文章目录 【 1. DFS 深度优先搜索 】 【 2. BFS 广度优先搜索 】 【 3. 深度优先生成树、广度优先生成树 】 【 4. 深度优先生成森林、广度优先生成森林 】
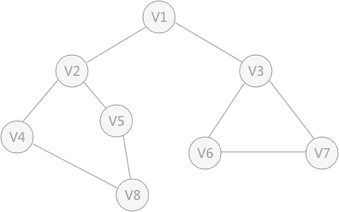
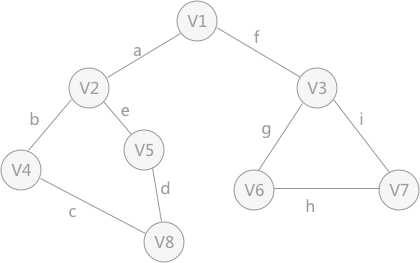
对存储的图中的顶点进行遍历搜索,常用的遍历方式有两种:深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索。 深度优先搜索的过程 类似于树的先序遍历 ,首先从例子中体会深度优先搜索。例如下图是一个无向图,采用深度优先算法遍历这个图的过程为: 首先任意找一个未被遍历过的顶点,例如从 V1 开始,由于 V1 率先访问过了,所以,需要标记 V1 的状态为访问过; 然后遍历 V1 的邻接点,例如访问 V2 ,并做标记,然后访问 V2 的邻接点,例如 V4 (做标记),然后 V8 ,然后 V5 ; 当继续遍历 V5 的邻接点时,根据之前做的标记显示,所有V5 的邻接点都被访问过了。此时,从 V5 回退到 V8 ,看 V8 是否有未被访问过的邻接点,如果没有,继续回退到 V4 , V2 ,V1 ; 通过查看 V1 ,找到一个未被访问过的顶点 V3 ,继续遍历,然后访问 V3 邻接点 V6 ,然后 V7 ; 由于 V7 没有未被访问的邻接点,所以回退到 V6 ,继续回退至 V3 ,最后到达 V1 ,发现没有未被访问的; 最后一步需要判断是否所有顶点都被访问,如果还有没被访问的,以未被访问的顶点为第一个顶点,继续依照上边的方式进行遍历。 根据上边的过程,可以得到下图通过深度优先搜索获得的顶点的遍历次序为: 总结:深度优先搜索 # define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 # include <stdio.h> # define MAX_VERtEX_NUM 20 # define VertexType int # define VRType int # define InfoType char bool visited[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ;
typedef struct { VRType adj; InfoType* info;
} ArcCell, AdjMatrix[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] [ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ;
typedef struct { VertexType vexs[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ; AdjMatrix arcs; int vexnum, arcnum;
} MGraph;
int LocateVex ( MGraph* G, VertexType v) { int i = 0 ; for ( ; i < G-> vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G-> vexs[ i] == v) { break ; } } if ( i > G-> vexnum) { printf ( "no such vertex.\n" ) ; return - 1 ; } return i;
}
void CreateDN ( MGraph* G) { scanf ( "%d,%d" , & ( G-> vexnum) , & ( G-> arcnum) ) ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < G-> vexnum; i++ ) { scanf ( "%d" , & ( G-> vexs[ i] ) ) ; } for ( int i = 0 ; i < G-> vexnum; i++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < G-> vexnum; j++ ) { G-> arcs[ i] [ j] . adj = 0 ; G-> arcs[ i] [ j] . info = NULL ; } } for ( int i = 0 ; i < G-> arcnum; i++ ) { int v1, v2; scanf ( "%d,%d" , & v1, & v2) ; int n = LocateVex ( G, v1) ; int m = LocateVex ( G, v2) ; if ( m == - 1 || n == - 1 ) { printf ( "no this vertex\n" ) ; return ; } G-> arcs[ n] [ m] . adj = 1 ; G-> arcs[ m] [ n] . adj = 1 ; }
}
int FirstAdjVex ( MGraph G, int v)
{ for ( int i = 0 ; i < G. vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G. arcs[ v] [ i] . adj) { return i; } } return - 1 ;
}
int NextAdjVex ( MGraph G, int v, int w)
{ for ( int i = w + 1 ; i < G. vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G. arcs[ v] [ i] . adj) { return i; } } return - 1 ;
}
void visitVex ( MGraph G, int v) { printf ( "%d " , G. vexs[ v] ) ;
}
void DFS ( MGraph G, int v) { visited[ v] = true ; visitVex ( G, v) ; for ( int w = FirstAdjVex ( G, v) ; w >= 0 ; w = NextAdjVex ( G, v, w) ) { if ( ! visited[ w] ) { DFS ( G, w) ; } }
}
void DFSTraverse ( MGraph G)
{ int v; for ( v = 0 ; v < G. vexnum; ++ v) { visited[ v] = false ; } for ( v = 0 ; v < G. vexnum; v++ ) { if ( ! visited[ v] ) { DFS ( G, v) ; } }
} int main ( ) { MGraph G; CreateDN ( & G) ; DFSTraverse ( G) ; return 0 ;
}
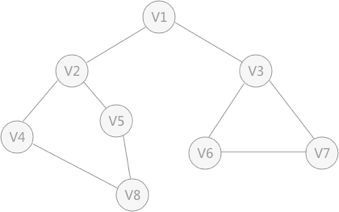
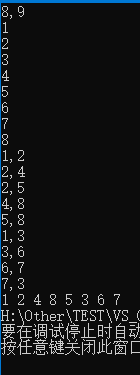
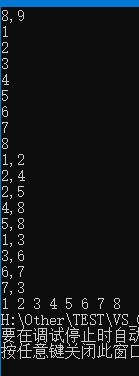
使用上述程序存储下图的无向图时,输入如下数据,得到DFS的输出结果:
8 , 9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 , 2
2 , 4
2 , 5
4 , 8
5 , 8
1 , 3
3 , 6
6 , 7
7 , 3
广度优先搜索 类似于树的层次遍历 。以下图的无向图为例,假设 V1 作为起始点,遍历其所有的邻接点 V2 和 V3 ,以 V2 为起始点,访问邻接点 V4 和 V5 ,以 V3 为起始点,访问邻接点 V6 、 V7 ,以 V4 为起始点访问 V8 ,以 V5 为起始点,由于 V5 所有的起始点已经全部被访问,所有直接略过, V6 和 V7 也是如此。总结:广度优先搜索 广度优先搜索的实现需要借助 队列 # define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 # include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> # define MAX_VERtEX_NUM 20 # define VertexType int # define VRType int # define InfoType char bool visited[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ;
typedef struct Queue { VertexType data; struct Queue * next;
} Queue;
typedef struct { VRType adj; InfoType* info;
} ArcCell, AdjMatrix[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] [ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ;
typedef struct { VertexType vexs[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ; AdjMatrix arcs; int vexnum, arcnum;
} MGraph;
int LocateVex ( MGraph* G, VertexType v) { int i = 0 ; for ( ; i < G-> vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G-> vexs[ i] == v) { break ; } } if ( i > G-> vexnum) { printf ( "no such vertex.\n" ) ; return - 1 ; } return i;
}
void CreateDN ( MGraph* G) { scanf ( "%d,%d" , & ( G-> vexnum) , & ( G-> arcnum) ) ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < G-> vexnum; i++ ) { scanf ( "%d" , & ( G-> vexs[ i] ) ) ; } for ( int i = 0 ; i < G-> vexnum; i++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < G-> vexnum; j++ ) { G-> arcs[ i] [ j] . adj = 0 ; G-> arcs[ i] [ j] . info = NULL ; } } for ( int i = 0 ; i < G-> arcnum; i++ ) { int v1, v2; scanf ( "%d,%d" , & v1, & v2) ; int n = LocateVex ( G, v1) ; int m = LocateVex ( G, v2) ; if ( m == - 1 || n == - 1 ) { printf ( "no this vertex\n" ) ; return ; } G-> arcs[ n] [ m] . adj = 1 ; G-> arcs[ m] [ n] . adj = 1 ; }
}
int FirstAdjVex ( MGraph G, int v)
{ for ( int i = 0 ; i < G. vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G. arcs[ v] [ i] . adj) { return i; } } return - 1 ;
}
int NextAdjVex ( MGraph G, int v, int w)
{ for ( int i = w + 1 ; i < G. vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G. arcs[ v] [ i] . adj) { return i; } } return - 1 ;
}
void visitVex ( MGraph G, int v) { printf ( "%d " , G. vexs[ v] ) ;
}
void InitQueue ( Queue* * Q) { ( * Q) = ( Queue* ) malloc ( sizeof ( Queue) ) ; ( * Q) -> next = NULL ;
}
void EnQueue ( Queue* * Q, VertexType v) { Queue* element = ( Queue* ) malloc ( sizeof ( Queue) ) ; element-> data = v; element-> next = NULL ; Queue* temp = ( * Q) ; while ( temp-> next != NULL ) { temp = temp-> next; } temp-> next = element;
}
void DeQueue ( Queue* * Q, int * u) { ( * u) = ( * Q) -> next-> data; ( * Q) -> next = ( * Q) -> next-> next;
}
bool QueueEmpty ( Queue* Q) { if ( Q-> next == NULL ) { return true ; } return false ;
}
void BFSTraverse ( MGraph G) { int v; for ( v = 0 ; v < G. vexnum; ++ v) { visited[ v] = false ; } Queue* Q; InitQueue ( & Q) ; for ( v = 0 ; v < G. vexnum; v++ ) { if ( ! visited[ v] ) { visited[ v] = true ; visitVex ( G, v) ; EnQueue ( & Q, G. vexs[ v] ) ; while ( ! QueueEmpty ( Q) ) { int u; DeQueue ( & Q, & u) ; u = LocateVex ( & G, u) ; for ( int w = FirstAdjVex ( G, u) ; w >= 0 ; w = NextAdjVex ( G, u, w) ) { if ( ! visited[ w] ) { visited[ w] = true ; visitVex ( G, w) ; EnQueue ( & Q, G. vexs[ w] ) ; } } } } }
} int main ( ) { MGraph G; CreateDN ( & G) ; BFSTraverse ( G) ; return 0 ;
}
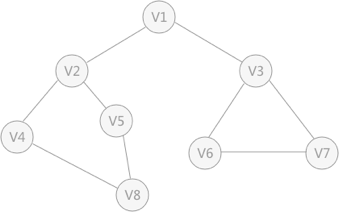
使用上述程序存储下图的无向图时,输入如下数据,得到DFS的输出结果:
8 , 9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 , 2
2 , 4
2 , 5
4 , 8
5 , 8
1 , 3
3 , 6
6 , 7
7 , 3
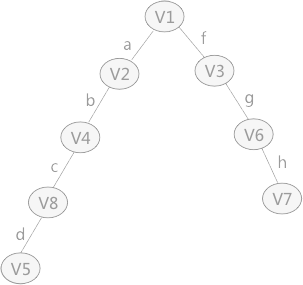
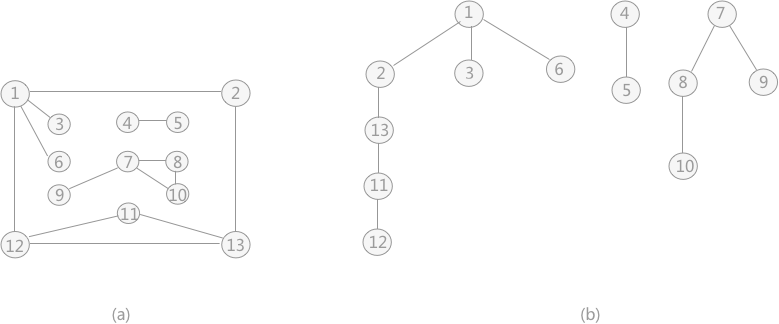
无向图遍历过程中所经历过的图中的顶点和边的组合,就是图的生成树或者生成森林。 由深度优先搜索得到的树为 深度优先生成树 同理,广度优先搜索生成的树为 广度优先生成树 前言回顾:详情见:【C 数据结构】图。 对下图 a 的非连通图采用深度优先搜索算法遍历时,得到的深度优先生成森林(由 3 个深度优先生成树构成)如下图 b 所示(不唯一)。
# define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 # include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> # define MAX_VERtEX_NUM 20 # define VertexType int # define VRType int bool visited[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ;
typedef struct
{ VRType adj;
} ArcCell, AdjMatrix[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] [ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ;
typedef struct { VertexType vexs[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ; AdjMatrix arcs; int vexnum, arcnum;
} MGraph;
typedef struct CSNode { VertexType data; struct CSNode * lchild; struct CSNode * nextsibling;
} * CSTree, CSNode;
int LocateVex ( MGraph G, VertexType v) { int i = 0 ; for ( ; i < G. vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G. vexs[ i] == v) { break ; } } if ( i > G. vexnum) { printf ( "no such vertex.\n" ) ; return - 1 ; } return i;
}
void CreateDN ( MGraph* G) { scanf ( "%d,%d" , & ( G-> vexnum) , & ( G-> arcnum) ) ; getchar ( ) ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < G-> vexnum; i++ ) { scanf ( "%d" , & ( G-> vexs[ i] ) ) ; } for ( int i = 0 ; i < G-> vexnum; i++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < G-> vexnum; j++ ) { G-> arcs[ i] [ j] . adj = 0 ; } } for ( int i = 0 ; i < G-> arcnum; i++ ) { int v1, v2; scanf ( "%d,%d" , & v1, & v2) ; int n = LocateVex ( * G, v1) ; int m = LocateVex ( * G, v2) ; if ( m == - 1 || n == - 1 ) { printf ( "no this vertex\n" ) ; return ; } G-> arcs[ n] [ m] . adj = 1 ; G-> arcs[ m] [ n] . adj = 1 ; }
}
int FirstAdjVex ( MGraph G, int v)
{ for ( int i = 0 ; i < G. vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G. arcs[ v] [ i] . adj) { return i; } } return - 1 ;
}
int NextAdjVex ( MGraph G, int v, int w)
{ for ( int i = w + 1 ; i < G. vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G. arcs[ v] [ i] . adj) { return i; } } return - 1 ;
} void DFSTree ( MGraph G, int v, CSTree* T) { visited[ v] = true ; bool first = true ; CSTree q = NULL ; for ( int w = FirstAdjVex ( G, v) ; w >= 0 ; w = NextAdjVex ( G, v, w) ) { if ( ! visited[ w] ) { CSTree p = ( CSTree) malloc ( sizeof ( CSNode) ) ; p-> data = G. vexs[ w] ; p-> lchild = NULL ; p-> nextsibling = NULL ; if ( first) { ( * T) -> lchild = p; first = false ; } else { q-> nextsibling = p; } q = p; DFSTree ( G, w, & q) ; } }
}
void DFSForest ( MGraph G, CSTree* T) { ( * T) = NULL ; for ( int v = 0 ; v < G. vexnum; v++ ) { visited[ v] = false ; } CSTree q = NULL ; for ( int v = 0 ; v < G. vexnum; v++ ) { if ( ! ( visited[ v] ) ) { CSTree p = ( CSTree) malloc ( sizeof ( CSNode) ) ; p-> data = G. vexs[ v] ; p-> lchild = NULL ; p-> nextsibling = NULL ; if ( ! ( * T) ) { ( * T) = p; } else { q-> nextsibling = p; } q = p; DFSTree ( G, v, & p) ; } }
}
void PreOrderTraverse ( CSTree T) { if ( T) { printf ( "%d " , T-> data) ; PreOrderTraverse ( T-> lchild) ; PreOrderTraverse ( T-> nextsibling) ; } return ;
} int main ( ) { MGraph G; CreateDN ( & G) ; CSTree T; DFSForest ( G, & T) ; PreOrderTraverse ( T) ; return 0 ;
}
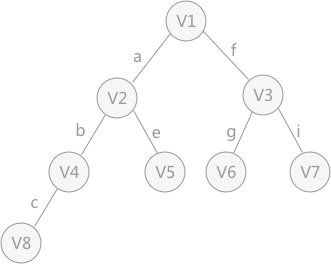
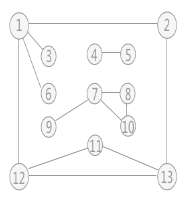
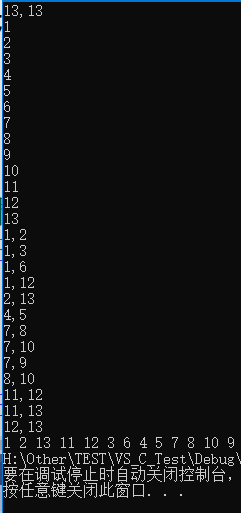
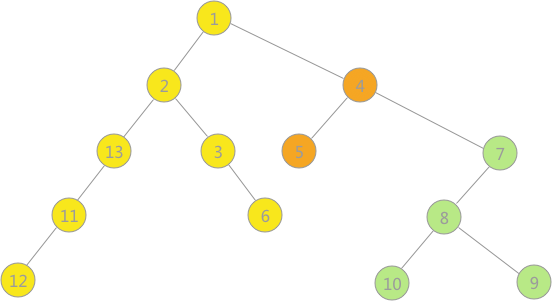
使用上述程序存储下图的无向图,输入如下数据,构建深度优先生成森林,得到DFS的输出结果: 构建的深度优先生成森林用孩子兄弟表示法如下所示:3 种颜色的树各代表一棵深度优先生成树,使用孩子兄弟表示法表示,也就是将三棵树的树根相连,第一棵树的树根作为整棵树的树根。
13 , 13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
1 , 2
1 , 3
1 , 6
1 , 12
2 , 13
4 , 5
7 , 8
7 , 10
7 , 9
8 , 10
11 , 12
11 , 13
12 , 13
非连通图采用广度优先搜索算法进行遍历时,经过的顶点以及边的集合为该图的 广度优先生成森林 C 实现: # include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> # define MAX_VERtEX_NUM 20 # define VRType int # define InfoType char # define VertexType int typedef enum { false , true } bool ;
bool visited[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ;
typedef struct { VRType adj; InfoType * info;
} ArcCell, AdjMatrix[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] [ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ; typedef struct { VertexType vexs[ MAX_VERtEX_NUM] ; AdjMatrix arcs; int vexnum, arcnum;
} MGraph; typedef struct CSNode { VertexType data; struct CSNode * lchild; struct CSNode * nextsibling;
} * CSTree, CSNode; typedef struct Queue { CSTree data; struct Queue * next;
} Queue;
int LocateVex ( MGraph * G, VertexType v) { int i= 0 ; for ( ; i< G-> vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G-> vexs[ i] == v) { break ; } } if ( i> G-> vexnum) { printf ( "no such vertex.\n" ) ; return - 1 ; } return i;
}
void CreateDN ( MGraph * G) { scanf ( "%d,%d" , & ( G-> vexnum) , & ( G-> arcnum) ) ; for ( int i= 0 ; i< G-> vexnum; i++ ) { scanf ( "%d" , & ( G-> vexs[ i] ) ) ; } for ( int i= 0 ; i< G-> vexnum; i++ ) { for ( int j= 0 ; j< G-> vexnum; j++ ) { G-> arcs[ i] [ j] . adj= 0 ; G-> arcs[ i] [ j] . info= NULL ; } } for ( int i= 0 ; i< G-> arcnum; i++ ) { int v1, v2; scanf ( "%d,%d" , & v1, & v2) ; int n= LocateVex ( G, v1) ; int m= LocateVex ( G, v2) ; if ( m== - 1 || n== - 1 ) { printf ( "no this vertex\n" ) ; return ; } G-> arcs[ n] [ m] . adj= 1 ; G-> arcs[ m] [ n] . adj= 1 ; }
} int FirstAdjVex ( MGraph G, int v)
{ for ( int i = 0 ; i< G. vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G. arcs[ v] [ i] . adj ) { return i; } } return - 1 ;
}
int NextAdjVex ( MGraph G, int v, int w)
{ for ( int i = w+ 1 ; i< G. vexnum; i++ ) { if ( G. arcs[ v] [ i] . adj) { return i; } } return - 1 ;
}
void InitQueue ( Queue * * Q) { ( * Q) = ( Queue* ) malloc ( sizeof ( Queue) ) ; ( * Q) -> next= NULL ;
}
void EnQueue ( Queue * * Q, CSTree T) { Queue * element= ( Queue* ) malloc ( sizeof ( Queue) ) ; element-> data= T; element-> next= NULL ; Queue * temp= ( * Q) ; while ( temp-> next!= NULL ) { temp= temp-> next; } temp-> next= element;
}
void DeQueue ( Queue * * Q, CSTree * u) { ( * u) = ( * Q) -> next-> data; ( * Q) -> next= ( * Q) -> next-> next;
}
bool QueueEmpty ( Queue * Q) { if ( Q-> next== NULL ) { return true ; } return false ;
} void BFSTree ( MGraph G, int v, CSTree* T) { CSTree q= NULL ; Queue * Q; InitQueue ( & Q) ; EnQueue ( & Q, ( * T) ) ; while ( ! QueueEmpty ( Q) ) { bool first= true ; DeQueue ( & Q, & q) ; int v= LocateVex ( & G, q-> data) ; visited[ v] = true ; for ( int w= FirstAdjVex ( G, v) ; w>= 0 ; w= NextAdjVex ( G, v, w) ) { if ( ! visited[ w] ) { CSTree p= ( CSTree) malloc ( sizeof ( CSNode) ) ; p-> data= G. vexs[ w] ; p-> lchild= NULL ; p-> nextsibling= NULL ; EnQueue ( & Q, p) ; visited[ w] = true ; if ( first) { q-> lchild= p; first= false ; } else { q-> nextsibling= p; } q= p; } } }
}
void BFSForest ( MGraph G, CSTree * T) { ( * T) = NULL ; for ( int v= 0 ; v< G. vexnum; v++ ) { visited[ v] = false ; } CSTree q= NULL ; for ( int v= 0 ; v< G. vexnum; v++ ) { if ( ! ( visited[ v] ) ) { CSTree p= ( CSTree) malloc ( sizeof ( CSNode) ) ; p-> data= G. vexs[ v] ; p-> lchild= NULL ; p-> nextsibling= NULL ; if ( ! ( * T) ) { ( * T) = p; } else { q-> nextsibling= p; } q= p; BFSTree ( G, v, & p) ; } }
}
void PreOrderTraverse ( CSTree T) { if ( T) { printf ( "%d " , T-> data) ; PreOrderTraverse ( T-> lchild) ; PreOrderTraverse ( T-> nextsibling) ; } return ;
}
int main ( ) { MGraph G; CreateDN ( & G) ; CSTree T; BFSForest ( G, & T) ; PreOrderTraverse ( T) ; return 0 ;
}
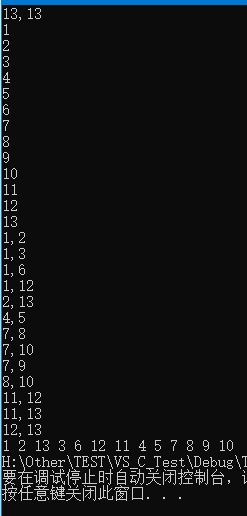
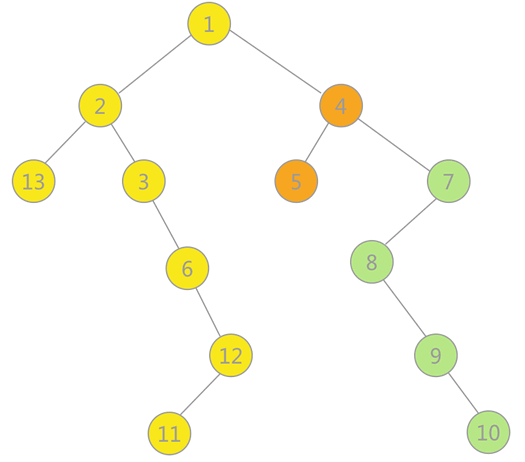
使用上述程序存储下图的无向图,输入如下数据,构建广度优先生成森林,得到BFS的输出结果: 对上图通过广度优先搜索得到的广度优先生成森林用孩子兄弟表示法如下图所示:
13 , 13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
1 , 2
1 , 3
1 , 6
1 , 12
2 , 13
4 , 5
7 , 8
7 , 10
7 , 9
8 , 10
11 , 12
11 , 13
12 , 13




)





)








)

