹matched, unmatched_dets, unmatched_trks = associate_detections_to_trackers(dets,trks, self.iou_threshold) # 第一帧没有轨迹,# update matched trackers with assigned detections 对匹配的轨迹更新for m in matched: # 根据当前轨迹和检测得到当前最优估计self.trackers[m[1]].update(dets[m[0], :])# create and initialise new trackers for unmatched detectionsfor i in unmatched_dets: # 对于没有被匹配上的检测框生成新的跟踪器,并添加到轨迹中trk = KalmanBoxTracker(dets[i,:])self.trackers.append(trk)i = len(self.trackers)for trk in reversed(self.trackers):d = trk.get_state()[0]if (trk.time_since_update < 1) and (trk.hit_streak >= self.min_hits or self.frame_count <= self.min_hits): #(当前更新的轨迹)and (连续匹配超过min_hits or 检测帧数小于min_hits)ret.append(np.concatenate((d,[trk.id+1])).reshape(1,-1)) # +1 as MOT benchmark requires positivei -= 1# remove dead trackletif(trk.time_since_update > self.max_age):self.trackers.pop(i)if(len(ret)>0):return np.concatenate(ret)return np.empty((0,5))def parse_args():"""Parse input arguments."""parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='SORT demo')parser.add_argument('--display', dest='display', help='Display online tracker output (slow) [False]',action='store_true')parser.add_argument("--seq_path", help="Path to detections.", type=str, default='data')parser.add_argument("--phase", help="Subdirectory in seq_path.", type=str, default='train')parser.add_argument("--max_age", help="Maximum number of frames to keep alive a track without associated detections.", type=int, default=1)parser.add_argument("--min_hits", help="Minimum number of associated detections before track is initialised.", type=int, default=3)parser.add_argument("--iou_threshold", help="Minimum IOU for match.", type=float, default=0.3)args = parser.parse_args()return argsif __name__ == '__main__':# all trainargs = parse_args()display = args.display # 是否显示结果phase = args.phase # 'trian'total_time = 0.0 # 总时长total_frames = 0 # 记录检测的帧数colours = np.random.rand(32, 3) # \used only for display [32,3]if(display):if not os.path.exists('mot_benchmark'):print('\n\tERROR: mot_benchmark link not found!\n\n Create a symbolic link to the MOT benchmark\n (https://motchallenge.net/data/2D_MOT_2015/#download). E.g.:\n\n $ ln -s /path/to/MOT2015_challenge/2DMOT2015 mot_benchmark\n\n')exit()plt.ion()fig = plt.figure()ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111, aspect='equal')if not os.path.exists('output'):os.makedirs('output')pattern = os.path.join(args.seq_path, phase, '*', 'det', 'det.txt') # 相对路径 'data/train/*/det/det.txt'# 1. 数据准备for seq_dets_fn in glob.glob(pattern):mot_tracker = Sort(max_age=args.max_age, # 1.1 初始化跟踪器min_hits=args.min_hits,iou_threshold=args.iou_threshold) # create instance of the SORT trackerseq_dets = np.loadtxt(seq_dets_fn, delimiter=',') # 1.2 加载数据seq = seq_dets_fn[pattern.find('*'):].split(os.path.sep)[0] # 'data/train/ETH-Bahnhof/det/det.txt' --> ['ETH-Bahnhof', 'det', 'det.txt'] --> 'ETH-Bahnhof'with open(os.path.join('output', '%s.txt'%(seq)),'w') as out_file: # 'output/ETH-Bahnhof.txt'print("Processing %s."%(seq))for frame in range(int(seq_dets[:,0].max())): # seq_dets[:,0]第一列为图片的序列号,遍历每一帧的检测结果frame += 1 # detection and frame numbers begin at 1dets = seq_dets[seq_dets[:, 0]==frame, 2:7] # x1,y1,w,h,cdets[:, 2:4] += dets[:, 0:2] # convert to [x1,y1,w,h] to [x1,y1,x2,y2]total_frames += 1if(display):fn = os.path.join('mot_benchmark', phase, seq, 'img1', '%06d.jpg'%(frame))im = io.imread(fn)ax1.imshow(im)plt.title(seq + ' Tracked Targets')start_time = time.time()trackers = mot_tracker.update(dets) # 2. 获取跟踪结果cycle_time = time.time() - start_timetotal_time += cycle_timefor d in trackers: # 画的是跟踪到的轨迹print('%d,%d,%.2f,%.2f,%.2f,%.2f,1,-1,-1,-1'%(frame,d[4],d[0],d[1],d[2]-d[0],d[3]-d[1]),file=out_file)if(display):d = d.astype(np.int32)ax1.add_patch(patches.Rectangle((d[0],d[1]),d[2]-d[0],d[3]-d[1],fill=False,lw=3,ec=colours[d[4]%32,:]))if(display):fig.canvas.flush_events()plt.draw()ax1.cla()print("Total Tracking took: %.3f seconds for %d frames or %.1f FPS" % (total_time, total_frames, total_frames / total_time))if(display):print("Note: to get real runtime results run without the option: --display")
概率论基础知识-贝叶斯公式)

)
)






)
)






